1. EARLY DEVELOPMENT OF A BEAN
 Here is a bean. It is actually a seed.
Here is a bean. It is actually a seed.
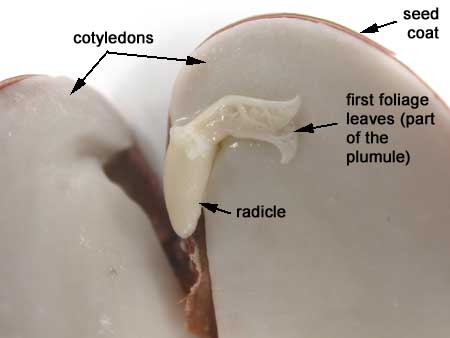
If you break the seed open you will find that it splits into two. The large pieces are the cotyledons. They are embryonic leaves. In this case they function in nutrient storage. The rest of the embryo is much smaller. The little root (radicle can be seen here). The rest of the embryo (all of which is above the point of attachment of the cotyledons) is called the plumule.
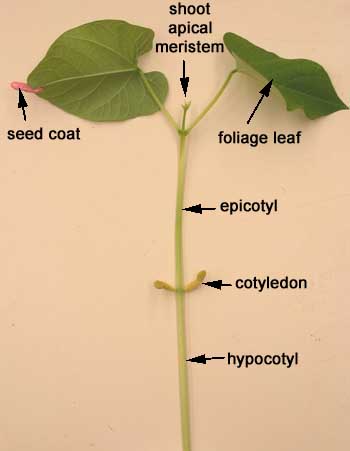
Here is a germinating seedling. You can see the hooked hypocotyl which elbows its way out of the ground. The hypocotyl is the portion of the stem below the point of attachment of the cotyledons.
This picture shows it at a little older stage.
…and a little older. You can see the foliage leaves emerging from between the cotyledons.
This is a picture of an older seedling.
1. EARLY DEVELOPMENT OF BEAN
2. STEM APICAL MERISTEM
3. PRIMARY TO SECONDARY GROWTH
4. MONOCOT STEM
5. STEM MODIFICATIONS
BACK TO STEM FRONTPAGE