Add Users
If you want to add yourself to this blog, please log in.
-
Recent Posts
Archives
Categories
Authors
You will never know, what happens in an organic chemistry lab.
“Organic synthesis”, seems like a mysterious area to many people without a chemistry degree. Generally, organic chemists synthesize molecules with academic values or commercial values, like drugs and catalysts. However, there are some chemists like to create some fun molecules, which are usually thought to be useless.
Dr. James Tour at Rice University is a famous chemist in building “useless” molecules, such as “NanoKid” and “NanoCar”. In April 2003, he published an article of synthesis “NanoKid”, as well as “NanoProfessionals” based on the NanoKid.
Synthesis and Modifications of the NanoKid
A NanoKid is formed by two parts: an upper body and a lower body. The upper and lower bodies were connected by a Pd/Cu-catalyst through a Sonogashira Reaction. Meanwhile, the “head” of a NanoKid can be changed by changing the ketal part of the NanoKid. Dr. James Tour used a variety of diols to make NanoProfessionals, such as NanoChef, NanoAthlete and NanoScholar. Furthermore, by hydrogenating the triple bond on the “waist” to a single bond, and coupling “hands” of NanoKids, the research team got NanoBalletDancers and NanoKid-Polymer respectively.
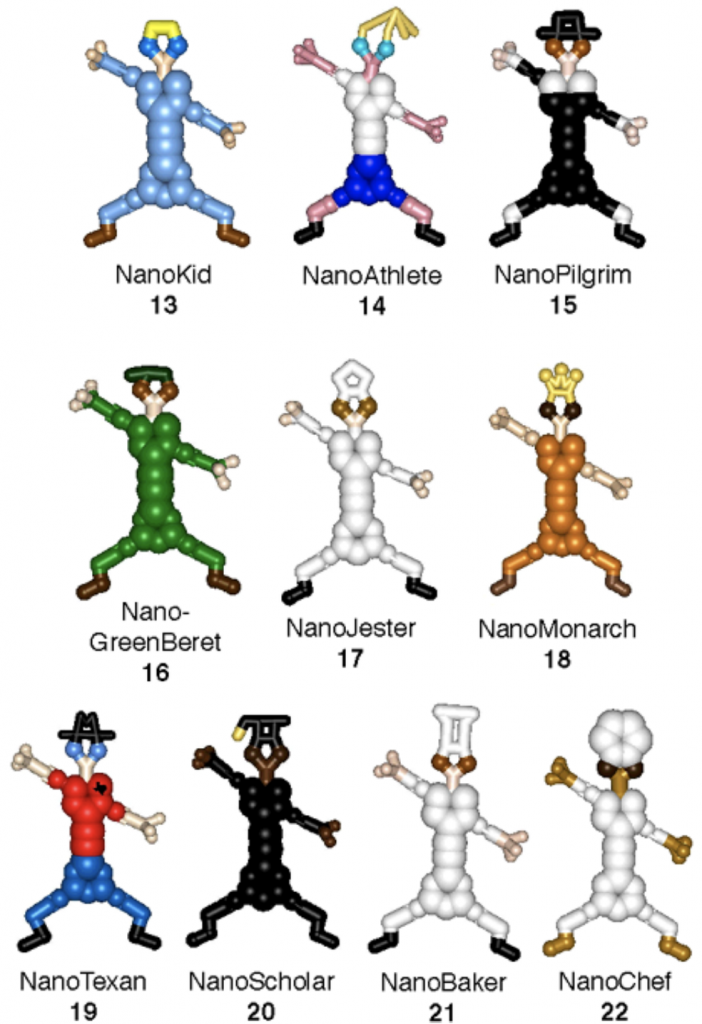

Electron cloud-based space-filling model of NanoProfessionals (Copyright: James M. Tour)
NanoCar
Other than NanoKids, the research group of Dr. Tour also built NanoCars by carbon-based molecules and won the first prize in the NanoCar Race in 2017.
