STELE TYPES
Phloem is blue
Xylem is red
PROTOSTELE solid column of vascular tissue; no pith
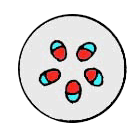
 l. Protostele This is the simplest type of stele; it has a xylem core, phloem in a layer around it.
l. Protostele This is the simplest type of stele; it has a xylem core, phloem in a layer around it.
ex. Psilotum (stem and root), Selaginella (stem and root), vascular plant root
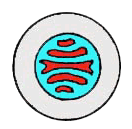 2. Plectostele xylem and phloem intermingled as strands or plates.
2. Plectostele xylem and phloem intermingled as strands or plates.
ex. Lycopodium stem
SIPHONOSTELE: characterized by central cylinder of primary vascular tissue (surrounded by endodermis) with a central core of pith.
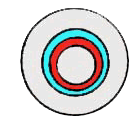 l. Ectophloic Siphonostele: phloem external to the xylem.
l. Ectophloic Siphonostele: phloem external to the xylem.
2. Amphiphloic Siphonostele: phloem external and internal to the xylem
(a) small leaf gaps which do not overlap
ex. Adiantum rhizome: This is a diagram of a section through the internode
 This is a diagram of a section through the node (where the leaf emerges from the stem). The space in the siphonostele is called a leaf gap. It represents where vascular tissue has branched off into the leaf.
This is a diagram of a section through the node (where the leaf emerges from the stem). The space in the siphonostele is called a leaf gap. It represents where vascular tissue has branched off into the leaf.
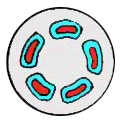 (b) Dictyostele= with large, overlapping leaf gaps which dissect the vascular system into a network. Each segment consists of a concentric vascular bundle.
(b) Dictyostele= with large, overlapping leaf gaps which dissect the vascular system into a network. Each segment consists of a concentric vascular bundle.
bundles in one ring
ex. Polypodium rhizome
 or more than one ring
or more than one ring
ex. Pteridium rhizome
EUSTELE:
with discrete primary vascular strandes in a ring around a central pith (no endodermis).
– often collateral (phloem outside, xylem inside) or bicollateral (phloem both inside and outside the xylem) type. Leaf gaps and spaces between bundles not directly associated with leaves difficult to distinguish from one another
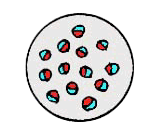 Atactostele: a modified eustele in which vascular bundles are arranged irregularly in the ground tissue.
Atactostele: a modified eustele in which vascular bundles are arranged irregularly in the ground tissue.
Ex. monocot stems