– ALTERNATION OF GENERATIONS –
If you have taken Biology 209 you are already familiar with life histories which have an alternation of generations. Remember the bryophytes’ life history has a dominant gametophytic (N) phase and a dependent sporophytic (2N) phase. The ferns are similar. However, they have a dominant sporophytic stage and a reduced gametophytic stage. This is the pattern you will see throughout the vascular plants.
To demonstrate alternation of generations we will examine a typical fern. This is Adiantum pedatum (maidenhair fern). It is a common fern to coastal British Columbia. You can find it on stream-banks and rocky cliffs which are in the spray zone of waterfalls (Lynn Canyon is an excellent place to see these ferns).
The leaves of ferns are called fronds. You usually only see fronds when you are looking at ferns because the stems are underground. Underground stems are called rhizomes.
When you look at the underside of the fronds of the sporophyte some of them will have dark spots. These are called sori (sorus = singular). Each sorus is made up of a cluster of sporangia. Meiosis occurs within each sporangium to produce haploid spores.
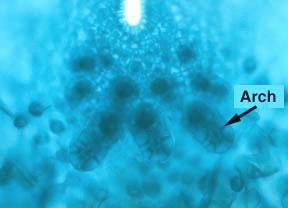
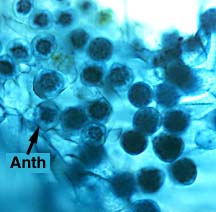
The fern spores are haploid and thus germinate to form haploid gametophytes (also called prothalli) pictured here. The gametophyte produces gametangia (archegonia in the notch and antheridia lower among the rhizoids).
Each archegonium (Arch) is a flask-shaped structure which houses one egg cell. The base of the archegonium which surrounds the egg is called the venter. The slender upper portion is called the neck.
Each antheridium (Anth) produces many flagellate sperms which swim toward the archegonia. They swim down the neck canal of the archegonium and fertilize the egg. The zygote (2N) will develop into a diploid embryo(the young sporophytic stage).
Here are two young sporophytes (Spor) which develop into the “ferns” you are familiar with. You can see the gametophyte (Gam) still attached at the base of the fronds. Spores are produced on the fern (sporophyte) by meiosis and so the life cycle is complete.
As already indicated alternation of generations occurs in all vascular plants. Keep this in mind as you wander through the world of plants. The trends you will observe include the reduction of the gametophytic stage and its increased dependency on the sporophyte.
FERN LIFE CYCLE DIAGRAM
FERNS (LAB #7)
BACK TO INTRO