1: General information
After watching the Chef’s Table episode on Enrique Olvera, it is likely that we are all familiar with the Mexican state of Oaxaca: one of the most ethnically and linguistically diverse regions of America. Located in southeastern Mexico along the Pacific Ocean coast, where the southern and eastern Sierra Madre intersect (Quinto-Cortés et al. 410), Oaxaca is often recognized by its beautiful coastal and highland valleys, rugged mountains and ethnic diversity (Joyce). While there are more than 60 Indigenous populations in Mexico, Oaxaca is home to the majority of them (Quinto-Cortés et al. 410). The Zapotecs are one of these various ethnolinguistic Indigenous groups in Oaxaca, and they are considered to be one of the most important cultures within Mesoamerican civilizations (Joyce). The Zapotecs live in four geographic regions of Oaxaca: the Central Valley, the Istmo, the Northern Sierra and the Southern Sierra (Luna-José 2). Together, the Zapotecs and the Mixtecs, another Indigenous group in Oaxaca, constitute just under 70 % of the Indigenous population in Mexico (Pavón 2), but the Zapotecs alone represent the third largest Indigenous group in Mexico (Luna-José 2). The present-day cultural diversity is rooted in the pre-Hispanic era, and despite the significant turmoil of the Spanish Conquest, pre-Hispanic traditions still greatly influence the lives and understandings of Indigenous communities (Joyce).
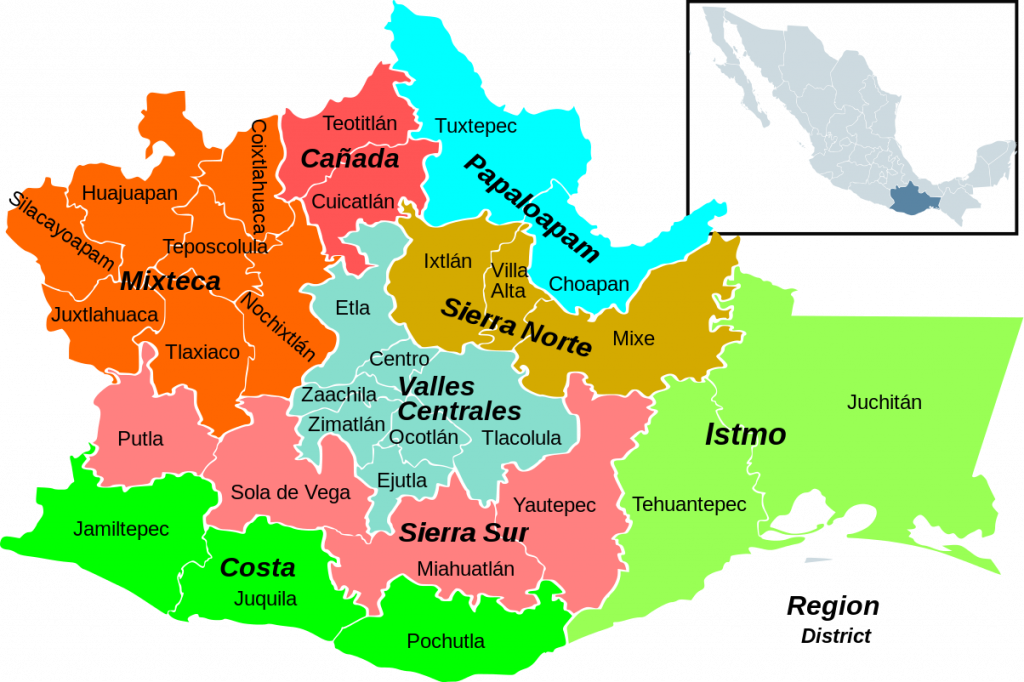
When roaming a market in Oaxaca, it is likely you will hear various native languages spoken, along with Spanish. It is no surprise that language, as a crucial feature of social cohesion, is an area of great diversity in Oaxaca, due to the fact that Oaxaca has a rich collection of different languages and dialects (Quinto-Cortés et al. 410). Around the time of the Spanish Conquest, there were probably over a million Mixtec, Chatino and Zapotec speakers (Quinto-
Cortés et al. 410). However, the uneven distribution of fertile lands divided by high mountains encouraged isolation, therefore influencing the emergence of linguistic and cultural diversity (Quinto-Cortés et al. 410). Today, at least 16 distinctive language groups are identified in Oaxaca, along with Spanish (Joyce); and in terms of language preservation, the Zapotecs have shown a great resistance to the loss of their native tongue (Saynes-Vásquez et al. 2).
