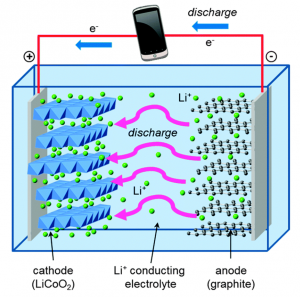
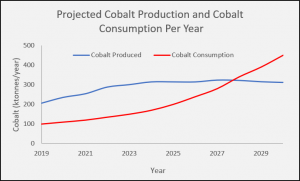
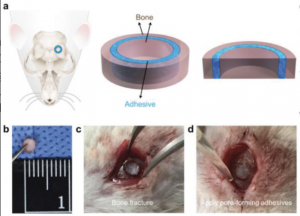
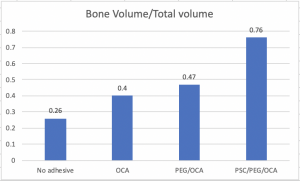
We have all heard about eating with our eyes first, but no one ever talks about how our environment affects our meals. Mother Nature Network (MNN) indicate that your environment plays big factor in your perception of food. Whether it’s lighting, furniture, or noise, they all play a role.

Figure 1 – Chocolate Ice Cream Retrived from: HandletheHeat
This study published in October 2019 explored temporal changes in how chocolate ice cream was perceived when eaten at different locations. Each participant had their electrophysisological properties, emotions, and temporal changes in flavour monitored, with 5 minute breaks inbetween each measurement. The participants were randomly assigned different environments such as a university study area, a bus stop, a cafe, or a sensory testing laboratory.

Figure 2 – The 4 locations in which tests were conducted. A – Sensory testing laboratory B – University study area C – Bus stop D – Cafe Retrieved from: Figure 2 of Xu et al.
Electrophysiological Responses
3 electrophysiological responses were measured, including skin conductance (SC), blood volume pulse (BVP), and heart rate (HR). They found that SC and HR was significantly influenced by different environments. Using the Tukey-Kramer test, they found that eating chocolate ice cream in the study space compared to the laboratory significantly increases SC (F(3,156) = 3.149, p < 0.05). Furthermore, the HR was significantly lower after consumption in the study area compared to a bus stop (F(3,156) = 2.673, p < 0.05).
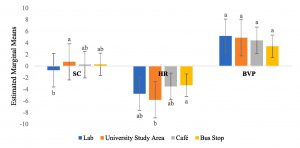
Figure 3 – Electrophysiological response measurements. n= 160 (50 males/110 females) Retrieved from: Figure 10 Xu et al.
Emotional Response
In a pilot study, the emotional responses were reported among 97 individuals. Positive emotions were noted such as happiness, cheerfulness, and joy. In addition, negative emotions were noted as well, such as tenseness, unhappiness, and anxiousness. Using a Cochran Q-test, they found that a significant number of negative emotions were associated with the bus stop compared to the other 3 environments. Furthermore, a significant number of positive emotions were expressed after consuming chocolate ice cream at a cafe or university compared to a bus stop.
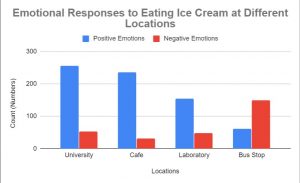
Figure 4 – Both positive and negative emotions associated with eating chocolate ice cream in 4 different environments. Data adapted from: Xu et al.
Taste
The dominance of different attributes were measured and converted to a percentage of time it spent as a dominant factor. Sweetness the dominant attribute across all environments (46% lab, 33% university, 48% cafe, 38% bus stop). Interestingly, the dominance of sweetness subsided overtime, and other attributes became dominant. Other factors such as creaminess, roastedness, and bitterness was noted as well. At the bus stop, bitterness became the most dominant factor after sweetness, while the other 3 locations reported either creaminess, cocoa, or vanilla flavours were dominant.
How do I improve my next meal?
Next time you’re at the dinner table, try some of these tricks to improve the taste of your meal. By listening to higher pitched music, sour and sweet flavours are highlighted, while lower pitched music enhances bitter flavours. Even something as simple as the way food is arranged on the plate will impact its flavour.
-Jackson Kuan









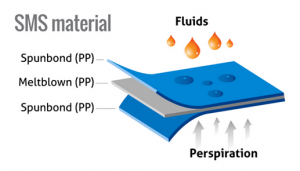
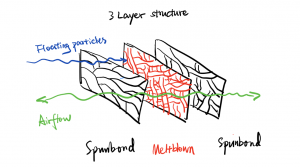
 But in the case of the new coronavirus, the most effective type of face masks are medical-surgical masks and masks filtering 95% or more of non-oily particles, such as N95, KN95, DS2, FFP2, etc. At present, China’s medical face masks are mainly divided into three types: medical protective masks with the highest protection level, medical-surgical masks commonly used in invasive operating environments such as operating rooms, and ordinary disposable medical masks.
But in the case of the new coronavirus, the most effective type of face masks are medical-surgical masks and masks filtering 95% or more of non-oily particles, such as N95, KN95, DS2, FFP2, etc. At present, China’s medical face masks are mainly divided into three types: medical protective masks with the highest protection level, medical-surgical masks commonly used in invasive operating environments such as operating rooms, and ordinary disposable medical masks.