Background
The current car market offers many choices regarding make, model, and fuel usage when determining which car to purchase. All of these options can be overwhelming to consider, which has lead to a large variability among car purchasing choices. Although electric vehicles are becoming more common within many metropolitan cities, they are currently seen only as a means for city driving, such as getting to and from work. The reality is many electric vehicles have the capacity to travel farther distances than expected. There is also a strong stigma behind the inconvenience associated with charging the vehicles. However, charging stations are located in many areas throughout Canada.
Our Focus
This project aims to break down the barriers associated with electric vehicle usage. In completing this project, the potential benefits of using an electric vehicle rather than a gas powered vehicle will be determined. Given the existing network of charging stations that are available across Canada, we seek to examine the possibility of traveling long distances in a more sustainable fashion by using an electric vehicle. By creating a network analysis of the travel route from UBC, Vancouver to UofT, Toronto, and incorporating charging station locations, the effectiveness of using electric, hybrid or gasoline powered vehicles to travel this distance can then be determined.
Study Objectives
- Determine the feasibility of driving a full electric vehicle from UBC to UofT
- Compare and contrast the time efficiency of using a gas powered vehicle, a hybrid vehicle, and both a high end and low end electric vehicle
Study Overview
Our project will focus on 4 vehicles:

Standard Electric (Ford Focus)
– Fuel Range: 122 km
– Price: starting at $29,120

High end Electric (Tesla Model S)
– Fuel Range: 507 km
– Price: starting at $72,700

Hybrid (Chevy Volt)
– Fuel Range: 85 km electric
5.7L/100km
– Price: starting at $33,220

Standard Fuel (Nissan Versa)
– Fuel Range: 7.2L/100km
– Price: starting at $11,990
The Route:
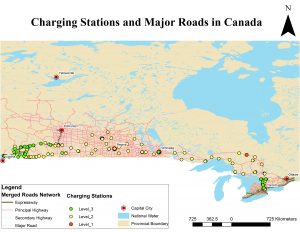
Charging Stations:
Electric car charging stations are categorized into three levels based on their power output capability, which influences the amount of time it takes to charge the vehicle at each site. It is important to consider charging times because excess charging time translates into additional costs in the form of hotel rooms, meals or activities purchased while waiting for the car to charge. We will also consider the different paths an electric vehicle might need to take in order to avoid running out of battery, and factor in how much extra time that adds to the journey.
Level 1: 9 hours for full charge
Level 2: 4-6 hours for full charge
Level 3: 45 mins for full charge
References:
Chevrolet (2016). Chevrolet Volt Hybrid
Electric Car Pledge (2016). How long does it take to charge an electric vehicle?
Ford Motor Company (2016). Ford Focus Electric
Nissan (2016). Nissan Versa Sedan
Tesla Motors (2016). Tesla Model S Electric