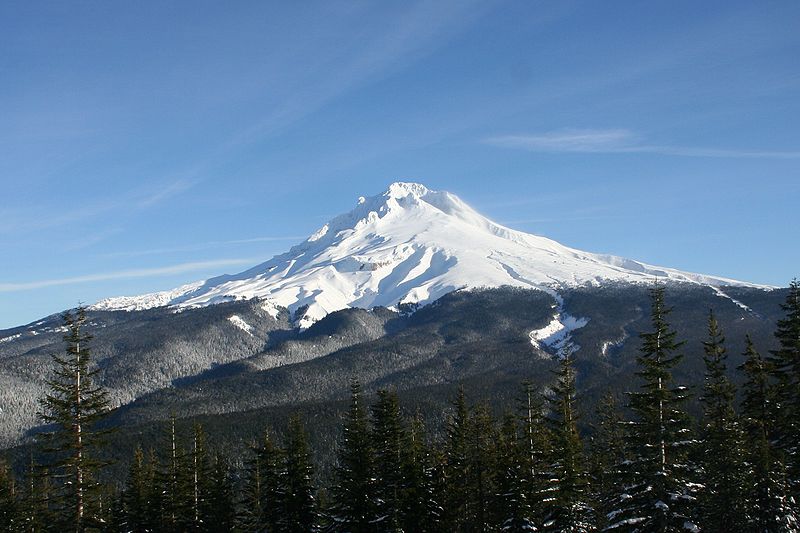
Mount Hood, an active volcano in Oregon, USA. Image source: wikimedia commons
How long does it take a volcano to convert its stored magma (molten rock) into moving, liquified magma which causes an eruption? According to new research done cooperatively by scientists at the Universities of Oregon and California, and published in the journal Nature, this time-span can possibly be as short as a few months!
This finding came from scientists who analyzed magma stored in Mount Hood, in Oregon, USA. Magma deep inside the earth is extremely hot and mobile. However magma stored about 4 to 5 km deep approximates a solid. In the case of Mount Hood, scientists examined the magma at the surface which had cooled to form crystals. Using radioactive dating they were able to determine the age of the crystals and thus the amount of time spent in “cold storage” when the deep magma was not heating the cooler magma to result in an eruption.
They determined that the upper magma had spent, for at least 88% of its time in this “cold storage” where an eruption is highly unlikely. By using technology to detect the initial liquefaction of the upper magma, scientists may now be able to more accurately predict future eruptions.
Here is a short video which explains volcanic eruptions in more detail:

Video Source: Twig World on Youtube
It is very important to be able to predict volcanic eruptions because as mentioned in the above video, volcanoes have the potential to do great harm. A few of main dangers associated with volcanic eruptions are: eruption clouds and gases, lava, pyroclastic flows, and lahars.
