Can you make anything you want? You might be able to, with a modified blueprint.
Following instructions step-by-step can can be challenging, especially if there are multiple pathways. A specialized method can be used to selectively hand-pick specific products.
A design is invented from existing functional methods to counteract the difficulties of multiple products. Dr. Schafer at the University of British Columbia implements a system to accurately isolate the desired product.
The study urges the importance of terpenoid-alkaloids, compounds used for their pharmacological properties, compared to individual terpenes and alkaloids. The problem lies in the mechanism of producing terpenoid-alkaloids.
Past studies show the use of catalysts, a tool that promotes reactions to occur, result in multiple products to be formed. To selectively form a single product, the catalyst must be optimized.
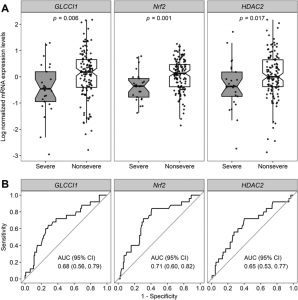
A tantalum-based, metal catalyst, precursor was used to test its reactivity to terpene substrates, and shows promising results. The terpenoid-alkaloid conversion rate for the Ta(CH2SiMe3)3Cl catalyst is higher than the other precursors, as seen in Figure 1.
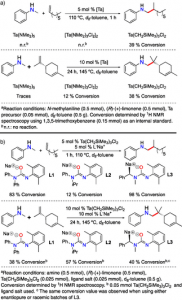
Figure 1. (a) Addition of Ta-based precursors in 1-octene and limonene (b) Ta-based precursor with N,O-chelating ligands in 1-octene and limonene (Source: Schafer)
An addition of various chelating ligands, molecules that attach to metal ion centers, to the Ta catalyst further increased the conversion rate. Different ligands show varying rates.
The reaction to synthesize terpenoid-alkaloids is called hydroaminoalkylation. Alongside the most optimal catalyst system created, terpenoid-alkaloids are produced with various yields and conversion rates on terpene substrates.
The selectivity factor can be supported by using NMR spectroscopy, a method that can determine the structure of the product. A chiral high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is used to determine if the product present is oriented in only one form.
The data is analyzed to determine the best possible reaction mechanism to accurately produce the desired product. The isolation and purification process is simple because the reaction went through to form one product.
The study experiments with different substrates of similar structure to further confirm their suspicions. The specificity of the reaction is recorded, including exact amounts of chemicals used and the reaction parameters studied in.
The hydroaminoalkylation reaction is chemically altered to regulate the formation of one specific product of terpenoid-alkaloids. More research is required to investigate reactivities of different substrates in various conditions to determine an even more optimal mechanism.
The act of modifying concrete steps to selectively isolate a distinct product is proven to succeed. The end result can offer enhanced properties to be applied.
Reference
Dipucchio, R. C.; Rosca, S. C.; Athavan, G.; Schafer, L. L. Exploiting Natural Complexity: Synthetic Terpenoid‐Alkaloids by Regioselective and Diastereoselective Hydroaminoalkylation Catalysis. ChemCatChem 2019, 11 (16), 3871–3876.
-Wilson Wong