Image of a news advisory for a hurricane
We have all seen images on the news depicting the devastating impact a Hurricane can have, Irene, Katrina and most recently hurricane Sandy. Hurricane Sandy has been described as a “super storm” causing nearly 90 deaths, leaving more than 8.2 million households without power in 17 states and causing more than $20 billion in damages. Hurricane Sandy began in the Atlantic then hit the Caribbean and subsequently made its way up the southeastern coast of the United States. With all the attention on the destructive effects a hurricane can have, do we really know what a hurricane is and how it occurs?
What is a hurricane?
A hurricane is a powerful, rotating weather system that forms and intensifies over tropical oceanic regions. Although they are most commonly referred to as hurricanes their technical name is tropical cyclone; tropical cyclones that form over the Atlantic Ocean or eastern Pacific Ocean are called hurricanes. These storm systems are characterized by having a low pressure center and surrounding thunderstorms that create strong winds and heavy rains. A unique characteristic of tropical cyclones that distinguish them from other cyclonic systems is that the center or “eye of the storm” remains warmer than its surroundings regardless of height in the atmosphere.

Hurricane Sandy is seen on the East Coast of the United States in this NASA satellite image taken at 3:55 a.m. ET Tuesday
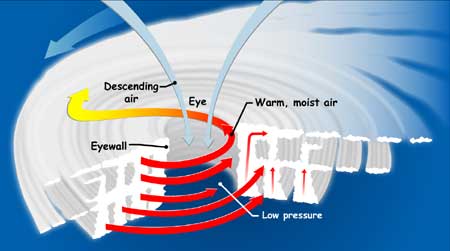
How do hurricanes occur?
Hurricanes occur only over warm ocean waters because they use warm, moist air to increase its energy. When the layer of warm, moist air above the ocean’s surface rises this creates an area of lower pressure below it. The surrounding higher pressure air begins to move into this lower pressure region and as it does it begins to warm and it too rises. As this air rises more high pressure air moves in to replace it. The moist, warmed air is cooled as it rises and as this occurs the water in the air forms clouds. This process is repeated continuously until an entire system of clouds and cyclonic winds is created.
What are the effects of a hurricane?
With the heavy winds and rains associated with hurricanes, there are several devastating consequences of a hurricane. As the hurricane approaches the coastline the extremely forceful winds push water towards the coast creating what is better known as a storm surge. This abnormal rise of water is able to infiltrate inland causing flooding and destruction due to its force along its path. Another source of flooding during a hurricane comes from the heavy rainfall. Anywhere from 15-24cm of rain can fall in a very short time. Arguably the source of the most damage caused by hurricanes comes as a result of the high and powerful winds. The shear forces involved in these winds can alone cause damage to homes, street lights, roads, vehicles, trees and power lines. The most damaging effect of these high winds comes from falling trees and power lines. As trees and power lines are knocked down, they may land in any direction, causing harm to property, a loss of power or even worse, causing a loss of life. In the case of hurricane Sandy, 18 people were killed in New York City, including 2 drowning deaths, 1 death caused by a fallen tree and 1 death caused by a live electrical wire landing in a puddle.
To see the latest update on the damage caused by Hurricane Sandy watch here.