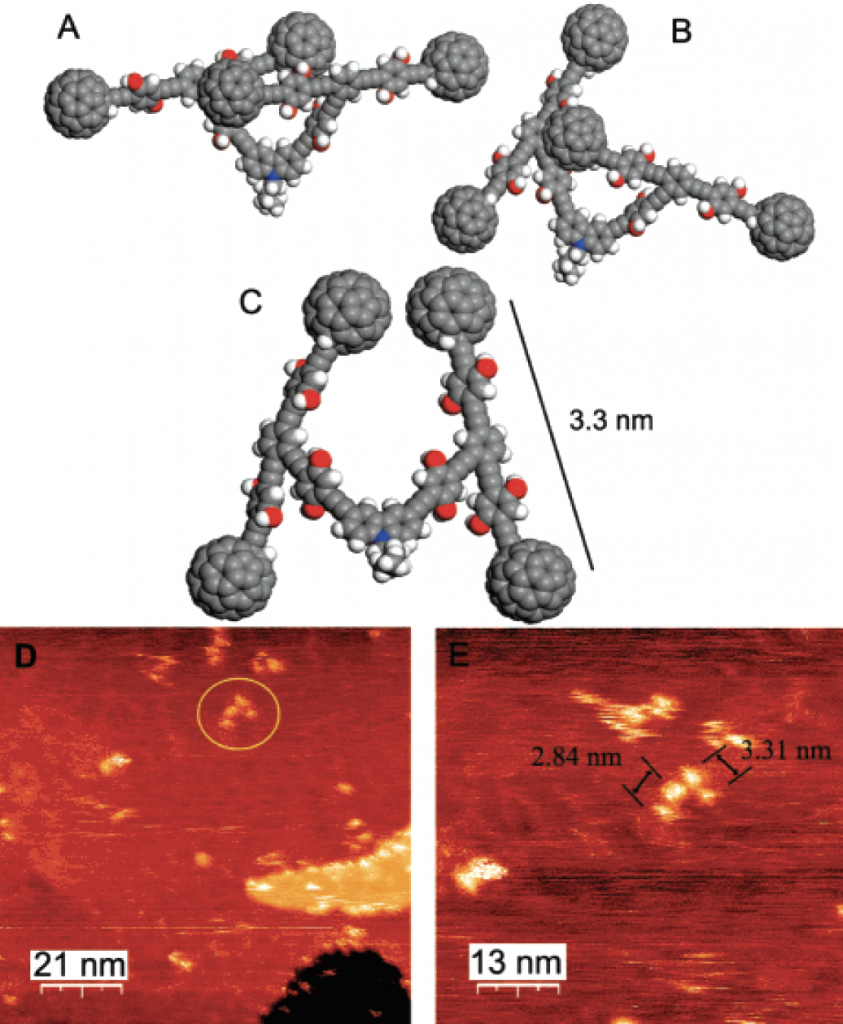
Three models of possible conformations of NanoCars under the scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) (Copyright: Organic Letters)
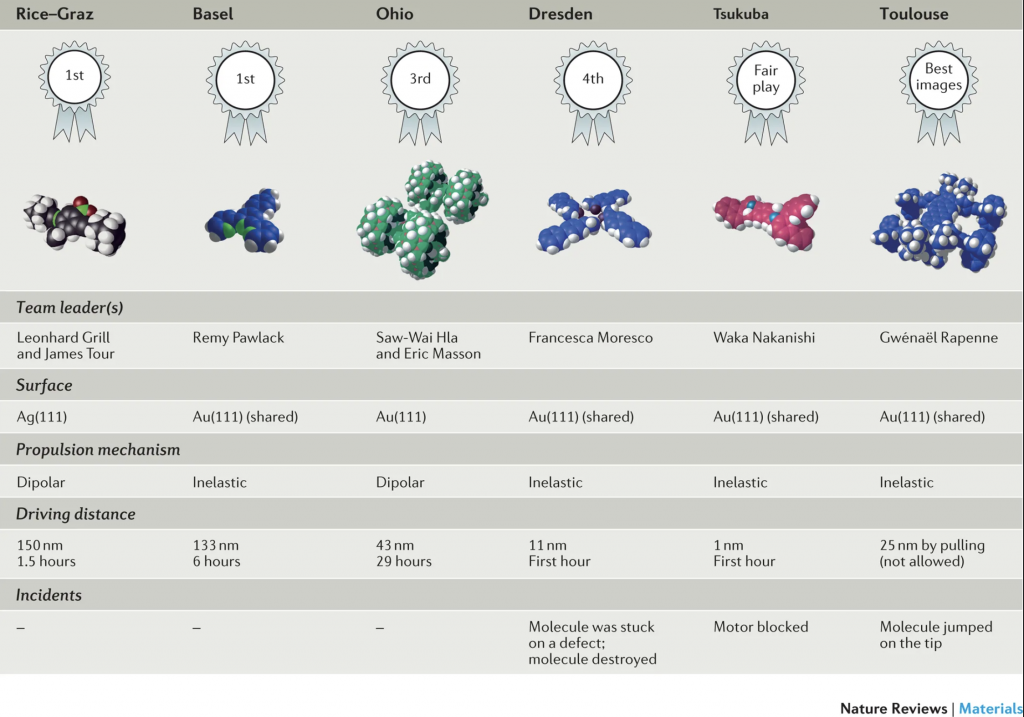
Summary of the NanoCar Race results. (Copyright: Nature)
Recently, many organic chemists use carbon atoms as building blocks to build molecules with unusual names. Such as “Broken Windowpane” which has a molecular formula of C8H12 and looks like a broken window, “Housane” which looks like a house and “Churchane” which looks like a church.
Is it a waste of taxpayers’ money?
Chemists have already synthesized the NanoKid, NanoCar and Broken Windowpane. In the future, chemists might build more interesting Nano-things. These research outcomes are very delighted, but some people might ask: Is it a waste of money? What is the meaning of these chemicals?
To synthesize a Broken Windowpane, chemists need to overcome an extraordinary intramolecular tension, to give birth to a NanoKid, researchers had to design and control the reaction accurately. “Beyond the molecular-sized domain, there is no conceivable entity upon which to tailor architectures that could have programmed cohesive interactions between the individual building blocks. It is at this size region that synthetic chemists have been inherently captivated; however, their fascination is rarely shared by the layperson.” Dr. Tour said. The Broken Windowpane might be adapted for more fantastic molecules, and the NanoCar might be used to deliver targeted drugs to a certain part of the body one day in the future. These molecules show that chemists can make whatever they want, and how magic chemistry is.
Posted in Chemistry News, Organic Chemistry, Popular Science
Tagged NanoCar, NanoKid, Nanomaterials, OrganicChemistry
Microplastic issues? PLA can solve the problems!
Did you know that less than 11% of plastics have been recycled in Canada since the 1950s? Many plastics, such as water bottles, bags, and takeaway coffee cups, are buried in landfills and are disposed of into the oceans.
Over a long period of exposure to air, sunlight, and moisture, they eventually “disappear” – becoming invisible to the naked eye. In this case, are plastics degradable? While we may use the word “degradation”, they do not actually disappear. The invisible ones have taken the form of microplastics, thereby still existing and still polluting our ecosystem.
Video clip 1. Microplastics as a food for baby fishes.
To mitigate this issue, chemists have made an effort to develop biodegradable polymers that can be applied to produce commercial plastics. In modern polymer chemistry, considerable attention has been paid to polylactic acid, so-called PLA. Polylactic acid is produced from lactide which is derived from renewable resources such as corn and potato starch.
