Criteria of the Assignment
- Reading Situation
- Parenthetical definition
- Sentence definition
- Expanded definition
Objectives of the Assignment
- Apply the importance and role of definitions in technical writing from the textbook to a reading situation
- Understand how audience and purpose indicate the need for definition
- Distinguish the following levels of details in definition: Parenthetical, Sentence, Expanded
- Provide sufficient detail to the reading situation
Reading Situation
A science student is explaining to their friend about “Machine Learning” as a form of studying for an upcoming midterm. The science student is taking a degree in computer science. The friend is an art student taking a degree in film production.
Parenthetical definition
Machine Learning (a type of artificial intelligence) requires historical data.
Sentence definition
| Term | Class | Distinguish Feature |
| Machine Learning | Branch of AI (Artificial Intelligence) | Machine learns from past data without explicit programming |
Machine Learning is a type of Artificial Intelligence that predicts or classifies new information based on a large volume of historical data. It can provide a meaningful result based on probability or statistics.
Expanded definition
Machine Learning (ML) is a type of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that uses data and algorithms to imitate how humans process information. It trains a model (a file meant to recognize patterns) from input data (ex. Description of dog) and the data’s corresponding targets (ex. Type of dog) to predict targets for new data.
ML and AI are not the same terms to be used interchangeably.AI is a broad concept of machines able to do tasks that humans consider “smart” while machine learning is an application of AI with humans giving machines access to data to let it learn for itself.
The term “machine learning” came from a logician, Walter Pitts, and a neuroscientist, Warren McCulloch. Their 1943 paper attempted to mathematically visualize thought processes and decision-making in humans. Their mathematical modelling of the nervous system’s network was called “machine learning.”
Machine Learning starts by collecting the data (ex. List of reviews for a movie). That data will be edited and visualized to look for patterns and outliers. Following the data analysis and a set goal (ex. Determine if the review was positive or negative), a model will be chosen. The model is an algorithm meant to detect patterns. The data will be split into a training and test set. The training set will be used to improve the predictions of the model. The predictions will be scored by accuracy. After a series of evaluations and tuning to improve the accuracy of the model, it is used on the test set (ie. unseen data). The test set determines if the model meets the set goal mentioned earlier. A simplified visualization of this process is provided in Figure 1.
Examples of using Machine Learning include social media features and product recommendations. Facebook takes note of a user’s activities, chats, likes, comments, and the time spent on specific kinds of posts. From the user’s behaviours, machine learning learns to make friends and page suggestions for the user’s profile. Similarly, Amazon tracks a user’s behaviour based on their previous purchases, searching patterns, and cart history to make product recommendations shown in Figure 2.
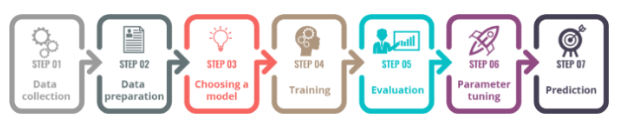
Figure 1: 7 Steps to Machine Learning by Dr Mark van Rijmenam, Published in DataSeries
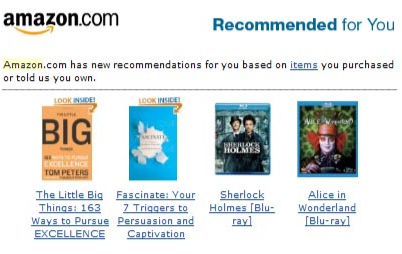
Figure 2. A screenshot of recommendations made by Amazon based on the user’s history of items purchased.
References:
- Marr, Bernard. “What Is the Difference Between Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning?” Forbes, Forbes Magazine, 10 Dec. 2021,
- Chai, Wesley. “A Timeline of Machine Learning History.” WhatIs.com, TechTarget, 20 Oct. 2020, https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/A-Timeline-of-Machine-Learning-History.
- Rijmenam, Dr Mark van. “7 Steps to Machine Learning: How to Prepare for an Automated Future.” Medium, DataSeries, 14 Aug. 2019, https://medium.com/dataseries/7-steps-to-machine-learning-how-to-prepare-for-an-automated-future-78c7918cb35d.
Link to Peer Review by Olivia: https://blogs.ubc.ca/engl30198a2022s12/2022/06/10/peer-review-definitions-assignment-izabel/
Leave a Reply