2: Ecological knowledge and Classification Systems
Ecological Knowledge
Global changes that affect local communities have the potential to cause severe loss of ecological knowledge (Saynes-Vásquez et al. 2). Saynes-Vásquez et al. refer to this knowledge as “Traditional Ecological Knowledge” (TEK), which is the “knowledge, beliefs, and practices that have to do with the relationship that human societies have with their natural surroundings” (2). Their study analyzed cultural change among the Zapotec peoples, specifically those from the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. They found that cultural change experienced by these peoples, as a result of regional development processes, is related with the deterioration in TEK (Saynes-Vásquez et al. 9). They also claim there has been a significant decrease in local botanical knowledge as a result of the change in occupational activities, from primary activities to secondary economic activities and services, which has forced a large portion of the population to have less contact with the natural surroundings (Saynes-Vásquez et al. 9). Their data suggests that formal education programs disregard local knowledge and encourage a change in cultural attitudes that support a more urban lifestyle, while deflecting the attention away from nature and the local natural environment (Saynes-Vásquez et al. 9). In addition, schooling is also a contributing factor, as it encourages neglect of the native tongue which Saynes-Vásquez et al. describe as the “fundamental instrument of transmission of local knowledge” (9). Lastly, ethnobotanical knowledge itself is decreasing rapidly due increased deforestation (Saynes-Vásquez et al. 9).
Classification Systems
Traditional classification systems are examples of expressions in traditional knowledge, and, for the Zapotecs, knowledge that is produced through daily exchanges with plants and animals, as well as elements such as climate and soil, is organized and integrated in distinct ways (Luna-José 2). A study that aimed to both (1) describe traditional ecological knowledge through classification and (2) determine the role this knowledge plays in plant resource management and conservation, was conducted in the Zapotec municipality of San Agustín Loxicha, in the Sierra Sur of Oaxaca. The Zapotecs of this region heavily rely on agriculture and gathering of forest products to support themselves, and it is their connection with nature in daily life that has allowed for knowledge to be constructed about plant resources (Luna-José 2). This knowledge is reflected in traditional classification systems, particularly the plant classification system. Luna-José and Aguilar found that based on both ecological and morphological characteristics, the Zapotecs name and group plants in a hierarchic system; however, they not only recognize, name and classify plants that are useful to them for medicinal or nutritional purposes, but also plants that don’t offer an immediate use (Luna-José 10). Due to the different strategies Zapotecs have developed through generations, such as using plants for timber, food and medicine, and being in charge of their own productive systems (milpa, etc.), they have become experts in their field through experimentation and hold a high level of traditional ecological knowledge (Luna-José 11).
3: Foodways
As a reminder: foodways may be understood as the beliefs, behaviors, and practices surrounding the production, distribution, preparation, and consumption of food. Zapotec traditional agriculture systems used Milpa: squash, beans and maize, also known as the three sisters. Zapotec diets also included maguey, cacao, chilis, and a wide variety of wild plants. Spanish introduced new crops and domesticated animals to the Zapotec culture shortly after the conquest. Sugarcane, lettuce, onions, radishes, pomegranates, melons, and lemons are among the crops introduced by the Spaniards (Whitecotton 177). Today, Mexican cuisine is a fusion of native and new crops. In this section we will focus on two native crops: squashes and maguey.
