BMI
is a number obtained through a simple equation that measures body shape and helps 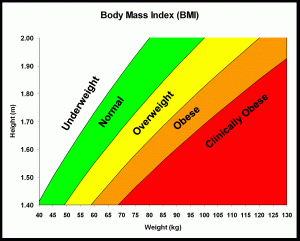 determine individual health risks through categorizing them into predetermined groups. It is an indirect measure of body fat based on height and weight (BMI= mass (kg)/ height (m2). After obtaining BMI, the individual will be placed in an underweight, normal weight, overweight or obese category. It is a quick, inexpensive, and easy measure, which gives a rough estimate of a person’s health status. BMI is limited because it does not take into account individual body composition (fat mass, bone density, and lean body mass). Age, ethnicity, body build, and frame size also affect the relationship of BMI to BF% and equations accounting for these factors provide a more accurate insight into individual body composition.
determine individual health risks through categorizing them into predetermined groups. It is an indirect measure of body fat based on height and weight (BMI= mass (kg)/ height (m2). After obtaining BMI, the individual will be placed in an underweight, normal weight, overweight or obese category. It is a quick, inexpensive, and easy measure, which gives a rough estimate of a person’s health status. BMI is limited because it does not take into account individual body composition (fat mass, bone density, and lean body mass). Age, ethnicity, body build, and frame size also affect the relationship of BMI to BF% and equations accounting for these factors provide a more accurate insight into individual body composition.
Waist Circumference (WC)
is a simple measurement taken at the most narrow portion of the trunk. It is used as an indirect measure to determine visceral (internal) fat. Increased visceral fat has been linked to increased disease rate. It is quick, easy, and affordable way to determine health risks, like cardiovascular disease, associated with increased visceral fat. It is not a direct measure and may be difficult on lean males. Waist Circumference is used to assess central fat distribution and degree of abdominal obesity. Males typically store fat around the abdominal region (apple shape) while women store fat around the hips (pear shape). WC cutoffs: Males < 102 cm Females < 88 cm
Skin Folds
is a technique used by fitness professionals used to measure subcutaneous fat, or fat beneath the skin, surrounding the muscle. There are different measurement sites around the body, by determining the sum of these skin folds and inputting them into a prediction equation, total body fatness percentage can be determined. From these measures, observations of the distributions of fat around the body can be made. Skinfold measurements are done by using skin calipers. The skin caliper technique is performed by pinching the top two layers on skin as well as the underlying subcutaneous fat layer. The test may be slightly uncomfortable and skin may be temporarily red and feel tender after the measurement. Although this test doesn’t measure internal fat (visceral), the fat directly 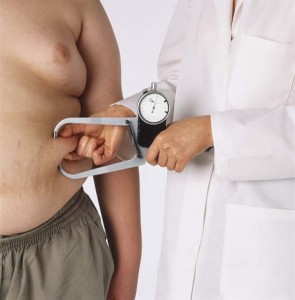 below the skin (subcutaneous fat) is related to the amount of internal fat. This measure is generally used to predict body density and percent body fat. A limitation of this measure is it is a prediction and an indirect measure, so error does exist in the measure. The body fat calculated is +/- 3.5% correct. To reduce error and increase reproducibility of the results, measurements should all be taken on the right side of the body. The measure is best for endomorphs, but may be difficult on overly muscular or overly obese populations.
below the skin (subcutaneous fat) is related to the amount of internal fat. This measure is generally used to predict body density and percent body fat. A limitation of this measure is it is a prediction and an indirect measure, so error does exist in the measure. The body fat calculated is +/- 3.5% correct. To reduce error and increase reproducibility of the results, measurements should all be taken on the right side of the body. The measure is best for endomorphs, but may be difficult on overly muscular or overly obese populations.
Other Health Assessments Include:
Client Evaluation (i.e., PAR-Q, Resting Blood Pressure/Heart Rate, Height & Weight)
Muscular Fitness Testing (i.e., Grip Strength, Leg Power, Back Health, Upper Strength etc.)
General Aerobic Fitness Tests (i.e., mCAFT, YMCA, Step Test, etc)
Sport Performance/Specific Assessments
Performance Tests (i.e., Shuttle Run, Broad Jump, 40yd Dash, Vertical Jump)
Muscular Tests (i.e., 1RM Testing)
For More Information;
- Click here to find out more about pre-exercise screening
- Click here to find out more about body composition measurements
- Click here to find out more about endurance (aerobic) exercise
- Click here to find out more about musculoskeletal fitness testing
- Click here to find out more about back health assessment testing