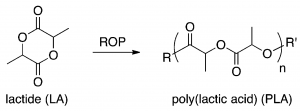 Figure 1. Chemical structures of lactide (monomer) and polylactic acid (polymer) . ROP stands for ring-opening polymerization (a type of polymerization). DOI:10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00447
Figure 1. Chemical structures of lactide (monomer) and polylactic acid (polymer) . ROP stands for ring-opening polymerization (a type of polymerization). DOI:10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00447
Unlike petroleum-based polymers used in plastics such as polyethylene (PE), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and polypropylene (PP), PLA has biodegradability and biocompatibility.The enriched oxygen atoms in PLA and its structural flexibility make it undergo hydrolytic and enzymatic degradations, regenerating monomers and oligomers. The degraded substances are further broken down to water and carbon dioxide, precluding the formation of microplastics. Therefore, PLA is a great candidate to substitute for plastics derived from petroleum sources.
Although there are some general issues to resolve from an economical perspective, the environmentally friendly outcomes and industrial applications have made PLA a more attractive material for plastics PLA certainly has the potential to save our future!
-Young Cho
Posted in Biological Chemistry, Organic Chemistry
Tagged biodegradable polymer, microplastic, PLA, polylactic acid
These Ingredients in Sunscreen Might Promote Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most diagnosed cancer with an estimated diagnosis of 331,530 women and 2670 men this year in the US alone. Research by the University of Massachusetts Amherst published on January 15 2020 observed that chemicals in everyday items can increase the chances of breast cancer in women.
Cancer is a dangerous illness, caused by the uncontrolled division of cells in the body. It is predicted that this year 41,760 women and 500 men will die of breast cancer in the US. These estimations may now have to take into consideration th
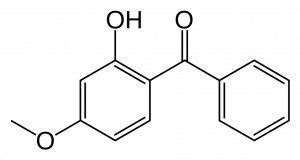
Chemical Structure of Benzophenone-3 aka Oxybenzone Source: Wikipedia
e dangers of sunscreen and cosmetics, including makeup, hair products, and moisturizers.These everyday products are known to contain the chemicals benzophenone-3 (BP-3) and propylparaben (PP).
The study indicates that previous research into the effects of BP-3 had shown that only extremely high concentrations could promote cancer growth. Since these concentrations were far beyond the n
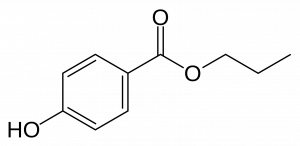
Chemical Structure of Propylparaben Source: Wikipedia
ormal levels of exposure to women, there was no cause for concern.
However, the study showed that mice exposed to oils containing BP-3 and PP had an increase in cancer. The results suggest that BP-3 and PP effect cells that contain oestrogen receptors. High levels of oestrogen has previously been linked to an increase in breast cancer. The exposure to BP-3 and PP at only a fraction of the cancer promoting concentration was shown to increase DNA damage by causing structures known as R-Loops.

Dr Joesph Jerry of UMass Amherst, science director of Pioneer Valley Institute, and co-director of Rays of Hope Centre for Breast Cancer. Source: UMass Amherst from EurekAlert!
Based on the results, Dr Joseph Jerry, the professor of Veterinary & Animal Sciences at the University of Massachusetts Amherst warns that, “There may be a risk at lower levels than we would have previously understood,”.
The study shows that DNA damage only occurs in cells containing oestrogen receptors, and that all other cells show no adverse effects.
It might be time to take a look at the ingredients in your everyday items!
– Chantell Jansz
Posted in Biological Chemistry, Chemistry News, Popular Science
Tagged biochemistry, breast cancer, cancer, cancer research, cosmetics, research, sunscreen
Revised: Xenobots: World’s First Living ‘Flesh Robot’ was Created from Frog Cells
Scientists have created the world’s first living, self-healing robots using stem cells from frogs.
Published on PNAS, a team of scientists from the University of Tufts and the University of Vermont created the first living robot named Xenobots without using any metals or plastics.
