The gastric-brooding frog was first discovered in 1972 and was native to Queensland, Australia. This frog belongs to the genus Rheobatrachus which contains only two species. Both are now extinct. These two species were so fascinating because of their unique way of reproduction. The female would swallow the eggs after fertilization, carry them in her stomach and then orally give birth to the offspring. The average number of juveniles that was observed in the stomach of a female was 21-26.
Below is a picture of a female frog giving birth orally to one of her offspring:
While the offspring are in the mother’s stomach, she does not eat, and as her stomach grows larger in size, the lungs deflate to make room. In order to breathe, she must rely on gas exchange that occurs across the surface of her skin.
The gastric-brooding frog went extinct in 1983 and it has been suggested that this may have occurred due to a variety of reasons: habitat loss, pollution and/or pathogens. The other species in the genus Rheobatrachu, the Platypus frog, also went extinct in the early 80s.
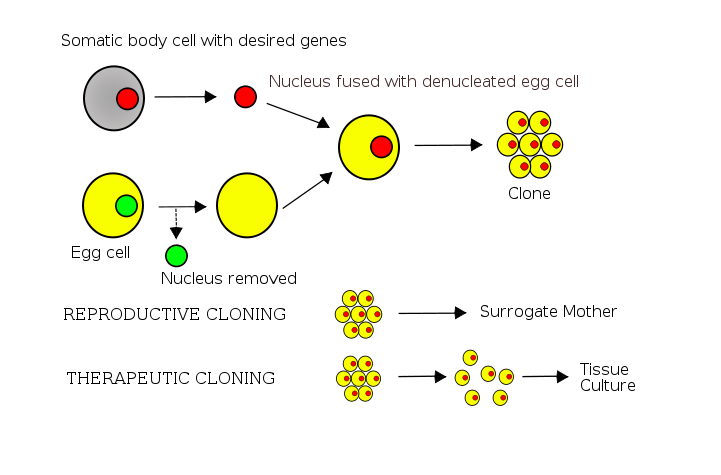
According to this article, scientists in Australia are now trying to bring the gastric-brooding frog back from extinction through a cloning technique called somatic-cell nuclear transfer.
Basically, the researchers extracted cell nuclei from tissues of the gastric-brooding frog (which was collected in the 1970s and frozen) and implanted these nuclei into donor eggs. The donor eggs used in this case were from the Great Barred Frog, Mixophyes fasciolatu, which is distantly related to the gastric-brooding frog. The nuclei in the donor eggs were inactivated and replaced with the nuclei from the extinct species. After this occurred, some of the eggs started to spontaneously divide and formed into early embryos. None of the embryos survived for more than a couple of days. Genetic tests were done to confirm that the genes in the embryos were those of the gastric-brooding frog.
Below is a simplistic diagram of how somatic-cell nuclear transfer works:
Even though the experiment did not successful create an adult specimen of the extinct frog, the researchers are confident that it won’t be long until such a procedure will be able to be performed successfully.
The article further states that researchers from all over the world recently gathered in Washington for a conference in order to discuss the progress being made in the attempts to bring other extinct species back to life.
Possible candidates include the woolly mammoth and the dodo.
I find this so exciting!
Can you imagine having a zoo full of “extinct” animals, or even dinosaurs!?
Dragana Savic
Reference: