Introduction: This assignment focuses on the application of three definition styles: parenthetical, sentence, and expanded. The goal is to understand how the audience and purpose influence the need for definition, differentiate between levels of detail in definition, and select the suitable level of detail based on the situation.
Term: Phototropism
Target Audience and Situation: Third year Biology students in a Plant Biology course.
Parenthetical Definition: Phototropism is the growth of an organism in response to light.
Sentence Definition: Phototropism is the biological phenomenon where an organism exhibits growth movement towards or away from a light source, which is crucial for the survival and adaptation of plants and some other organisms within their environment.
Expanded Definition:
History and Background
The concept of “phototropism” originated in the late 19th century to describe the directional growth response of plants to light. Phototropism is a type of tropism, a general term for growth or movement responses to a specific stimulus. This response is vital for plants to maximize light exposure, which is necessary for photosynthesis and overall growth.
Negation
Phototropism involves an organism’s growth movement towards or away from a light source. Therefore, the opposite would be the lack of a growth response to the presence or absence of light. This absence could be due to various factors, such as the organism’s inability to detect light, failure to respond to the stimulus, lack of necessary photoreceptors or signalling pathways, or insufficient resources to generate a response.
Operating Principle
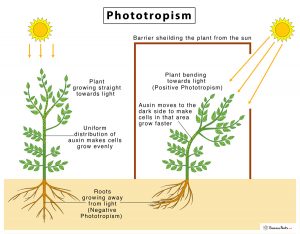
Phototropism is regulated by photoreceptors within the organism that perceive light presence and direction. This information is transformed into biochemical signals that prompt growth towards or away from the light source. The specific process depends on the organism and type of phototropism but generally involves hormonal changes and alterations in the organism’s cellular orientation.
Illustrative Example
A prime example of phototropism is the growth of a plant stem towards a light source. The stem’s photoreceptors identify the light direction and prompt cells on the side of the stem opposite the light to elongate. This bending of the stem towards the light source enables the plant to optimize light exposure for photosynthesis.
Work Cited
Julie A. Zickel, Phototropism, Editor(s): Mark D. D. Brown, Plant Development: Physiology, Molecular Biology, and Biotechnology Applications, Wiley-Blackwell, 2011, Pages 29-33, ISBN 9781405185869
Leave a Reply