Those flesh robots constructed from frog cells can manipulate objects, move as directed and even interact with each other. The success of Xenobots promises advances in safe drug delivery, environmental remediation and understanding origins of life.
A New Star in Robotics
“They’re neither a traditional robot nor a known species of animal. It’s a new class of artifact: a living, programmable organism.”
explained by computer scientist Joshua Bongard, a collaborator of this project. Before Xenobots, genetic modifications on a single cell or 3D printing tissues have been attempted to construct living systems. Despite the success in simulating biological structures, those methods cannot predict any behaviors. So the question became how to construct a biological system that ‘knows’ what to behave.
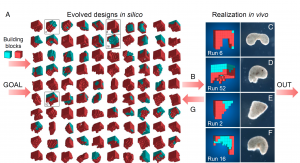
A behavioral goal (e.g., maximize displacement), along with structural building blocks designed by computer. The blue and red regions indicate two types of cells. Source: PNAS
The Birth of Xenbots
Thanks to computer scientists, a method called ‘evolutionary algorism’ has been developed to achieve this goal.
During the robot design process, scientists first input some behavioral goals, for example, maximizing the moving area or leaving a hole in the center to carry drug molecules. The computer would then explore different building blocks with the assistance of evolutionary algorism. There are two types of frog cells for the building block, and by cleverly combining those cells, the robot may move as expected.
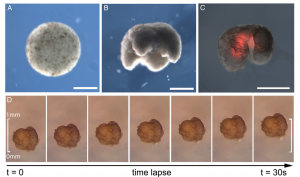
Xenobot under the microscope. The diameter is less than 1mm. Source: PNAS
Finally, from thousands of building block combinations, less than ten designs were selected for the experiment in vivo. The robots were manufactured under microscopy through a series of steps and tested in real conditions.
The result is surprising. Those robots can live for weeks in the water environment without additional energy. Once the energy dissipated, the cells die naturally and degrade as common organisms. Although they lack a nervous system, the robots can still change their motion regularly, and different individuals tend to exhibit various moving patterns.
 Video from the University of Vermont
Video from the University of Vermont
Will The Terminator Come True?
The incredible character of the living robot is the ability to self-repair in the face of damage. This feature is reflected in the Terminator, in which robots dominate the world.
Sam Kriegman, the first author of the study, admitted the moral issues brought by this project: the living robot variations may develop cognitive ability in the future. He also pointed out that, because this study is open to the public, society can discuss the topic and regulators should also formulate applicable policies. However, in the short term, this study is more likely to inspire future robotics and help us understand the innate creativity in life.
-Bokang Hou
Should you be worried?—An Outbreak of Novel Coronavirus!
Since December 2019, an unexplained pneumonia epidemic has occurred in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China. An investigation found that these were related to Wuhan’s “South China Seafood Market”. Wuhan organized a multi-disciplinary expert consultation survey and used laboratory testing to identify pneumonia in Wuhan as viral pneumonia. On January 8, 2020, a new coronavirus was initially identified as the pathogen of the epidemic.