Squashes
In Mexico, squashes, pumpkins and gourds (Cucurbita spp.) were domesticated around 10,000 years ago. The wild forms of Cucurbita do not have a pleasant taste (bitter) to humans. Although wild Cucurbita species declined, they thrived in domestication, and there are now hundreds of different varieties of Cucurbita grown worldwide (Kistler et al. 1). Cucurbita varieties differ in shape, size, and flavor and Zapotecs have been using them for millennia as part of their diets (Mulík and Ozuna 1). Zapotecs eat not only the fruit, as you have probably tried before, but they also eat the young stem, seeds, leaves and blossoms. In Oaxaca, squash blossoms, also known as “flor de calabaza” or “flor de pipiana” are very popular and are sold in markets either alone or with other edible parts of the plant. The flower is sold in bunches by local producers. Once the flower has been removed from the plant, it has a relatively short shelf life (2-3 days in the fridge). That helps to explain why most of the flor de calabaza eaten in Oaxaca comes from nearby locations. Cucurbita is used in numerous recipes and preparation varies among Zapotec groups and families. For squash blossoms alone, more than 40 recipes that use them as the main ingredient have been documented (Mulík and Ozuna 4). The two most common ways to eat them are in soups and as a filling in a great variety of Mexican dishes such as tamales or quesadillas. However, nowadays, they are used in Mexican haute cuisine in salads and desserts.
Figure 2. Flor de calabaza getting ready to be cooked.

Maguey
Maguey is generally grown in less fertile land, and it has a variety of uses. The use of maguey has changed with time. Before the arrival of the Spaniards, the stock of the maguey was roasted and eaten, a syrup was made from the plant, and the maguey’s fibres were used for clothing for the peasant class (Whitecotton 134). Pulque, an alcoholic beverage made from maguey was also consumed. The production origin of Mezcal, another alcoholic beverage obtained from maguey, is still very controversial. Some anthropologists affirm it was not produced in pre-Spanish times (Whitecotton 134), while others suggest that Mezcal was produced up to 25 centuries before the Spanish arrived (Goguitchaichvili et al. 1). Even if we are not sure about its exact origin, mezcal is a great example of Indigenous foodways beyond food consumption, as it is often used in healing. In contrast to Western thinking, in the Zapotec cosmovision, the world is not segmented into physiological, psychological, social and cosmic phenomena (López-Sanchez and Douglas 237). In Indigenous communities, foods such as eggs and mezcal are frequently used in healing by curanderos. The two main illnesses they are used for are tiricia (sadness of the soul) and mal de ojo (evil eye) (López-Sanchez and Douglas 239). The treatment consists of a limpia (a spiritual cleansing) where an egg is passed over the body and broken open in a glass of water for the diagnosis. It is then followed by brushing the body with mezcal, basil, rue, and copal incense (López-Sanchez & Douglas 239).
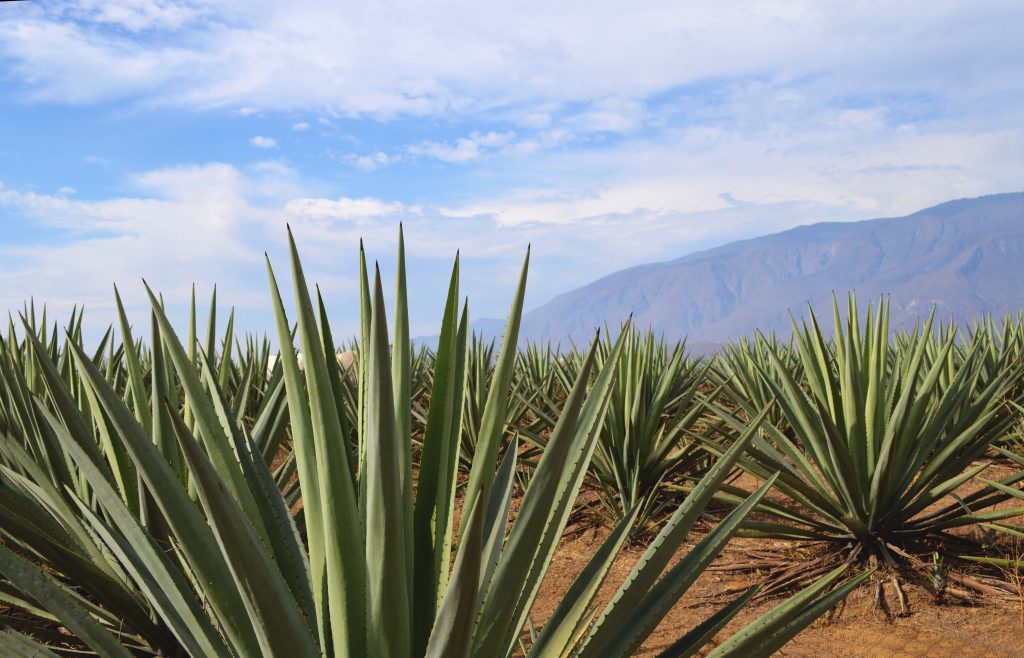

