Alzheimer’s disease is an incurable disorder and mainly affects people over the age of 65. It is a fatal disease that must be treated early and carefully. A new method to detect early signs of the disease is currently being investigated. Researchers at the University of Porto studied carbon nanomaterials and their biosensing applications to determine the biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease.
A recent study in 2019 urged the importance of biomarkers for indication of Alzheimer’s disease. It is estimated that 5.5 million Americans suffer from Alzheimer’s disease without a cure, and is rapidly increasing. This does not mean nothing can be done to help treat the disease. To enhance treatment for this disease, early diagnosis is necessary and requires a method of indication. The study focused on biomarkers of pre-clinical stages of Alzheimer’s. Stage 1 includes increased amyloid burden, stage 2 includes neuronal injury and evidence of neurodegenerative change, and stage 3 includes subtle cognitive decline. Although the biomarkers developed can provide good results, various criteria must be met.
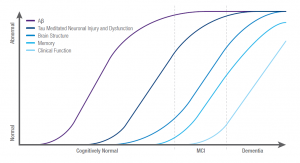
Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease (Source: Laurent Hemoye)
Another study mentions the ability to produce biosensors from nanomaterials mainly because of their electrochemical activity and biocompatibility. Carbon nanotubes display exceptional electronic properties, due to its high surface-to-volume ratio, and is most commonly used for biosensing. Graphene is also common, and can be functionalized by various functional groups to improve selectivity to biomolecules.
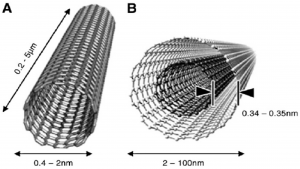
Structure of Nanotubes (Source: Carneiro et al.)
A demand for more research on developing credible biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease is crucial for early diagnosis, as more studies show biosensing as a challenge. This could potentially enhance the understanding of the disease and invent a cure.
-Wilson Wong
