It may sound counterintuitive, but it is in fact a reality. Organic solvent waste is one of the main contributors to pollution generated by the pharmaceutical industry worldwide. These substances are widely used in the preparation of drugs and other vital compounds, and recycling them represents a great challenge for many other industries. Fortunately, a team of researchers from the University of California Santa Barbara, has figured out a way to dramatically reduce the use of organic solvents in widely used synthetic procedures using micellar nano-reactors.
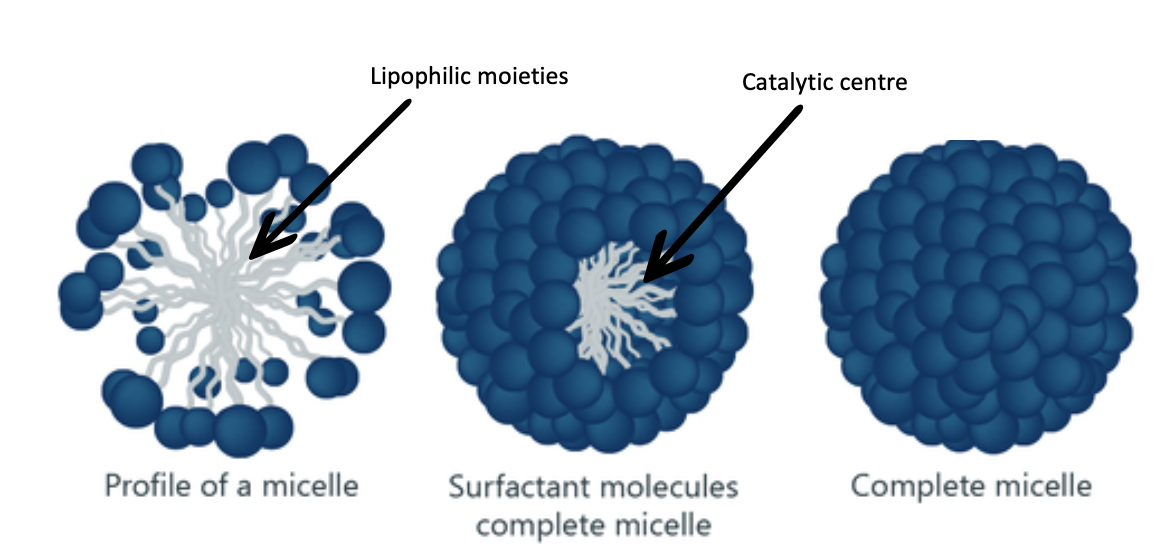
Formation of a Micelle Nano-reactor in aqueous medium. Adapted from https://www.kruss-scientific.com.
It is now possible to perform synthetic procedures in an inorganic solvent, such as water. The key aspect of this technology is the use of functionalized Vitamin E derivatives as nano-catalytic centres that enable organic molecules to react in an inorganic medium. Vitamin E is a lipid-soluble compound, when functionalized, it is able to form micelles in an aqueous environment that dissolve organic compounds as well as other reactants. Reactions take place inside each of these micelles due to their lipophilic character, enabling the entire process to be carried out in water.
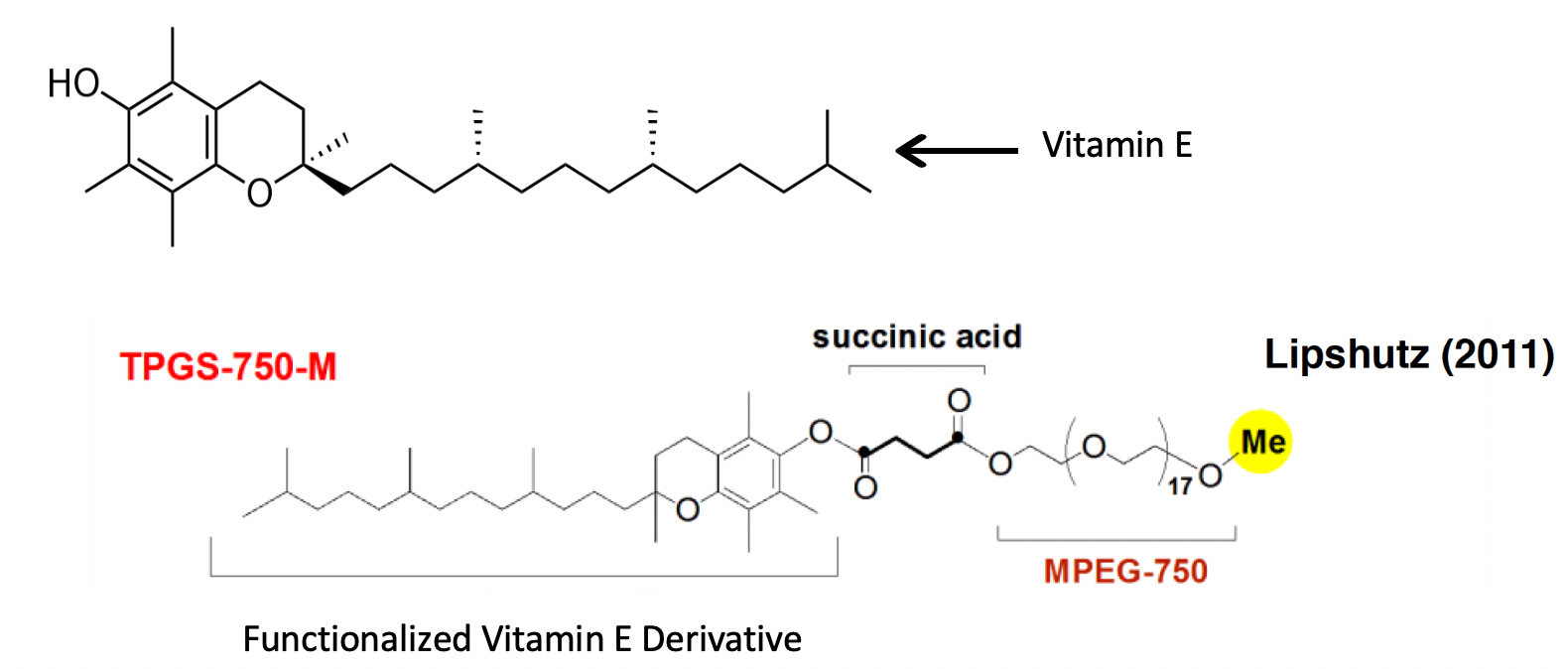
Structure of Micellar nano-reactor. Adapted from ACS.