Mezcal also allows us to appreciate the role of globalization in Zapotec culture. Until a couple of years ago, Mezcal was not a word that foreigners would recognize while reading a drinks menu. However, in the last decade it has received a lot of media attention and exports have increased substantially (Bowen 128). Most of the exported Mezcal is produced by bigger distilleries that are able to profit from economies of scale and afford certification. Many of the small mezcal producers have been forced out of business (Bowen 130).
4: Agriculture
Agricultural Knowledge Systems
The Zapotec knowledge systems heavily stem from their knowledge of agricultural practices and their process of growing key crops. Referring back to the keywords, knowledge systems encompass practices, theories, instruments and people who together help acquire knowledge that contribute to the lifestyle of an Indigenous group. In context of the Zapotec, their large-scale success is heavily associated with the extensive and efficient development of agricultural technologies that allowed their community to grow squash, maize, and beans. Because the Zapotec were located in valleys and mountainous terrain, traditional farming methods as we know them would be difficult and inefficient. The Zapotec developed elevated agriculture technologies that would allow them to grow and sustain crops to feed their people. The Oaxaca valley allowed for an advantageous head start due to the large flat floor, high water table, low erosion rate and frost-free floodplain (Flannery et al. 446). As a result, the Zapotec also developed water features and land structures that facilitated the growth of squash and other key crops resulting in an abundance of nutrient filled food.
-
-
Barbecho rotation system
-
The Zapotec used the Barbecho rotation system that allowed land to be used and reused for agriculture purposes. As a refresher, Barbecho is when land is used for agriculture for 1- 2 years and then left to rest and re-fertilize for another 2-3 years. This agricultural technique allows land to re-establish nutrient-rich soil through a natural process, without causing long-term damage on the environment. This benefits both the Zapotec and the environment. Barbecho is reflective of the relationship the Zapotec have with nature. The Zapotec knew that if they were to obtain resources from the land, they must treat the land with care. This form of reciprocity shows how the Zapotec values are visible in many areas of their lifestyle, down to the cultivation of their food.
-
-
Canal Irrigation
-
Irrigation systems are one of the earliest forms of efficient pumping to date. These were multipurpose systems that facilitated water access used for the drainage of waste, farming and personal uses. Canal irrigation is a type of irrigation system that was used in Zapotec communities which was particularly important for agriculture. These water channels ran through the agricultural terrain and provided water from a water source (usually a dam) to farms located in different areas. The objective of this practice is to facilitate water access and to also reduce crop failure caused by erosion and degradation of water quality. By using water channels, it also created efficient use of water by minimizing conveyance losses from seepage or structural failure. As a result, canal irrigation became a key technology that contributed to the success rate of crop growth due to its multipurpose benefits in agriculture.
