New studies have shown that anxiety level and the development of Alzheimer’s Disease are correlated in older adults.
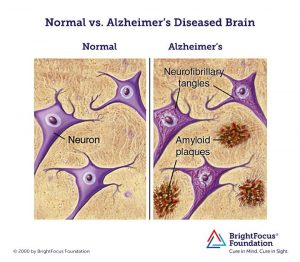
Alzheimer’s Disease is a common type of dementia that inhibits cognitive ability. Although Alzheimer’s is not solely due to old age, increasing age is known to be the greatest risk factor, with majority of the population over 65 years of age diagnosed with this disease. Alzheimer’s develops from the accumulation of plaques (β-amyloid) between nerve cells in the brain and tau tangles, which are twisted fibers inside nerve cells. β-amyloid protein in a normal brain breaks down and is eliminated, but they clump together to form insoluble plaques in an Alzheimer’s Diseased brain. The protein, tau, forms the microtubule which transports nutrients from one nerve cell to another; however, the tau protein within Alzheimer’s individuals is abnormal and doesn’t transport nutrients and other essential supplies through the cell, which leads to cell death. https://www.brightfocus.org/alzheimers/infographic/progression-alzheimers-disease
Researchers of Brigham and Women’s Hospital discovered that higher anxiety level may relate to increasing levels of β-amyloid plaques. They compared symptoms of anxiety with symptoms of depression through baseline imaging scans and assessments on the Geriatric Depression Scale on 270 cognitively normal men and women between ages of 62 and 90. Individuals with higher β-amyloid also acquired higher anxiety level, which suggests that anxiety symptoms could be a leading factor prior to the early stages of cognitive impairment and thus Alzheimer’s development in normal adults.
An example of nerve cells within a normal individual versus an individual with Alzheimer’s Disease. Plaques accumulate around the cells and tau tangles form inside the cells. Image credit: https://www.brightfocus.org/alzheimers/infographic/amyloid-plaques-and-neurofibrillary-tangles
The development of Alzheimer’s Disease can occur over a number of years before cognitive symptoms show; the stages of Alzheimer’s is known from healthy aging, to preclinical Alzheimer’s, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and finally dementia. It may be difficult to distinguish between a decline in cognitive ability due to an increase in age and signs that represent early stage dementia.
The symptoms of Alzheimer’s worsen over the years for an individual, from mild memory loss to the inability of carrying out daily tasks and becoming unresponsive to their environment. With no cure available yet, the discovery of a correlation between anxiety and an increasing plaque growth within nerve cells could be important in slowing down the onset of the disease and treating the symptoms to prevent the development of Alzheimer’s.
-Anita Wang
References:
Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Anxiety: An early indicator of Alzheimer’s disease? https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2018/01/180112091206.htm (accessed Jan 18, 2018).
Alzheimer’s Association. https://www.alz.org/braintour/plaques.asp (accessed Jan 20, 2018).
DeFina, P. A., Moser, R. S., M. G., Lichtenstein, J. D., & Fellus, J. (2013). Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical and Research Update for Health Care Practitioners. Journal of Aging Research. Accessed Jan 21, 2018, from https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jar/2013/207178/.
Alzheimer’s Association. What is Alzheimer’s? https://www.alz.org/alzheimers_disease_what_is_alzheimers.asp (accessed Jan 20, 2018).