As we may have noticed, the gases prices are going higher and higher. And as we are continuing to purchase more gas for our daily commute, our daily emissions of greenhouse gas creates global warming by changing the atmosphere. So as a result, we are stuck with two problems: Running low of fossil fuels as a energy resource and the build up of carbon dioxide as a by-product in the atmosphere. How can we escape this cycle of energy doom?
A Possible Solution that’s Almost Too Good to be True

Image Source:
http://inhabitat.com/british-firm-produces-liquid-fuel-
from-water-and-thin-air/air-fuel-synthesis-2/
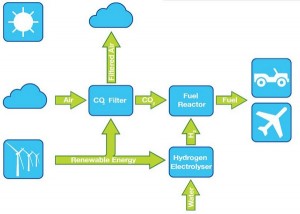
If we are currently running of fuel and have too much carbon dioxide, why not just take the carbon dioxide from the air and make it back into fuel? A small British firm called the Air Fuel Synthesis (AFS) had claimed to succeed in synthesizing gasoline to be usable for any vehicle. By using carbon dioxide and water extracted from the air, they were able to create a fuel that is clearer and cleaner than petrol derived from fossil oil. Since August of 2012, the firm was able to extract 5 liters of gas using a small refinery. By capturing the moisture in air to collect water and electrolyze the water into hydrogen, the hydrogen is then used to react with carbon dioxide extracted from the air to create hydrocarbon fuels. This process is called the Air Fuel Synthesis Process. Despite the fact that at the moment only a small amount of fuel can be produced at an early demonstrative stage, AFS plans to have larger commercial-scale productions. This process will not only reverse the large amount of carbon dioxide in the air, it could mean the future for our main energy resource. The best part of the AFS Process is that it uses renewable energy such as wind power as the energy input for conducting its processes.
Here is an interview with Peter Harrison CEO of Air Fuel Synthesis from BBC News:

“We are converting renewable electricity into a more versatile, usable and storable form of energy, namely liquid transport fuels,” Harrison had told the UK News The Independent. “We think that by the end of 2014, provided we can get the funding going, we can be producing petrol using renewable energy and doing it on a commercial basis.”
Here is an interview with Professor Tony Marmont of Loughborough University on the future of fossil fuels:

It looks good and sounds good, but skeptics about the procedure remains. Using this method, it is estimated to cost about $650 for every one ton of carbon monoxide. If it proves to work and begins for mass production, current oil companies are not going to be happy. Douglas Stephan, a Canadian chemist who is also doing research on production of fuel from carbon dioxide, states to the New Scientist Magazine “Until a detailed assessment of the energy efficiency is enunciated, I would remain skeptical about this technology.”
I personally hope that this is true and becomes a solution to our fossil fuel crisis. What do you think?
Blog by Andy Wang
Read more: British Firm Produces Liquid Fuel From Water and Thin Air Air Fuel Synthesis – Inhabitat – Sustainable Design Innovation, Eco Architecture, Green Building
Read more: http://newsfeed.time.com/2012/10/23/company-says-it-can-make-fuel-out-of-thin-air/#ixzz2AZ5SnvFK