-
-
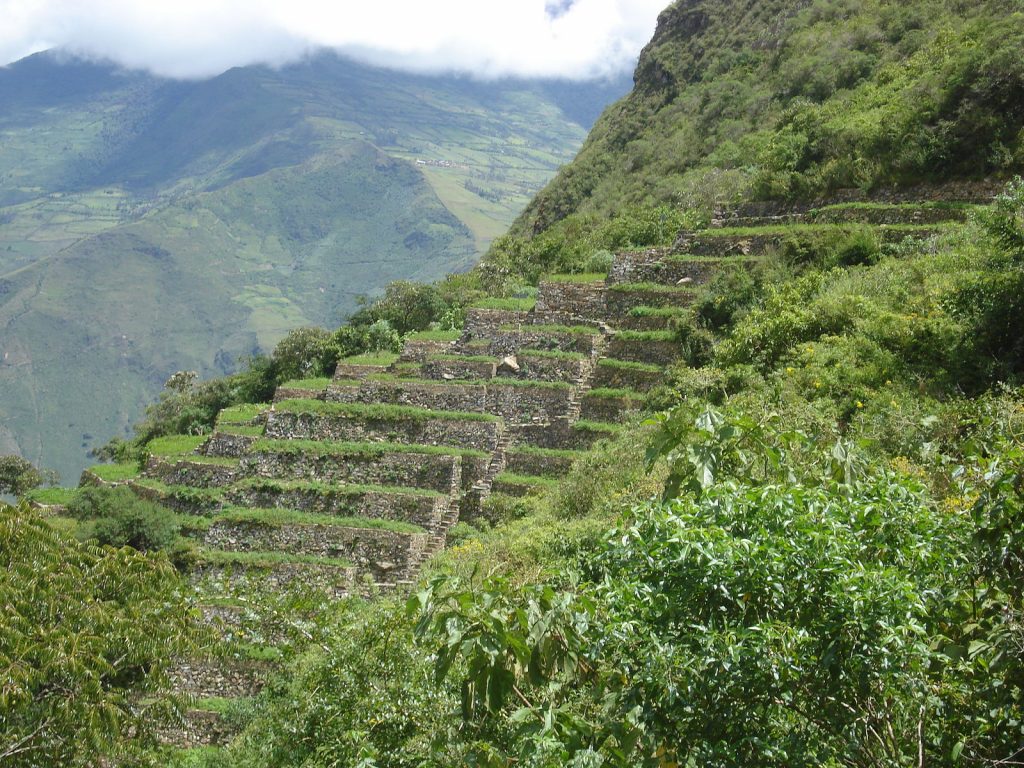
Terrace farming
-
As mentioned earlier, the Oaxacan valleys made it difficult to use the same farming methods as used on flat surfaces. The solution was to work with the land by implementing a technique that would support crop growth. As a result, Terrace farming became an innovation used by the Zapotec that contributed to successful food production. Terrace farming is a level farming technique that is distinguished for its step-like structure. It is useful in mountainous terrain, valleys or hills because it is the most efficient to sustain crops and prevent ecological damage. The small plateau of each level plays a number of significant roles to the sustainability of crops. Firstly, it prevents water from seeping down the hill, ensuring that crops receive sufficient water. This also prevents soil erosion from occurring, which is also a way to keep nutrients from draining down the land. Secondly, the level-like structure also acts as a form of stability on uneven ground: this prevents mudslides from occurring and ruining farmland and growing crops. Terrace farming was and continues to be a commonly used technique in many areas of the world. Due to its innovative structure, it provided the ability to farm on rugged land helping support and sustain civilizations.

Agricultural changes
For more than 5000 years, the Zapotec have developed and evolved techniques for producing, processing, preserving and preparing squash and other crops… to the point that agricultural surpluses supported a series of civilizations, including that of the Olmec, Maya, Toltec, Aztec Zapotec and Mixtec (Gonzalez, Robert 1). Even though pre-Hispanic cultivation techniques are still being used (Gonzalez 2), globalization and modern technology have impacted farming for the Zapotec. Since the Spanish colonial era, animal driven plows have been used instead of performing the labour firsthand and in the 1960’s, the introduction of pesticides have also been utilized to ensure the survival of crops against pests. Although terrace farming and canal irrigations are still part of the farming units in Oaxaca, farmers of Zapotec descent now utilize modern farming methods to facilitate the growth of these crops. Furthermore, farmers are becoming more involved in larger/global markets, and therefore require modern technology in order to produce larger quantities of food and meet the demands of large-scale markets.