So far, this technique has been used in a wide variety of reactions which include but is not limited to: Cross-couplings, olefin metatheses, trifluoromethylations and aminations, with high yields, little waste and reduced costs. In many industries, waste is measured in E factors. An E factor is defined as the quotient between the amount of produced waste in kg, divided by the amount of desired product obtained by the process.
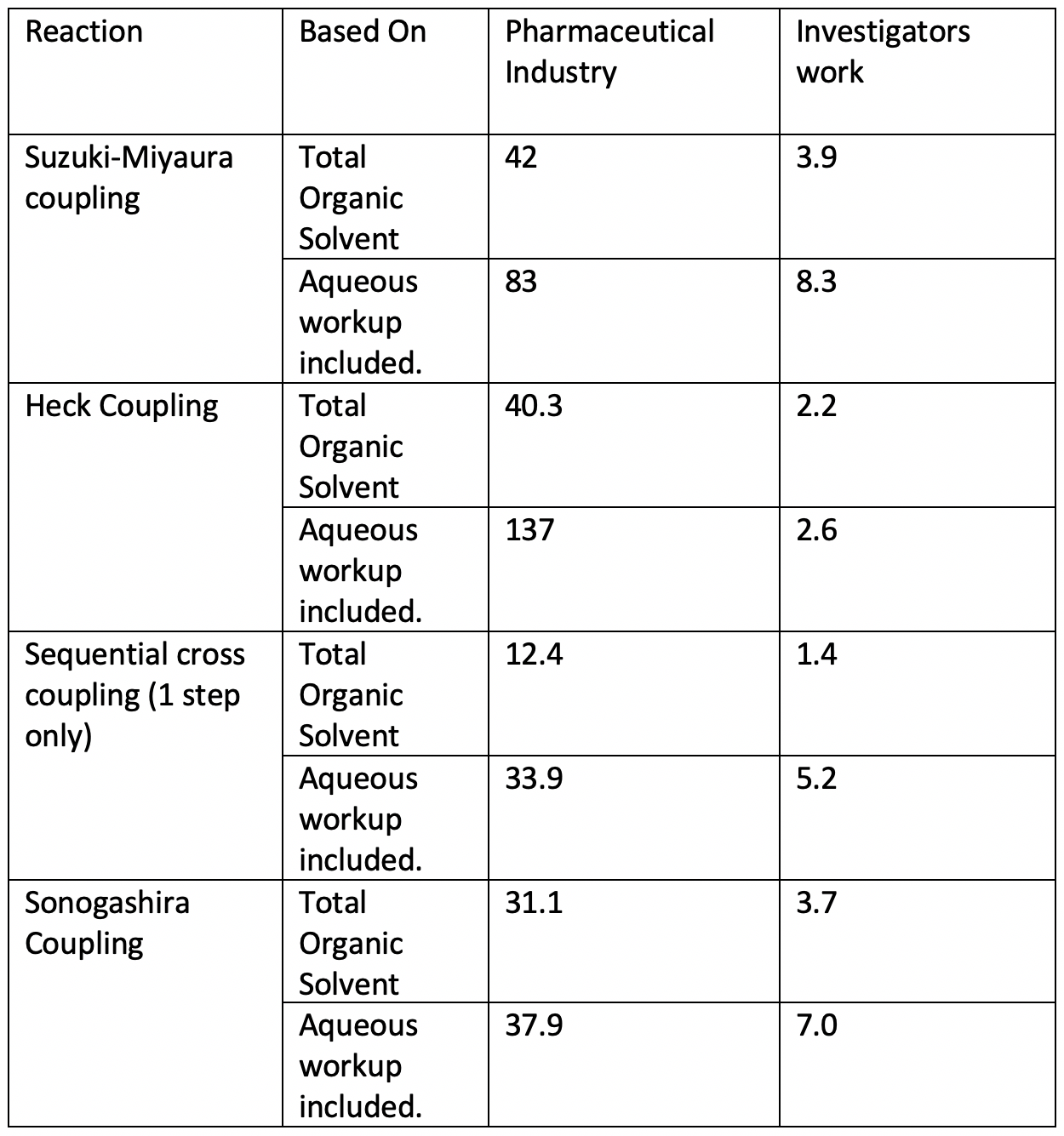
E Factor comparison between pharmaceutical methods and researchers work for cross coupling reactions. Adapted from Green Chemistry
The nano-reactor technology has demonstrated a decrease in E factors for as much as 98%, meaning that this method could drastically change the effect of big corporations in our environment.
-Aron Engelhard

3 responses to “A greener approach to organic synthesis with reduced organic waste”