Have you ever wondered why we have desires for sweet food but not bitter food? Dr. Li Wang and other scientists at Columbia University have discovered that mammalian brains for tasting can be re-patterned or erased by performing a series of experiments on mice. This study has significance for future studies in eating disorders and weight management.
The taste sensory system
Mammalians have a developed sensory system for identifying tastes and associating tastes with mechanisms of reward and aversion. This sensory system has two main parts: the tongue and the brain. There are many sensory neurons in our tongues. These sensory neurons, the detectors of the five basic tastes (sweet, sour, salty, bitter and umami), signal our brains and turn on the amygdala of the brains responsible for identifying and interpreting tastes. Dr. Li Wang and her team have confirmed that neurons in the sweet-responsive cortex project to a different area compared to those in the bitter-responsive cortex. The strong segregation of neuron projection transmits desirable, or aversive taste signals, as shown in Figures 1 and 2. Therefore, we cannot stop eating sweets since our amygdala associate sweets with appetitive, desirable signals.
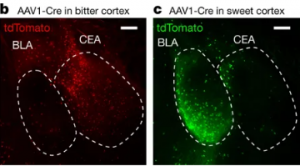
Figure 1. b and c show the active bitter taste cortex and active sweet taste cortex respectively. Source: “Nature Journal”
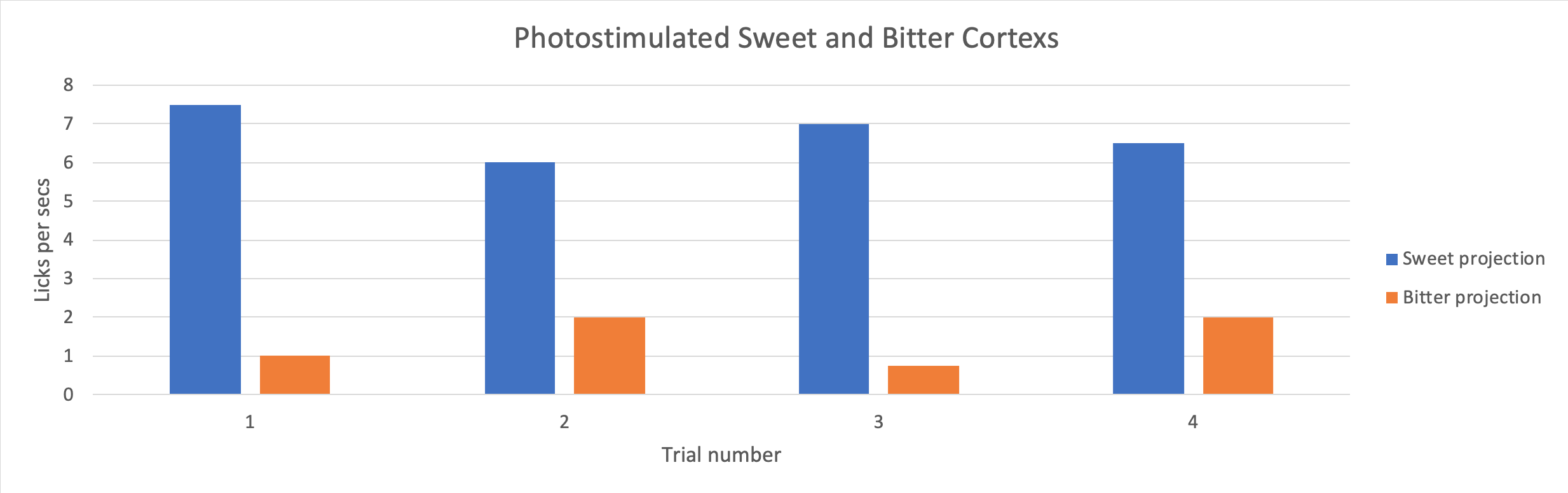
Figure 2. Licks per second (Licks rate) of mice upon photostimulation of the sweet and bitter cortexes. Adapted from “Nature Journal“
Rewiring the brain on taste
Dr. Wang and her team rewound the brain of mice on taste by using a drug to silence the neurons in the sweet-responsive cortex and the bitter-responsive cortex, respectively. The team used licks per second to quantify and verify the appetitive and aversive responses of the mice upon photo-stimulating the sweet and bitter cortexes independently. The team found out that by silencing the neurons in the sweet cortex, the lick rate decreased, according to Figure3. This showed that the mice could not recognize sweet when the neurons were silenced by the drug. This confirmed that the taste specific neurons are essential to recognize tastes.
Figure 3 also showed another interesting phenomenon that the team made the animals think they were tasting sweet, even when the animal was drinking water. In Figure3, without the presence of the sweet neuron silencer, the lick rate of the mice with their sweet cortex stimulated was two times higher compared to the mice without the stimulation. The increase in the lick rate in Figure 3. showed that neurons in the amygdala control an animal’s sensory perception of taste.
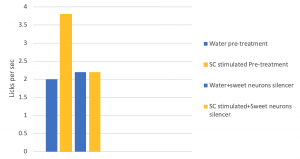
Figure 3. Photostimulated sweet cortex in the presence or absence of sweet neuron inhibitor. Adapted from “Nature Journal”
The finding that animals’ brains can be manipulated and rewound to change the perceptions of taste has implications in future studies in weight management and eating disorders. By using small drugs to target these taste-specific neurons, we may say no for eating more and more sweets.
Reference
Li Wang. The coding of valence and identity in the mammalian taste system. Nature Journal, 2018; 558, 127-131. DOI: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0165-4
Pricia
2020-03-02

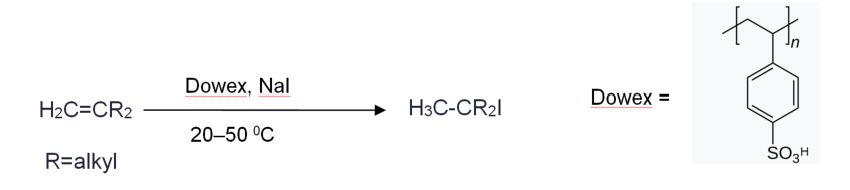






 Source:
Source:  Source:
Source: Source:
Source: