So, what do the pyramids in Egypt, the population growth of rabbits, Leonardo da Vinci’s portrait of the Mona Lisa, the branching structure of the bronchi in our lungs, and the structure of DNA have in common? The answer to such an intriguing question lies within a special series of numbers discovered by the Italian mathematician, Leonardo Fibonacci.

A portrait of Leonardo Fibonacci.
Source: Wikipedia
These special series of numbers are known as the Fibonacci Numbers. The characteristic of these numbers is that each one is the sum of the preceding two numbers. For example, if 1 and 2 are Fibonacci Numbers, then the next number would be 3, then 5, then 8, and so on.
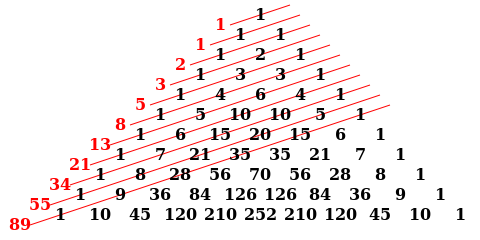
Diagonal sums (shown in red) of Pascal’s Triangle yield the Fibonacci Numbers.
Source: Wikipedia
What is particularly interesting about these numbers is that when one divides a random Fibonacci Number by the one preceding it and continues the process, the ratio always approaches an infinite decimal beginning with the numbers 1.618. This ratio, which is commonly denoted as the Greek letter ϕ (phi), is known as the “golden ratio.”
Why is ϕ Golden?
It is believed by many mathematicians that ϕ provides a mathematical key to beauty due to its high degree of symmetry. For example, the very early evidences of using ϕ in architectural design dates back to 2,600 BCE (around 4,600 years ago), the construction of the earliest Egyptian pyramids. Although it is believed today that using ϕ in the pyramid’s design was not intentional, it reinforces the idea that ϕ holds some aesthetic appeal.
Moreover, Leonardo da Vinci is famous for incorporating ϕ in many of his works, such as the Mona Lisa. Although no documentations indicate that Leonardo used ϕ intentionally in his work (Livio 2002), many analysts claim that extensive use of ϕ is observable in his Mona Lisa; some claim that his use of ϕ is what gives the painting beauty (due to very high degree of uniformity) as it portrays idealistic features of a human being.

The use of ϕ in the Mona Lisa. The quotients B/A, B’/A’, and B”/A” all yield ϕ.
Source: SineArch
The video below is about how the Fibonacci series is one of world’s most mysterious numbers:

Not only is ϕ observed in architectural design and art, it is also evident in biology and human anatomy. In several studies conducted by West and Goldberger in 1986 and 1987, the studies revealed the existence of ϕ in the structure of the lungs. One anatomical feature of the bronchi that constitute the lungs is that they are asymmetric. For example, the trachea divides into two main bronchi, one long (on the left) and the other short (on the right). This asymmetrical division continues into the subsequent subdivisions of the bronchi. It was determined that in all these divisions the ratio of the short bronchus to the long was always 1:1.618.
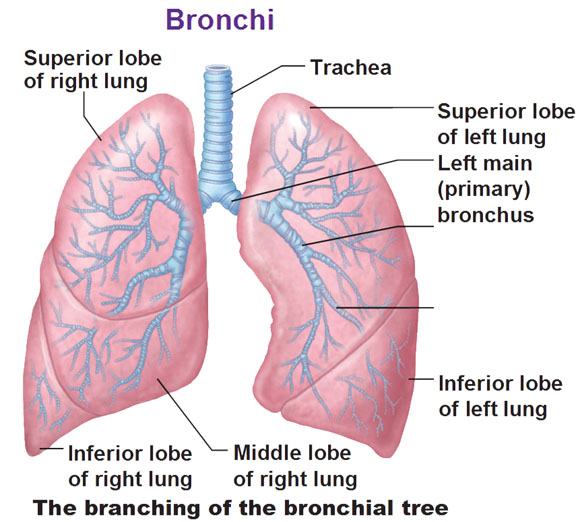
The asymmetric branching of the bronchi in humans.
Source: Antranik
In genetics, we learn that DNA carries the genetic code of organisms. This complex molecule consists of two intertwined perpendicular helices, in which the length and width of each full cycle of the spiral is about 34 Å and 21 Å, respectively. If we divide the length by the width, we approximately get ϕ.
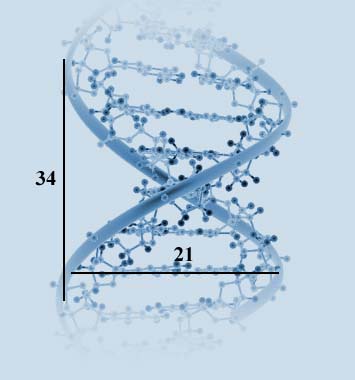
The length and width of one full cycle of DNA. If we divide the length by the width, we approximately get ϕ.
Source: Sacred Geometry
The video below explains the existence of ϕ in the human body:
Please skip to 5:07 marker for relevant content.

Why is ϕ divine?
As a result, ϕ is not only observed in what we have created in the past, but also in areas, such as biological systems, in which we do not have a say in (or cannot control). This exact idea has led many people to think that ϕ originates from divine creation, hence its other name: the “divine proportion.” The video below investigates how ϕ plays a role in religious examples and how its nature is not a coincidence; or in other words, why it is known as the divine proportion.

In conclusion, ϕ is not only a mathematical key to beauty, but an ideal proportion in which many systems function on. If these systems, such as the bronchi network in our lungs, or the structure of DNA, were deviated slightly away from ϕ, they might not have functioned as properly as they do now.
– Pedram Laghaei