The spread of the novel Coronavirus
The outbreak of this infectious disease was first occured in Wuhan in December, 2019 and then spreaded globally since the huge flow og people in Wuhan during lunar new year. According to the New York Times, there are more than 4,500 people in Asia infected the coronavirus as well as many other are suspected. At least 106 people have died as of Jan. 27, 20.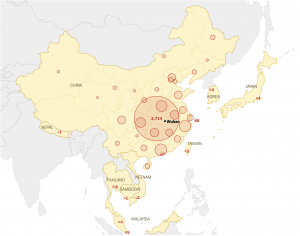 Sources: National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China; local governments. Note: Data as of 9 p.m E.T., Jan. 27
Sources: National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China; local governments. Note: Data as of 9 p.m E.T., Jan. 27
Evolutionary sources of coronavirus and molecular pathways for infecting humans
To analyze the evolutionary source and possible natural host of the novel coronavirus, the researchers in this paper analyzed genetic evolution by comparing the novel coronavirus with collected large amount of coronavirus data. It was found that the novel coronavirus of Wuhan belongs to Betacoronavirus which is a RNA virus that parasitizes and infects higher animals (including humans). It is adjacent to the SARS virus and the SARS-like virus group in the position of the evolutionary tree. Interestingly, their evolutionarily common outgroup is an HKU9-1 coronavirus parasitic to Rousettus bats. Therefore, the common ancestor of Wuhan coronavirus and SARS or SARS-like coronavirus is a virus similar to HKU9-1. As the evolutionary neighbors and outgroups of Wuhan coronavirus have been found in various types of bats, it is speculated that the natural host of Wuhan coronavirus may also be bats and Wuhan coronavirus is likely to have unknown intermediate host vectors during the transmission from bat to human.
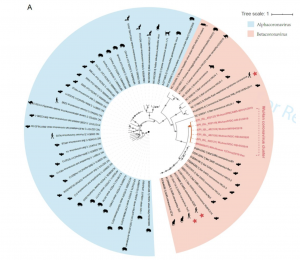 Phylogenetic tree (Source)
Phylogenetic tree (Source)
The authors used molecular computational simulation methods to perform structural docking studies on Wuhan coronavirus S-protein and human ACE2 protein, and found that although 4 of the 5 key amino acids that bind to ACE2 protein in Wuhan coronavirus S-protein have changed, the amino acids after the change have perfectly maintained the interaction between SARS virus S-protein and ACE2 protein. This result indicates that Wuhan coronavirus infects human respiratory epithelial cells through the molecular mechanism of S-protein interaction with human ACE2 protein, predicitng that Wuhan coronavirus has strong ability to infect humans.
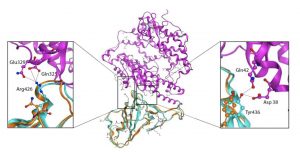 Cα RMSD of 1.45 Å on the RBD domain compared to the SARS-CoV S-protein structure (Source)
Cα RMSD of 1.45 Å on the RBD domain compared to the SARS-CoV S-protein structure (Source)
Tips for prevention of coronavirus (source):
- Wash your hands with soap for at least 20 seconds and avoid touching you mouth, nose and eyes with unwashed hands.
- Keep a safe distance with people who are sick
- Cover your cough or sneeze with tissue and throw the tissue in the trash
- Clean frequently touched surfaces
-Xinyue Yang
Posted on Jan. 27th. 2020
Posted in Biological Chemistry, Chemistry News, Popular Science
Tagged Coronavirus, Evolution, Protein, Wuhan
Toxic Receipt – Another BPA Problem After Baby Bottles
Remember BPA was banned for making baby bottles by the Canadian government in 2010 due to its hormone-disrupting? You may think the problem is solved but BPA is still sneaking into people’s bodies and harm people’s health through a thing we are using daily—receipt.
 Source: http://k.sina.com.cn/
Source: http://k.sina.com.cn/
After almost every payment is made, whether needed or not, the receipt will be printed out. These receipts are usually made of Bisphenol A (BPA)-containing thermal paper, which is an ink-free choice for most of the banks, supermarket, pos machine, etc. You may think that is not a problem since you will only touch it for a few seconds rather than use it for daily drinking.
However, researchers at the University of Missouri have shown that BPA found on the heat-sensitive paper used in shopping receipts can be absorbed through the skin, significantly raising BPA levels in the body.
What is BPA Exactly?
BPA is the initial of Bisphenol A, it is a chemical raw material that can be added to plastics to make them colorless, transparent, durable, lightweight and impact resistant. BPA was widely used in the manufacture of baby bottles, water bottles, sealants for dental fillings, eye lenses and hundreds of other commodities until banned in 2010.
