Writers must choose a word that is not used in day-to-day vocabulary. The objective of this assignment is to create 3 types of definitions which can be used for different situations. The criteria indicates that writers must create an expanded definition, a parenthetical definition and a sentence definition based on a chosen word typically used in professional or academic settings. Situation: A school nurse is explaining the different types of agonist drugs to a high school class.
Parenthetical Definition: The agonist (drug-heightening effect) can alleviate chronic pain.
Sentence Definition: Agonist is a drug that affects the brain on a cellular level. This type of drug stimulates brain chemicals to increase its function.
Operating Principle
In order for an agonist to work, it needs to bind to a chemical neurotransmitter in order to heighten the response of the chemical. A natural or pharmaceutical agonist drug attaches itself on a receptor as a way to signal the chemicals to turn on (Modi, “Agonist vs. Antagonist: What’s the Difference?”).
Compare and Contrast
Human bodies also create agonists such as endorphins to alleviate pain (Modi, “Agonist vs. Antagonist: What’s the Difference?”). In comparison, opioids are pharmaceutical agonist drugs which display similar properties to body-producing endorphins.
Examples
Agonists such as hallucinogens, hallucinogens, opioids and heroin are different pharmaceutical agonist drugs (Indian Health Service). In contrast to agonists, Advil inhibits chemicals and does not cause a response from the brain. As seen in Figure 1, an antagonist inhibits an agonist to function.
Visual/Diagram
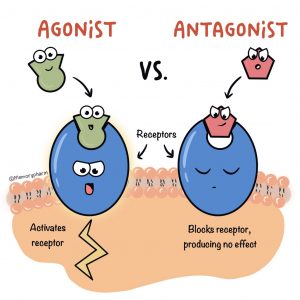
Figure 1: Agonist is shown activating receptor whereas an antagonist inhibits receptor to function.
Work Cited
Modi, Juhi. “Agonist vs. Antagonist: What’s the Difference?” Buzzrx.com, BuzzRx, 18 Feb. 2022, https://www.buzzrx.com/blog/agonist-vs-antagonist-whats-the-difference.
Pharm, Memory [Memory Pharm]. “How agonists & antagonists work. An agonist is a drug that binds to a receptor & activates it. An antagonist is a drug that binds to a receptor without activating it, but instead, blocks the receptor from being activated by other chemicals in the body.” Twitter, 3 August 2021, https://twitter.com/MemoryPharm/status/1422565665504993284/photo/1
“Pharmacological Treatment: Medication Assisted Recovery.” Opioids, Indian Health Service, https://www.ihs.gov/opioids/recovery/pharmatreatment/#:~:text=An%20agonist%20is%20a%20drug,%2C%20morphine%2C%20opium%20and%20others.
Leave a Reply