Herd immunity is often generated through vaccination or widespread infection. For the current Covid-19 pandemic, many scientists and experts advocate social distancing to avoid overwhelming hospitals while buying more time for the inventions of vaccines and treatments. Why is vaccination favored by scientists and medical experts than a widespread infection? How is herd immunity achieved through vaccination?
What is herd immunity?
Herd immunity refers to a means of protecting a whole community from disease by immunizing a critical portion of its populace. Vaccination protects the vaccinated person but also the people who are not immunized. However, to achieve herd immunity, we need a certain percentage of people in a community to be vaccinated.
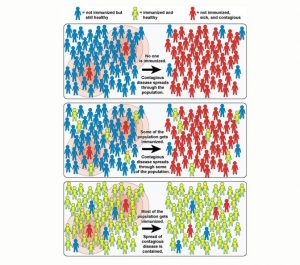
Herd immunity, the result of a high immunization rate. Source: The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease (NIAID)
To reach the herd immunity threshold, different vaccination coverages which depend on the basic reproduction number (Ro) are required. Vaccination coverage is the estimated percentage of people who have received specific vaccines. For example, measles, a highly contagious virus, has a Ro value between 12 and 18. This high Ro value calls for a high vaccine coverage which is 92-94%. In other words, to reach the herd immunity threshold, at least 92% of the population needs to be vaccinated.
The higher the vaccine coverage the better…
Does it mean that measles will die out as long as 92% of the population is vaccinated against measles? The answer is no. Dr. Plans-Rubio, an epidemiology expert in Europe, found a significant negative correlation (P<0.05) between the incidence of measles in 2017–2018 in different countries of the European Union and measles vaccination coverage with herd immunity levels in the target measles vaccination population during 2015–2017. According to Dr. Plans-Rubio, low percentages of measles vaccination coverage with two doses of vaccine and the resulting low herd immunity levels explained measles incidence and persistence of measles in the European Union in 2017-2018. To eliminate the measles virus in the European Union, W.H.O must improve routine measles vaccination coverage and conduct supplementary measles vaccination campaigns.
| Linear correlation coefficient | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage with two doses of measles vaccine | − 0.533 | 0.003 |
| Coverage with one dose of measles vaccine | 0.523 | 0.004 |
| Coverage with first dose of measles vaccine | − 0.332 | 0.079 |
| Coverage with second dose of measles vaccine | − 0.559 | 0.002 |
| Prevalence of individuals with vaccine-induced measles protection (Iv) | − 0.580 | 0.001 |
| Herd immunity gap (94.5 − Iv)a | − 0.580 | 0.001 |
(Table source: European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases)
Relating to Covid-19 pandemic
Without measles vaccines, we would not have lowered the mortality rate of measles and reached herd immunity in most countries. The novel coronavirus, similar to measles, is also contagious. To lower the mortality rate of Covid-19 and reach herd immunity, the corresponding vaccine is required. Hence, every single one of us should practice social distancing to avoid overwhelming our healthcare system while scientists strive to invent the corresponding vaccine.
Reference:
Plans-Rubio Pedro. Low percentages of measles vaccination coverage with two doses of vaccine and low herd immunity levels explain measles incidence and persistence of measles in the European Union in 2017–2018. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, 2019; 38, 1719-1729. DOI: https://link-springer-com.ezproxy.library.ubc.ca/article/10.1007%2Fs10096-019-03604-0#Sec2
-Pricia
