Introduction:
The objective of this assignment is to understand the importance of definitions and to convey a complex term to varying audiences by tailoring the level of details according to the circumstances. In this assignment, students are to describe a complex term using a parenthetical definition, sentence definition, and expanded definition tailored to a specific, “non-technical” audience.
Term:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Target Audience:
This situation/audience is youth and first-year science students partaking in a medical technology seminar. This information is tailored to those who have some general science background and are interested in medical technology. The information depicted may also be of interest to those who are having an MRI for the first time.
Parenthetical Definition:
Those who come to the hospital may require an MRI (a detailed medical imaging test done by a complex machine).
Sentence Definition:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging test utilized by medical professionals to obtain detailed images of internal structures in the human body.
Expanded Defintion:
History:
The history of MRI began in 1937 when physicist, Isidor Rabi, pioneered a technique to measure atomic nuclei movement. Although originally intended for analysis of chemical substances, scientists began to wonder if this technology could be applied to living beings. In the 1970s, the first images of a human were produced successfully and by the 1980s, the MRI machines were implemented in hospitals to be used clinically. Since then, further development and research led to the widespread usage of MRIs across the globe, providing crucial information to save countless lives.
Operation Principle:
A strong magnetic field is emitted from the MRI machine and causes atoms in the body to align. Radio waves are then emitted from the machine to push the atoms out of their original position. Once the radio waves are disabled and no longer being emitted, the atoms move back to their original position and emit radio waves that are received by a computer and converted into an image.
Analysis of Parts:
The MRI machine consists of four main components:
- A magnet formed by superconducting coils (coils that conduct electricity without loss of energy when temperatures are lowered).
- Gradient coils (coils made of thin wire/sheets for the purpose of adjusting frequencies).
- Radio frequency coils (coils made of thin wire/sheets which are used to send and receive signals from the body).
- Computer systems which interpret the signals to generate a image of the scanned area
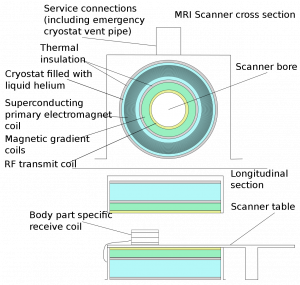
Figure 1: Components of an MRI machine (Source: File:Mri scanner schematic labelled.svg—Wikimedia Commons, n.d.)
Comparison:
There are many imaging techniques aside from the MRI that is just as useful. X-ray imaging is one technique that is quite well-known and often used to quickly spot injuries involving bones. However, X-rays are unable to detect inflammation or tissue injuries in contrast to the MRI. Therefore, it is common to begin with X-ray imaging and supplement with MRI if deemed necessary.
References:
CT Scan Versus MRI Versus X-Ray: What Type of Imaging Do I Need? (2022, September 6). https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/ct-vs-mri-vs-xray
File:Mri scanner schematic labelled.svg—Wikimedia Commons. (n.d.). Retrieved February 8, 2023, from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Mri_scanner_schematic_labelled.svg
History of magnetic resonance imaging. (2022). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=History_of_magnetic_resonance_imaging&oldid=1126552465
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). (n.d.). National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering. Retrieved February 8, 2023, from https://www.nibib.nih.gov/science-education/science-topics/magnetic-resonance-imaging-mri
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). (2021, December 6). https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/magnetic-resonance-imaging-mri
radlib. (2014, December 5). Featured History: Magnetic resonance imaging. UW Radiology. https://rad.washington.edu/blog/featured-history-magnetic-resonance-imaging/
Serai, S. D., Ho, M.-L., Artunduaga, M., Chan, S. S., & Chavhan, G. B. (2021). Components of a magnetic resonance imaging system and their relationship to safety and image quality. Pediatric Radiology, 51(5), 716–723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-020-04894-9
Leave a Reply