Introduction:
The main focus of the assignment is to improve students’ technical writing skills by teaching them the importance of defining complex terms in a clear and concise manner. The students are tasked with writing three different definitions of a term related to their discipline or profession: a parenthetical definition, a sentence definition, and an expanded definition. The expanded definition should include at least four expansion strategies and a visual, with citations from at least three outside sources. The assignment also includes hands-on practice in writing definitions, peer review, and reflection to help students better understand the audience and the appropriate level of detail for the situation. The ultimate goal is to improve students’ ability to effectively communicate technical information.
Term:
Machine Learning
Target Audience and Reading Situation:
Imagine a hypothetical scenario where a computer science professor must explain the concept of Machine Learning to university students who have limited background knowledge in the field. The technical term must be defined in a manner that is comprehensible for these students.
Parenthetical Definition:
Machine Learning (a field of study that uses algorithms and statistical models to enable computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed) algorithms can be used to analyze large sets of data and make predictions or identify patterns.
Sentence Definition:
Machine Learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence that involves using algorithms and statistical models to enable computers to learn from data, make predictions, and make decisions without being explicitly programmed. This type of learning involves analyzing large amounts of data, recognizing patterns, and making predictions based on that analysis, with the goal of allowing computers to continuously improve their performance.
Expanded Definition:
What is its history?
Machine Learning has a long history that can be traced back to the 1940s and 1950s, when researchers in the field of artificial intelligence began to develop mathematical models and algorithms to enable computers to perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence. Over the years, the field has evolved and expanded, and today machine learning is widely used in many different applications, including speech recognition, image recognition, and natural language processing.
How does it work?
Machine learning works by using algorithms and statistical models to enable computers to learn from data. The process typically involves three main steps: training, validation, and testing. In the training phase, the algorithms are fed large amounts of data, and the system uses this data to identify patterns and relationships between the inputs and outputs. In the validation phase, the system uses a subset of the data to evaluate its performance and make adjustments as necessary. Finally, in the testing phase, the system is evaluated on a separate set of data to determine its accuracy and make any final adjustments.
How is it applied?
Machine learning has many practical applications across various industries. It is used for image and video analysis, natural language processing, recommender systems, predictive maintenance, fraud detection, healthcare, and marketing. In image and video analysis, machine learning algorithms are used to recognize patterns and objects. In natural language processing, machine learning is applied to understand and process human language. In recommender systems, machine learning is used to suggest items based on user preferences. Machine learning is also used in predictive maintenance to predict equipment failures and in healthcare for diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
How is it different from Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses specifically on algorithms that are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. Deep learning algorithms are designed to automatically learn representations of data, making them well-suited for applications such as image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing. Unlike traditional machine learning algorithms, deep learning algorithms do not require manually designing the characteristics that the algorithm uses to analyze data, as they can learn the most relevant features directly from the data. Additionally, deep learning algorithms are able to handle large amounts of data and perform well on highly complex tasks, making them a popular choice for many machine learning applications.
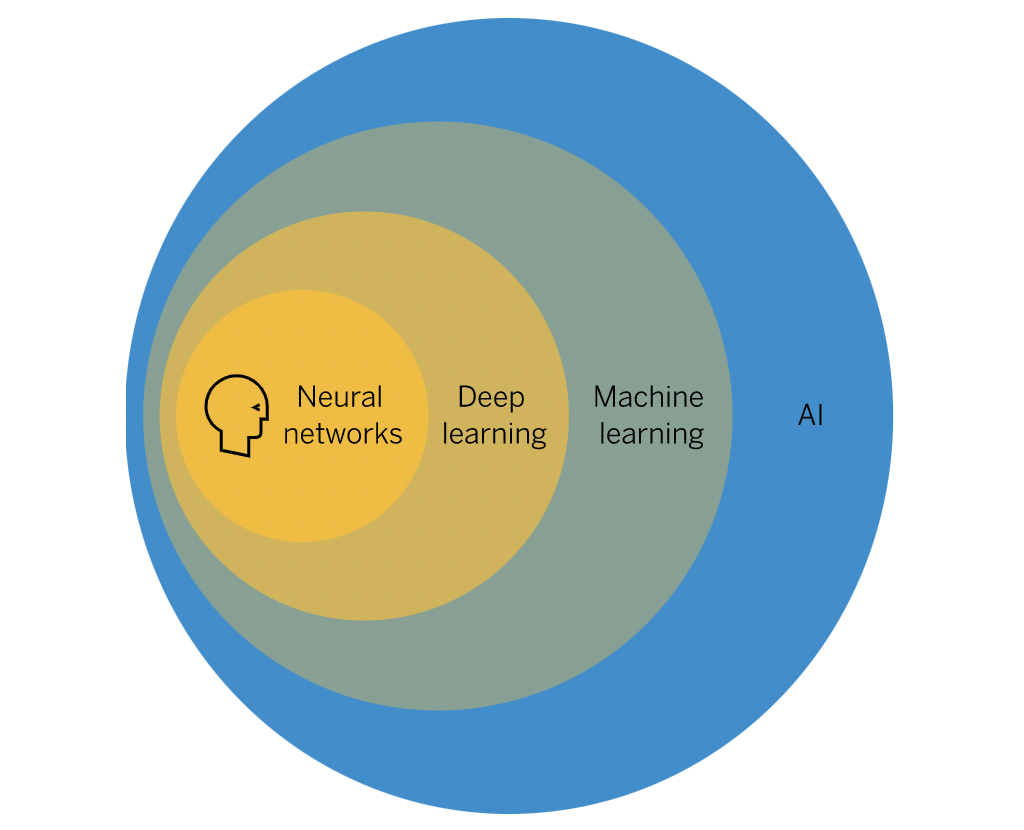
FIGURE 1 Diagram of the relationship between AI and machine learning.
Source: SAP. “What is machine learning?”.
Works Cited:
Brown, S. (2021, April 21). Machine Learning, explained. MIT Sloan. Retrieved February 8, 2023, from https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/machine-learning-explained
Sarker, I. H. (2021, March 22). Machine learning: Algorithms, real-world applications and research directions – SN computer science. SpringerLink. Retrieved February 8, 2023, from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42979-021-00592-x
What is machine learning? IBM. (n.d.). Retrieved February 8, 2023, from https://www.ibm.com/topics/machine-learning
Leave a Reply