Introduction:
Definitions play an important role in technical writing; they allow the reader to better comprehend the knowledge being provided by the writer. For a learner that is unfamiliar with the term, it is a great starting point to understand the basics of the term, prior to diving into the actual context of the text. For those who are familiar with the term, definitions serve the purpose of refreshing their vocabulary and perhaps learning a new perspective of the term. I will be providing a parenthetical, sentence, and expanded definitions of the term Periodontitis (Per-e-o-don-tie-tis). This definition is meant to serve an audience for a non-technical reader and can be used in a situation of a dental hygienist explaining the diagnosis of periodontitis to a patient.
Parenthetical Definition:
Periodontitis (gum disease) is a severe gum infection that can affect your oral health as well as overall health.
Sentence Definition:
Periodontitis is an inflammatory condition caused by bacteria that damages the tissues surrounding the tooth structure, such as gum tissue or the bone that supports your teeth.
Expanded Definition:
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis (“Perio” means around, “dontal” refers to teeth, and “itis” implies inflammation) is a chronic multifactorial inflammatory disease associated with plaque (biofilm). Periodontitis can lead to destruction of tooth supporting structures such as gum tissue, bone, and ligaments (muscles) holding the tooth in place (Prestige Dental Care [PDC], 2020). See figure 1 below to better understand the difference between a normal, healthy tooth versus a tooth effected by periodontitis.

Figure 1: Normal tooth versus tooth affected by Periodontitis
Source: The Family Dental Center accessed from: https://thefamilydentalcenter.com/blog/gingivitis-vs-periodontitis-what-is-the-difference/ (Internet)
What causes Periodontitis?
Bacteria in the mouth infect tissue surrounding the tooth, causing inflammation around the tooth leading to periodontal disease. When bacteria stay on the teeth long enough, they form a film called plaque, which eventually hardens to tartar, also called calculus. Tartar build-up can spread below the gum line, which makes the teeth harder to clean. Then, only a dental health professional can remove the tartar and stop the periodontal disease process (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC], 2012).
What is the difference between Gingivitis and Periodontitis?
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease. Improving your oral hygiene habits, such as more frequent brushing and flossing, can typically reverse it. Periodontitis is the second stage of gum disease, which occurs if gingivitis is not treated. Periodontitis is also considered to be an irreversible gum disease. With periodontitis, tooth roots and the bones in the jaw that support the teeth may be affected, which can lead to tooth loss (Glenwood Premier, 2020). Reference image below to understand the comparison between healthy gum, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
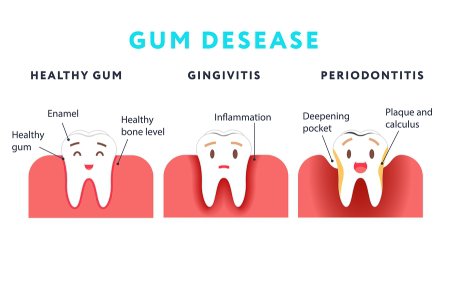
Figure 2: Comparison between Healthy Gum, Gingivitis and Periodontitis
Source: Glenwood Premier accessed from https://www.glenwooddentalgroup.com/blog/2018/04/what-is-the-difference-between-gingivitis-and-periodontitis/ (Internet)
Prevention of Periodontitis
The best way to prevent periodontitis is to have a good oral home care regimen.
- Good oral hygiene. That means brushing your teeth for two minutes at least twice daily — in the morning and before going to bed — and flossing at least once a day. Flossing before you brush allows you to clean away the loosened food particles and bacteria. Good oral hygiene prevents the development of an environment around your teeth that is favorable to specific bacteria that cause periodontal disease (Mayo Clinic. Periodontitis, 2020).
- Regular dental visits. See your dentist or dental hygienist regularly for cleanings, usually every six to 12 months. If you have risk factors that increase your chance of developing periodontitis — such as having dry mouth, taking certain medications, or smoking — you may need professional cleaning more often (Mayo Clinic. Periodontitis, 2020).
References:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Periodontal Disease (2012). Retrieved on June 8, 2022 from https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/conditions/periodontal-disease.html#:~:text=Reference-,What%20is%20periodontal%20disease%3F,red%2C%20and%20they%20may%20bleed. (Internet)
Glenwood Premier (Blog). What is the difference between Gingivitis and Periodontitis? (2020). Retrieved on June 8, 2022 from https://www.glenwooddentalgroup.com/blog/2018/04/what-is-the-difference-between-gingivitis-and-periodontitis/. (Internet)
Mayo Clinic. Periodontitis (2020). Retrieved on June 7, 2022 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/periodontitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354473#:~:text=Periodontitis%20(per%2De%2Do%2Ddon,is%20common%20but%20largely%20preventable. (Internet)
Prestige Dental Care. What is the Meaning of Periodontitis? (2020). Retrieved on June 7, 2022, from https://dentalclinicraipur.com/blog/periodontitis-gingivitis. (Internet)
Leave a Reply