5: Globalization
NAFTA
The North American Free Trade Agreement, also known as NAFTA, is a classic example of globalization that had a significant impact on the Indigenous peoples of Mexico. Oaxaca was no exception to the impacts of this agreement, which promised to bring prosperity, modernity, and overall improvements to quality of life. When NAFTA eliminated trade barriers across the North American continent, farmers were promised access to international markets — theoretically creating great demand for locally produced crops such as corn. In reality, the elimination of tariffs and political tensions between Mexico and the United States were carried out in tandem with subsidies for American corn farmers, meaning that unreasonably cheap GM corn flooded the Mexican market (Bacon). Mexican imports of agricultural products, including corn, surged to all time highs and migration from Oaxaca began to flow in the opposite direction. To this end, Bacon highlights that prior to NAFTA, “Indigenous people made up 7 percent of Mexican migrants” to the United States, while several years later, this group accounted for 29 percent (Bacon). Even for those who have resisted migration, the effects of both European colonization and more recent forms of globalization have led to distinct reductions in traditional agricultural practices, with many farmers transitioning toward commercialized crops and methods of farming (Soleri et al. 286).
“Usos y Costumbres”
In many ways the story of NAFTA epitomizes the globalization process in Oaxaca. The process of modernization, centralization, and consolidation of power at the national level often stands opposed to the historical cultures of Indigenous groups. This is especially true for the Zapotec people, whose geographic separations enforced many distinctions within their society. The transition from colonial subjugation to independence, the Mexican Revolution, and many events including the adoption of NAFTA were characterized by inextricable links to “global frameworks and market economies” which stand at odds with the plurality of Indigenous customs (Dürr 91). Efforts to homogenize Mexico at a national level, in an attempt to join the global framework, lead to the elimination of important cultural practices such as communal land use and customary tenure (Dürr 93). While the march of neoliberalism continues to challenge the Indigenous ways of life in Mexico, the preservation of tradition and culture has not been forgotten entirely. Usos y Costumbres is a system used in Oaxaca by which the plurality of traditional values, hierarchies, and methods of conflict resolution are integrated with national law. While Usos y Costumbres strive to acknowledge the diversity of cultures within Mexico and preserve the communal autonomy of indigenous peoples, this system itself is an example of the conflict between the increasingly homogenous structure of the nation and the granularity of its ancient cultures. Customary law, upon which Usos y Costumbres operates, “is primarily based on reciprocity, compromise, consent and discourse” all of which revolve around context and communal cohesion (Dürr 98). In contrast to this, capitalism and neoliberalism dictate that laws must be abstractly formulated and encoded to be applied universally.
Globalization has engendered the drive for political consensus, clear ideas of private ownership, and formal economic institutions in an effort to attract foreign investment. While this foreign investment can become beneficial to the country’s economy at large, the consolidation of industries such as farming causes undeniable harm to traditional foodways, viability of ancestral geographies, and incentive towards urban resettlement (Saynes-Vásquez et al. 9).
6: Conclusions
In closing, we would like to share the word “Guelaguetza” which, in Zapotec, means reciprocal exchange of gifts and services (Whiteford 1). Historically, Guelaguetza was a popular Zapotec community celebration based on reciprocity, but with time it has evolved to incorporate Catholic traditions and meet tourist demands. Nowadays, Guelaguetza is one of the biggest festivities in the State of Oaxaca, where the Zapotec together with other Indigenous groups of Oaxaca share their languages, dances and traditions. We invite you to watch the following Guelaguetza video featuring Academy Award winner, Yalitzia Aparicio.
7: Additional resources
- Instagram restaurants
- Music/videos:
-
- Nanga ti feo – Zapotec song by Camila, Mexican band
- Guelaguetza – Flor de Piña – https://youtu.be/YphmDYiEEwA
- Netflix show:
-
- Streetfood Latinoamérica – Season 1, Episode 3 – Oaxaca, Mexico
Lecture by:
Bibliography
Bacon, David. “Globalization and NAFTA caused migration from Mexico.” The Public Eye (2014): 19-21.