BPA is an endocrine disruptor that can interfere with the body’s endocrine system by mimicking the effects of estrogen. When BPA shows hormone-like effects, the real hormones in the body may not work properly.
And what’s worse is….
BPA Absorption Increased Significantly After Using Hand Sanitizer
One study showed that using hand sanitizer or other skincare products before handling receipts increases the absorption of BPA by up to 185 times, reaching levels that can lead to obesity, diabetes, coronary heart disease, infertility, and cancer.
The study mimics a common behavior seen in fast-food restaurants: wash your hands with hand sanitizer, hold the receipt for a while, and then eat with that hand.
By testing BPA on hands, they found that after using hand sanitizer, large amounts of BPA were transferred from heat-sensitive paper to hands in just a few seconds. BPA transfers hundreds of times faster than in dry hands.
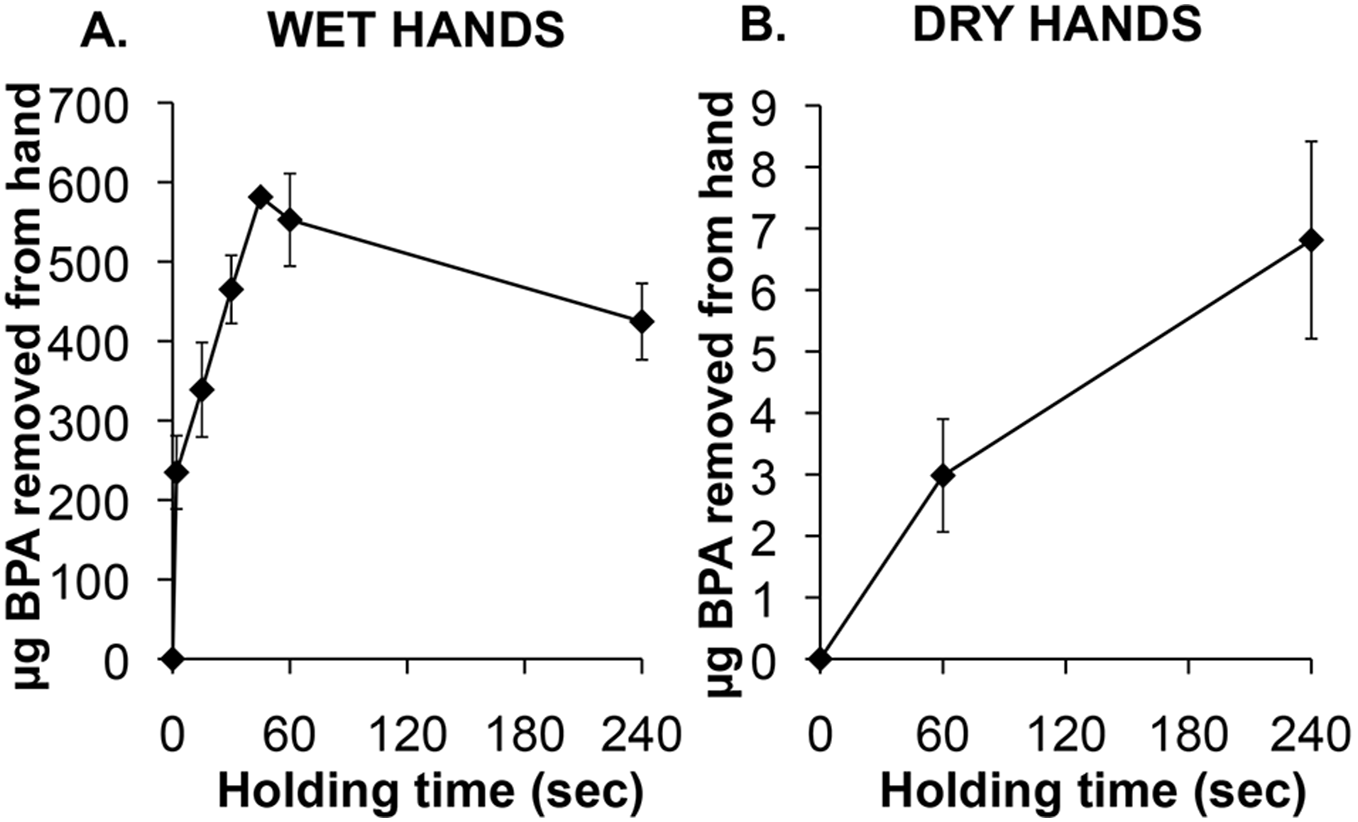 Source: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110509.g002
Source: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110509.g002
This is because hand sanitizers and skincare products (such as soaps, sunscreens, lotions) contain “dermal osmotic enhancers” used to enhance the delivery of the active ingredients in the products. This enhanced effect leads to a rapid transfer of BPA through the skin.
