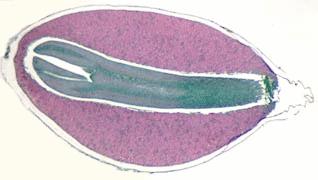
Pinus embryo
Note the embryonic root and, at the opposite end, the cotyledons. The cotyledons (seed leaves) serve to transfer stored food from the seed to the young plant, and later function as photosynthetic organs. The stem apex is located between the base of the cotyledons (See Raven 7th, p. 422, Fig.18-22; 8th, p. 446, Fig. 18-24; and your lab manual). The female gametophyte serves as nutritive tissue for the embryo. Be sure you understand the origin and ploidy of each structure within the mature seed.
This is what a mature seed of pine looks like. It has a wing which aids in dispersal.
REPRODUCTION INTRO
MALE CONES
FEMALE CONES
EMBRYO
PINE LIFE HISTORY IN MORE DETAIL