Bowen, Sarah. Divided Spirits: Tequila, Mezcal, and the Politics of Production, University of California Press, 2015. ProQuest Ebook Central, https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/ubc/detail.action?docID=2025587.
Britannica. “Terrace cultivation.” The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, https://www.britannica.com/topic/terrace-cultivation. Accessed 11 November 2020.
De Lourdes Luna-José, Azucena, and Beatriz Rendón Aguilar. “Traditional knowledge among Zapotecs of Sierra Madre Del Sur, Oaxaca. Does it represent a base for plant resources management and conservation?.” Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine 8.1 (2012): 24
Durr, Eveline. “Translating Democracy: Customary Law and Constitutional Rights in Mexico.” Sites: a Journal of Social Anthropology and Cultural Studies, vol. 2, no. 2, 2005, pp. 91 118., doi:10.11157/sites-vol2iss2id66.
Flannery, Kent V et al. “Farming Systems and Political Growth in Ancient Oaxaca: Physiography features and water-control techniques contributed to the rise of Zapotec Indian civilization.” Science. New York, vol. 158,3800 (1967): 445-54. doi:10.11.1126/science.158.3800.445
Goguitchaichvili, Avto, et al. “Archaeomagnetic evidence of pre-Hispanic origin of Mezcal.” Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports 21 (2018): 504-511.
González, Roberto J., and Project Muse University Press eBooks. Zapotec Science: Farming and Food in the Northern Sierra of Oaxaca. University of Texas Press, Austin, 2001.
Joyce, Arthur A. Mixtecs, Zapotecs, and Chatinos: ancient peoples of southern Mexico. Vol. 15. John Wiley & Sons, 2011.
Kistler, Logan, et al. “Gourds and squashes (Cucurbita spp.) adapted to megafaunal extinction and ecological anachronism through domestication.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 112.49 (2015): 15107-15112.
Lopez Sanchez, Oliva, and Douglas C. Nance. ““Something Born of the Heart”: Culturally Affiliated Illnesses of Older Adults in Oaxaca.” Issues in Mental Health Nursing 41.3 (2020): 235-242.
Mulík, Stanislav, and César Ozuna. “Mexican edible flowers: cultural background, traditional culinary uses, and potential health benefits.” International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science (2020): 100235.
Nader, L. 989 ‘The Crown, the Colonists, and the Course of Zapotec Village Law’, in J. Starr and J. F. Collier (eds) History and Power in the Study of Law, Ithaca/London: Cornell University Press: 320–344.
Pavón, Juan Carlos Pérez Velasco. “Economic behavior of indigenous peoples: the Mexican case.” Latin American Economic Review 23.1 (2014): 12.
Saynes-Vásquez, Alfredo, et al. “Cultural change and loss of ethnoecological knowledge among the Isthmus Zapotecs of Mexico.” Journal of ethnobiology and ethnomedicine 9.1 (2013): 40.
Soleri, Daniela Aragón, et al. “Food Globalization and Local Diversity.” Current Anthropology, vol. 49, no. 2, 2008, pp. 281–290., doi:10.1086/527562.
United States Department of Agriculture. Irrigation Canal or Lateral. Natural Resources Conservation Service. www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs143_026512.pd
Whitecotton, Joseph W. The Zapotecs: Princes, priests, and peasants. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1984.
Whitford, Michelle. “Oaxaca’s indigenous Guelaguetza festival: Not all that Glistens is Gold.” Event Management 12.3-4 (2008): 143-161.
Images sources:
Map of Oaxaca which highlights the four Zapotec regions: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Oaxaca_regions_and_districts.svg
Quesadilla de flor de calabaza: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Empanada_flor_de_Calabaza.jpg
Collection of four pictures about Flor de Calabaza in Oaxaca, Mexico. Property of Fernanda Díaz Osorio used with her authorization.
Terrace farming in Mexico: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Stone_terraces.JPG
Agave in Oaxaca: https://pxhere.com/es/photo/1427551






