ENGL 301: Assignment 1.3
Introduction: The objectives of this assignment is to appreciate the importance and role of definitions in technical writing, to understand how the audience and purpose indicate the need for definition, to differentiate between levels of detail in definitions and to select the right level for detail according to the situation. The criteria to select a complex term used in my profession and compose 3 different definitions. My chosen situation and audience is a developer/team manager explaining to a customer/stakeholder the what scrum is. In all of my coop terms, I was on team that used scrum, so I am familiar with its process and definition. Some companies choose to use a different framework for their development and management, but if a customer asked about what our strategy was to create a product, I would explain to them about our use of scrum.
Term: Scrum
Parenthetical Definition: A software development team may choose to use scrum (team-focused and flexible project management strategy) to achieve their requirements and goals.
Sentence Definition: Scrum is a type of project management structure that involves daily collaboration, and continuously adapting plans based on previous attempts to achieve a goal.
Expanded Definition:
The ideas behind Scrum was first introduced in an article published in 1986 (Takeuchi and Ikujiro). Due to the insufficiency of the pre-existing strategies to product development, a new method emerged. This method emphasized speed and flexibility and is analogous to rugby, where passes are made within the team as they move through sections of the field (Takeuchi and Ikujiro). At Easel Corporation in 1993, Jeff Sutherland, Ken Schwaber, and Mike Beedle, applied the ideas from the article to software development and created a method called Scrum (Sliger).
Scrum is a framework for project management that enables for an efficient and adaptive development process. Its defining characteristics involve an iterative and incremental product delivery (Sliger). This is a continuous empirical process of delivering a product, obtaining customer feedback and making the appropriate adjustments, in order to deliver the right product in a timely matter. A project begins with a customer’s vision and a desired set of features that make up a product backlog, and is ordered by importance (Sliger). The scrum process emphasizes team collaboration in solving complex problems. To fulfill these requirements, a team meets to discuss and plan the timeline of the project resulting in the creation of the sprint backlog, featuring the team’s sprints (Sliger). A sprint lasts between one and four weeks, and within that period of time, a list of features is chosen from the backlog to be completed (Altvater). Within a sprint, daily scrum meetings are held, where progress is reported by each member, as well as their plans and anything they are blocked on. These meetings allow for teams to stay focused on their project goals and priorities (Altvater). As a sprint is completed, the completed progress is reviewed by the customer, and the feedback is used and worked on in the next sprint (Sliger). This described process is illustrated in Figure 1.
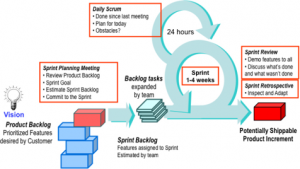
Figure 1: Basic Scrum Framework
Bibliography
Takeuchi, Hirotaka and Ikujiro Nonaka. “The New New Product Development Game.” Harvard Business Review, January 1986.
https://hbr.org/1986/01/the-new-new-product-development-game. Accessed 27 Sep. 2020.
Sliger, Michele. “Agile project management with Scrum”. Project Management Institute, 22 October 2011.
https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/agile-project-management-scrum-6269. Accessed 27 Sep. 2020.
Altvater, Alexandra. “What is Scrum? How Does Rugby Help Software Developers Create Quality Products?”. Stacktify, 11 May 2017.
https://stackify.com/what-is-scrum/#:~:text=Definition%20of%20Scrum,subset%20of%20agile%20software%20development. Accessed 27 Sep. 2020.
Leave a Reply