With the busy lives that humans now occupy within society, like post-secondary students during exam season for example, balanced and nutritional dietary and exercise are often disregarded or not of a major priority. As a result, the body begins to accumulate fats to act as a storage for excess energy from the foods we eat and thus leads to a case in what society would call “overweight”. The extreme case would result in obesity and this has been a growing concern (and a rather sensitive topic to some) over the past years because excessive body weight is associated with various cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, asthma, and overall, a reduction in life expectancy. However, there is one suggestion that is portrayed by media and human society that is supposedly a shortcut to this problem: weight loss supplements.
Weight loss supplements contain common active ingredients such as bitter orange (synephrine), chromium, guar gum, and Hoodia(1). Synephrine, the main composition of bitter orange, works to suppress appetite and increase the rate of metabolism, thus increasing the number of calories burned (1). Chromium is a mineral that helps to regulate insulin and helps promote muscle growth and fat reduction and guar gum helps block absorption of fats in the body and increase the feeling of fullness whereas Hoodia temporarily suppresses your appetite (1).
Although these active ingredients and their functionality seem to be the solution to obesity, there are many side effects. First of all, synephrine is very similar to ephedrine (see Figure 1), a banned stimulating drug by the Food and Drug Administration due to implications with stroke, heart attacks, and hypertensions, in chemical structure and have many similar characteristics (2).
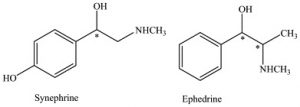
Figure 1: Chemical structure of synephrine compared to ephedrine
Secondly, although chromium exists naturally in our bodies and certain foods, the intake of excessive chromium is disadvantageous because chromium, like other heavy metals, is rather toxic to the human body even at low concentrations. Moreover, although guar gum and Hoodia (Figure 2) work in synch to suppress the production of fats for excessive energy storage as a result from eating food, the overall results are still not proven and can potentially lead to malnutrition (1).
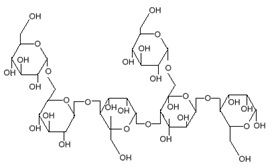
Figure 2: Chemical structure of guar gum (top) and Hoodia (bottom)
To note, a research by Eichner, Maguire, Shea, and Fete have determined that many weight loss supplements are still on the market today that contain other ingredients that are banned due to psychiatric issues and complications with the cardiovascular and nervous system (3). Other ingredients that are not banned but are subject to caution and consumer knowledge are also present in many weight loss supplements(3).
In conclusion, although shortcuts are available to everyday medical conditions such as obesity, there are also many drawbacks to such methods. The optimum method would be the natural method of weight loss which involves a balanced nutritional dietary and exercise, despite how busy our lives may be or what telemarketers or advertisements tell you.
-Andrew Siu
References
Eichner, S., Maguire, M., Shea, L.A., and Fete, M. Journal of the American Pharmacists Association 2016, 5, 538.
Fitday. How do weight loss pills work in the body? http://www.fitday.com/fitness-articles/fitness/weight-loss/how-do-weight-loss-pills-work-in-the-body.html (accessed Oct. 31, 2016).
Google Patents. Pharmaceutical compositions having appetite suppressant activity. http://www.google.com/patents/US7166611 (accessed Oct. 31, 2016)
Nutrient Journal. Is bitter orange fruit (citrus aurantum as synephrine) new ephedra? http://nutrientjournal.com/is-bitter-orange-fruit-citrus-aurantum-as-synephrine-new-ephedra/ (accessed Oct.31, 2016).
Sci-Toys. Guar gum. http://sci-toys.com/ingredients/guar_gum.html (accessed Oct. 31, 2016).











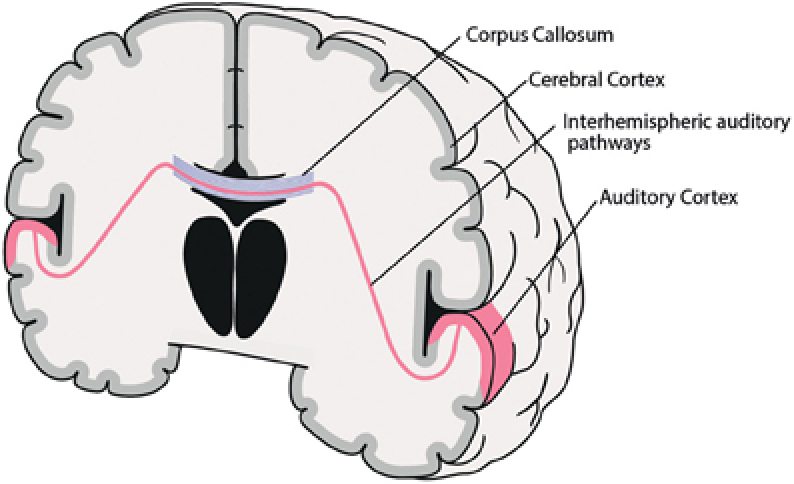 (Graph 2: The location of corpus Callosum) Author: Saskia Steinmann, Gregor Leicht and Christoph Mulert Source: pictures uploaded by the original photographer.
(Graph 2: The location of corpus Callosum) Author: Saskia Steinmann, Gregor Leicht and Christoph Mulert Source: pictures uploaded by the original photographer.