Tattoos, piercings, and other body modifications have slowly become the norm in everyday society. Items such as earrings have even become standards in fashion. Such modifications have been proven over time to be harmless to the human body, but recently a small association of body modding enthusiasts have taken it to the next level.
In risk of causing harm to their own bodies, these curious experimenters have began to incorporate different gadgets into their bodies in order to add more function to the human body. From sensing the north pole to seeing in the dark, these curious individuals seek to find ways to integrate technology into themselves.

Cool side effects of inserting a magnet into your finger includes neat party tricks. (Image courtesy of Dann Berg)
Using themselves as guinea pigs, the researchers (also known as grinders)have slowly and steadily in progress. From the initial stages of inserting magnets into their hands to feel for electronic signals, they have now been able to do much more miraculous things such as planting a solar panel under their skin as well as inject a special chlorophyll mixture into their eyes to give themselves temporary increased night vision.
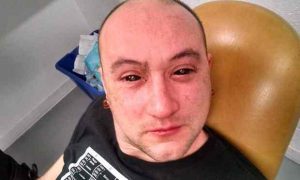
Body-hacker Gabriel Licina after being treated with a night-vision enhancing called Chlorin e6. (Image courtesy of Science.Mic)
While grinders have been largely successful in the research thus far, they have not been able to fully test for safety considerations, but it seems to be a price that they are willing to take. Many tests are done in private locations with limited safety and sanitation abilities, but these conditions do not seem to deter the enthusiasts. In fact, the ever-growing community has planned a convention in 2017 for fellow grinders to meet and discuss their results.
By risking themselves to propel science forward, perhaps a cyborg future isn’t as far as it seems.

-Dennis Lin
Reference:
9 Crazy Body Hacks that Give You Superhuman Powers. Popular Science. Sept. 8, 2015. http://www.popsci.com/9-body-hacks-superhuman-powers (Accessed Nov 11, 2016)
Body-hackers: the people who turn themselves into cyborgs. The Guardian. Aug. 15, 2015. https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/architecture-design-blog/2015/aug/14/body-hackers-the-people-who-turn-themselves-into-cyborgs (Accessed Nov 12, 2016)