BPA passed on to the hands is absorbed through the skin and under the tongue when eating, leading to higher levels of the chemical in the blood and urine.
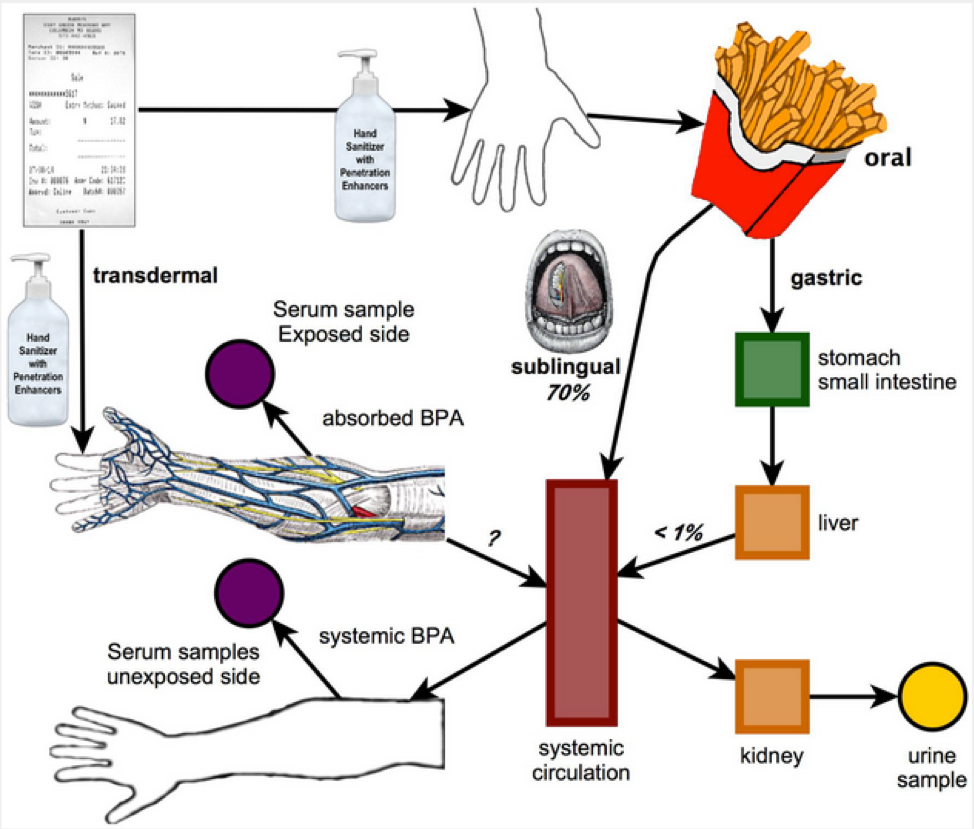 Source: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110509.g002
Source: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110509.g002
So, next time, remember to dry your hands before touching the receipt and wash your hands afterward. Or simply tell the waiter that you don’t need the receipt.
—–Yicheng Zhu
Posted in Biological Chemistry, Chemistry News, Uncategorized