So what are nanoparticles? What are they good for, and why should we care about them? Many of us might have heard of the terms “nanoparticles” or “nanotechnology,” but a good portion of us probably don’t know what these terms mean. Nanoparticles are incredibly small objects that span no more than 100 nanometers in size; a nanometer is one billionth of a meter! According to chemists and other scientists who study such tiny objects, nanoparticles behave as one whole unit regarding their characteristics and transport.
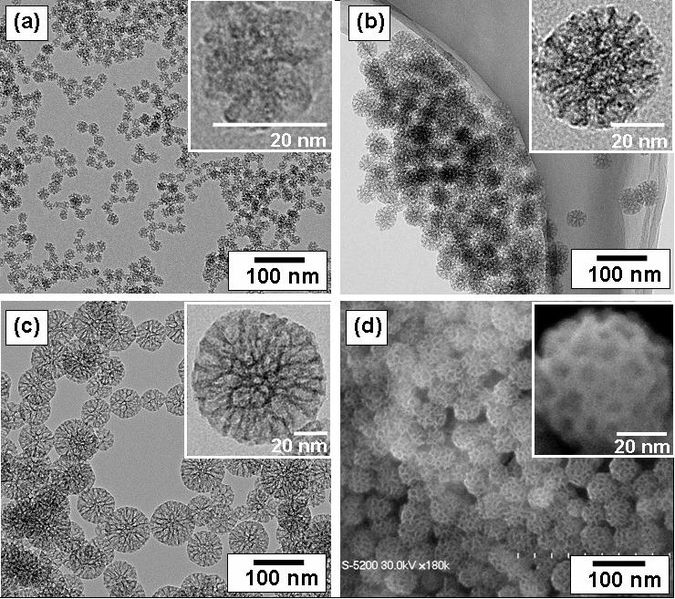
An image including several several nanoparticles with different sizes, visualized under transmission electron microscopy. One of these circular objects represents one nanoparticle; a group of nanoparticles is known as a nanocluster.
Image Source: Nanoparticle
Now that we’ve gotten definitions out of the way, what are nanoparticles really used for? According to Nanoparticle Blog, nanoparticles have a variety of applications, such as in medicine, electronics, renewable energy, and more. For example, according to Xiu et al. (2012), silver nanoparticles can aid silver ions to promote lysis in some bacteria, which is the process involving bacterial death by breaking their cell walls.

An image describing many applications of nanoparticles.
Image Source: Nanoparticle Blog
Although we know how to make use of nanoparticles, we do not necessarily know the mechanism behind the synthesis of these nanoparticles. This unknown factor could be very important. So far, for instance, chemists have understood that nanoparticles are made by mixing certain chemicals. However, there are almost always byproducts that are formed along with the desired compound(s) in chemical reactions. Let’s say that we’re using palladium nanoparticles to create a drug. What if these byproducts changed the properties of a drug? Thus, knowing the synthesis mechanism of such nanoparticles is potentially crucial with regards to how we use them.
Luckily, Renee Man, a graduate student of the Department of Chemistry at the University of British Columbia, together with Adam Brown and Dr. Michael Wolf published a scientific research article this year that proposed a mechanism directed specifically to palladium nanoparticles.
Below is a video that describes Man’s proposed mechanism and its advantages that make it an ideal model for the mechanism of palladium nanoparticles:

As mentioned in the video, there are three main important things to note when considering Man’s proposed mechanism of palladium nanoparticles. First, one can synthesize palladium nanoparticles at low temperatures when following this mechanism. Unlike other methods, used today, that require temperatures above 300˚ C, this mechanism works perfectly well at temperatures near 80˚ C! This means that the reaction can be relatively much safer to monitor; no one likes to stand beside reactions taking place at 300˚ C. Secondly, since the reaction can be done at lower temperatures, one can save a large amount of energy. This leads us to the last but not least benefit of the mechanism: by taking advantage of basic conditions, synthesis of palladium nanoparticles can be sped up by a significant amount, thus saving time, and again, energy.
Finally, below is a podcast of our interview with Renee Man. The podcast mainly discusses Man’s research with respect to the mechanism for palladium nanoparticles and how the mechanism came about:
Audio clip: Adobe Flash Player (version 9 or above) is required to play this audio clip. Download the latest version here. You also need to have JavaScript enabled in your browser.
By: Pedram Laghaei, Kathleen Leask, Alan Lam, and Fardad Behzadi
Video Credits:
Narrated by Alan Lam
Podcast Credits:
Narrated by Kathleen Leask
Special thanks to Renee Man for the interview.
















.jpg)