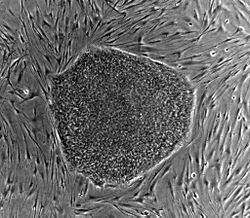
Human Embryonic Stem Cell http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/ thumb/3/3e/Human_embryonic_stem_cell_colo ny_phase.jpg/687px-Human_embryonic_stem_cell_colony_phase.jpg
For the past decade, an area of science that has been rapidly expanding is the topic of stem cell research. Stem cells have been helpful with understanding cancer, treatments for deafness, birth defects, and organ transplants. We have heard about the profound discoveries involving stem cells in every area of medicine so it would be appropriate to briefly discuss what these mysterious cells are and why scientists are so excited about it.
Stem cells are living cells that can be found in all multicellular organisms. There are 2 types: embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells are are found inside a blastocyst and the procedure used to extract the cell requires the destruction of a human embryo; the stem cell is capable of differentiating into 220 cell types in our body. Adult stem cells are also undifferentiated but they differ from the embryonic stem cells in that they exist in the body after development and multiply where there is damaged tissue.
The reason behind the excitement of scientists over stem cells is because stem cells play a large role in explaining why certain diseases or conditions arise in individuals. Scientists are able to study how the stem cells transform into the different kinds of specialized cells that make up a human being. Access to stem cells gives scientists a better understanding of how a normal cell is supposed to work.
Recently, a Nobel Prize was awarded to two scientists who made the incredible discovery of the procedure that can transform adult cells back into embryonic stem cells that can eventually grow into healthy tissue in damaged brains, hearts, or other organs. This means that a patient with Alzheimer could

Nobel Prize winners Shinya Yamanaka (left) and Joseph Gurdon (right) http://i.dailymail.co.uk/i/pix/2012/10/08/article-2214605-15689030000005DC-778_634x434.jpg
potentially regrow the damaged brain tissue and recover. This discovery, although is a great step forward for stem cell research, is still under revision because scientists are still unsure of the stem cell’s multiplying behavior if they were to implant this new kind of tissue into a person’s brain or heart. It could potentially multiply with no control and cause the growth of a tumor.
Of course, with any kind of new scientific discovery, comes debate and controversy over the ethics of the scientific advance. Due to the fact that stem cell research, namely embryonic stem cell research, involves destruction of a human embryo during the stem cell extraction, similar issues that revolve around abortions exist.
On a more political note, here is a video of President Obama supporting embryonic stem cell research by reversing the limits that President Bush placed on it:

Submitted by: Elsie Ng


3 responses to “Stem Cells? What’s That?”