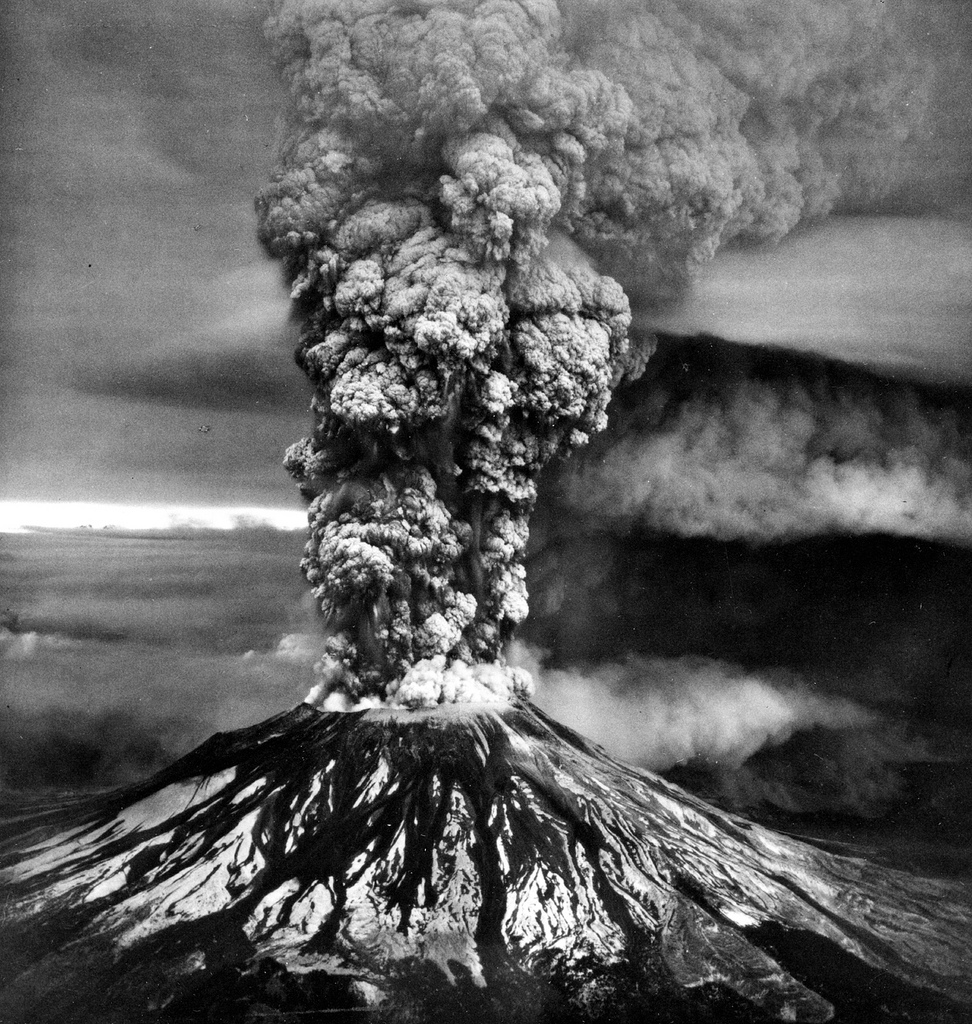

Image Source: U.S. Geological Survey on Flickr
Eruption Clouds and Gases
When eruptions occur, large pieces of rock (called bombs) are propelled into the air in combination with small rocks, minerals and glass (ash). Ash can harm airplane engines, collapse buildings and even destroy crops. This is then coupled with a large release of gases, mainly water (90%) , as well as others such as sulphur dioxide which leads to acid rain and fluorine which is toxic and can contaminate water supply.
Lava, Pyroclastic Flow and Lahars
When magma reaches the earth’s surface, it is called lava. Slow moving lava tends to form mounds (lava domes) which can collapse and travel away from the volcano carrying a mass of rock, ash and gases known as a pyroclastic flow. These are highly dangerous with temperatures up to 815 C, as they simply destroy everything in their path. When such a flow mixes with water, often from melted ice or snow, a mudflow forms, called a lahar, similar in consistency to wet concrete which can uproot homes and trees.
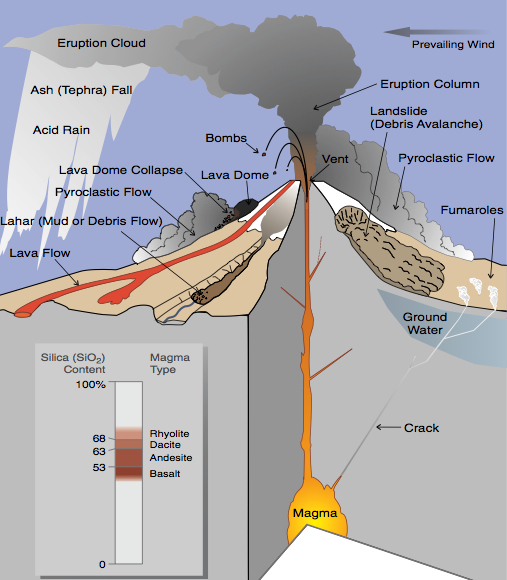
Image Source: U.S. Geological Survey
Thus given all these dangers, since this research helps to determine when a volcano will erupt, it could have lifesaving consequences. For more information on volcano monitoring in the USA see the U.S. Geological Survey.
Julia Brown