GYNOECIUM
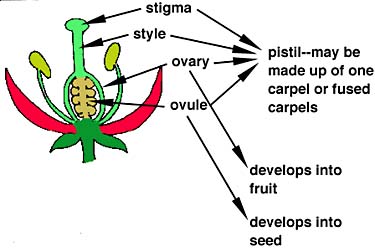
The carpels are collectively called the gynoecium. The carpel (not present in the conifers) encloses the ovules. Each flower may have a single carpel, or several. The carpel or fused carpels are made up of a basal ovary which contains ovules; a receptive surface for the pollen grains, called a stigma; and a stalk connecting the ovary and stigma, called a style. You may be familiar with the term pistil. This refers to the structure which has an ovary, stigma and style. The pistil may be made up of one carpel or a number of fused carpels.
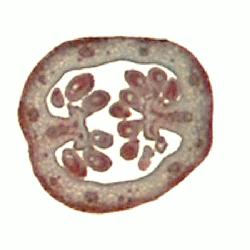
This is a cross-section through the ovary of lily. You can see the ovules within. Can you see that this structure is made up of three carpels? The space within the ovary is called the locule.
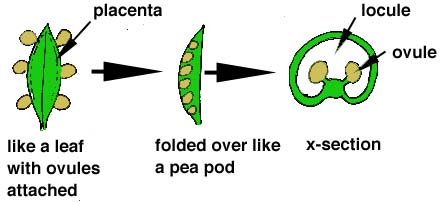
You may have a difficult time trying to understand what a carpel is. The diagram below demostrates the hypothetical evolution of a carpel. If you think of a megasporophyll (a leaf) with a number of ovules attached at its margin and folded over so that the ovules lie within the structure you can envision a carpel could be a modified leaf. Think about a pea pod. The flower of a pea has only one carpel. The peas within the pod represent the matured ovules.
Placentation refers to how the ovules are attached in the ovary. In lab we looked at two major types, but as you observed in the prepared slides there more types of attachment.
Parietal placentation is when the ovules are attached to the ovary wall, or to projections from the wall. How many locules do you see?
Axile placentation is when the ovules are attached to a central column in an ovary with more than one locule. How many locules do you see here?
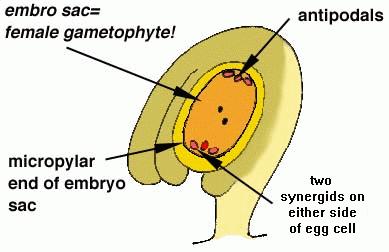
So what is an ovule?
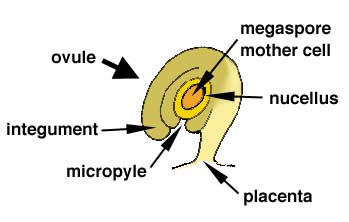
The ovule is an “integumented megasporangium”. This includes the megaspore mother cell which is surrounded by the megasporangium (nucellus) and the integument which is the outer covering of the structure.
Within the ovule the megapsore will undergo meiosis to yield four megaspores. One persists and develops into the female gametophyte (embryo sac).