Introduction
The objective of assignment 1.3 is to practice writing definitions (parenthetical, sentence, and expanded) for a complex technical term used in a specialized field to a novice non-technical reader with little to no experience in the subject. The writer is required to make up a scenario where these definitions could be used.
Complex Term
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
Scenario
As a part of a research study, participants must undergo an fMRI scan to determine eligibility. As the nurse working for the study, I am responsible for obtaining informed consent by explaining what an fMRI is, what a participant must do, and how it functions. The doctor will cover the risks involved.
Definitions
Parenthetical Definition: This study requires all applicants to undergo a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scan (an imaging technique used to take pictures of brain activity) to determine eligibility for participation.
Sentence Definition: Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is a non-invasive imaging technique used to observe brain activity. It creates images by using a magnetic field to measure the change of oxygen particles and blood flow in the brain tissues (Goldstein, 2021, Pedersen, 2021).
Expanded Definition:
Required Conditions
What is functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)? What does the participant need to do?
An fMRI test is a specialized type of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An fMRI scan is taken using an MRI scanner. Both tests use the same principles but have different functionality. An MRI produces pictures of the brain’s structure, whereas an fMRI takes scans of the brain’s activity. To complete the test there are a few key pieces of information to know, firstly the procedure takes about 45 minutes to complete and is non-invasive (Pedersen, 2021). Secondly, the machine is very noisy. Electricity passes through large metal coils to produce the magnetic field used to produce the images (Elliot Hospital, 2023). Noise-canceling headphones will be provided. Lastly, to get the best imaging possible, the space to lie in has to be compact. The closer the magnetic field is to the body, the better the image that is produced (DMS Health Technologies, 2023) (see Figure 1). It is advisable to let the researchers know if they suffer from claustrophobia (Pedersen, 2021).
Visuals
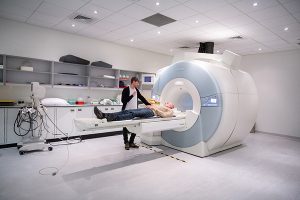
Fig. 1. A participant is getting ready to enter the scanner head first.
Source: Angus, Thomas. “Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging at the Imperial Centre for Psychedelic Research.”. 2019.
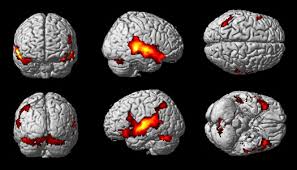
Fig. 2. Increased blood flow as illustrated by the red and yellow “blobs”.
Source: Galan, Juan. “Resonancia Funcional.”. 2013.
Operating Principle
How does it work?
To understand how fMRI works, a brief review of physiology is helpful. When the brain is performing actions (doing a task, thinking, or resting), neurological structures, called neurons (tiny connections in the brain that transmit signals), get activated. This activation causes an increase in blood flow and oxygen to those specific brain regions (Pedersen 2021). In the blood, there is an oxygen-transporting protein that contains hydrogen atoms. Hydrogen atoms naturally resonate (vibrate) when they encounter a magnetic field. The more oxygen the blood carries, the more magnetic it is (Pedersen, 2021). By rotating the magnetic field around the head and brain, the scanner measures the difference in the vibrations and direction of flow between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood (blood with no oxygen). This measured difference is what produces images (Figure 2) depicting brain activity (Goldstein, 2021; Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, 2023, Pedersen, 2021).
Negation
Ultimately, the fMRI scanner can only capture or “see” blood flow. It cannot see thoughts or read the mind.
Link to Original Definition
References
Angus, T. (2019, June 3). File: 190603 Functional magnetic resonance imaging at the Imperial Centre for Psychedelic Research.jpg. Wikimedia Commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:190603_Functional_magnetic_resonance_imaging_at_the_Imperial_Centre_for_Psychedelic_Research.jpg This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license.
DMS Health Technologies. (n.d.). Wide bore vs traditional: Is bigger always for MRI imagers?. DMS Health. https://www.dmshealth.com/08/wide-bore-vs-traditional-is-bigger-always-better-for-mri-imagers/
Elliot Hospital. (n.d.). Diagnostic imaging: Why does the MRI machine make so much noise?. https://www.elliothospital.org/website/diagnostic-imaging-mri-faqs-why-does-the-mri-machine-make-so-much-noise.php
Galan, J. (2013, September 13). File: Resonancia Funcional.jpg. Wikimedia Commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Resonancia_Funcional.jpg This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.
Goldstein, E. B., (2021). Cognitive psychology: Connecting mind, research, and everyday experience. 5E. Cengage Learning.
Nuffield department of clinical neurosciences: Medical sciences division. (n.d.). Introduction to FMRI. University of Oxford. https://www.ndcn.ox.ac.uk/divisions/fmrib/what-is-fmri/introduction-to-fmri
Pedersen, T. (2021, December 13). All about functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Psych central. https://psychcentral.com/lib/what-is-functional-magnetic-resonance-imaging-fmri
Leave a Reply