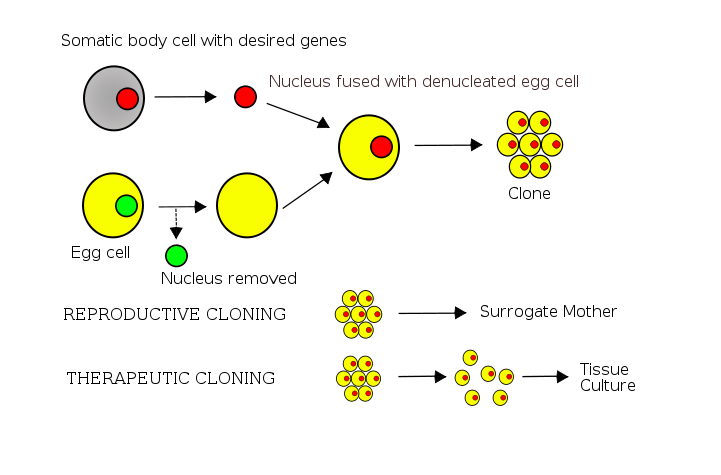
The term sea breeze in itself seems rather simple. In fact, the every-day person probably believes that a sea breeze is, well, just a breeze – they are commonly overlooked. Yet they would be surprised to learn how much research actually goes into studying sea breezes that occur all over the world and the huge impacts that they can have on society as a whole.
Dr.Steyn from the University of British Columbia (UBC) has dedicated many years of his life to studying sea breezes and the different interactions they can have with the atmosphere. He has found that sea breezes and the winds associated with them are actually involved in the spreading of pollution all around the world.

Image showing energy plant releasing pollution into the air. Image by flickr user thewritingzone
How might this affect the general public? Well, our governments spend millions of taxpayer dollars to implement pollution reduction programs in their countries but fail to realize that much of the pollution that they are trying to cleanup actually comes from other regions of the world through wind circulation.
Furthermore, the growing shortage of fossil fuels has become a major problem in our society. Researchers estimate that the petrochemical supply will run out in about 50 years. We are fortunate to have researchers like Dr.Steyn, who are investigating
the occurrence and frequency of sea breezes, and are collecting a vast body of knowledge that could be used to substitute many forms of unsustainable energy.
In the video below, Dr.Steyn explains how sea breezes form, how they can actually help pollution spread, and how sea breezes data can be used for energy production.

As you saw, sea breezes can be a major contributor to the way in which pollution is circulated around the world and can greatly influence where and how we build wind energy farms in the future.
The story doesn’t end there. Not only is collecting data and understanding sea breeze important for pollution and energy, it also influences the way we live our daily lives. It is surprising how great of an impact sea breeze can have on society and how less people know about them. From the way we travel, to the way that we spend our free time, sea breezes are everywhere.
Sea breezes can have a significant impact on the way that planes land at airports and how surfers spend their time in the water. These two everyday examples are influenced by the direction of the sea breeze. Sea breezes are very regular in that they are onshore by day and are offshore by night. During the day, the land heats up more than the ocean because it has a lower heat capacity.
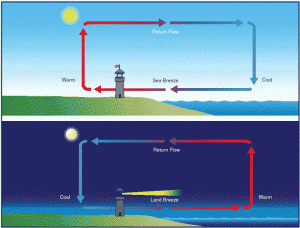
Image showing how sea breezes blow during the day and night. Image from Mr.Bent’s Educational Blog
This creates a low-pressure system near the land and causes the sea breeze to blow towards the shore. On the other hand, the complete opposite occurs during the night, when the land cools and creates a high-pressure system. This results in the sea breeze blowing towards the water. Surfers call this type of breeze an offshore wind, which is highly desired as it hollows out the wave, allowing for a more radical surf experience.
The podcast below gives a more in-depth explanation of how sea breezes affect people’s day-to-day lives.
Audio clip: Adobe Flash Player (version 9 or above) is required to play this audio clip. Download the latest version here. You also need to have JavaScript enabled in your browser.
Hopefully, you’re convinced that the sea breeze is not just any breeze; it is a very important atmospheric phenomenon that may influence your lifestyle more than you care to know. They are not to be overlooked – they help planes land, circulate pollution but still, as we found when interviewing UBC students on their opinion about sea breezes, most people only pay attention to sea breeze when it “affects what [they] wear when it’s cold out.”
A special thanks to Dr.Steyn for the Interview.
By: Gagandeep, Grattin, Ki Won, and Dragana.