Overview:
This assignment assumes a potential large explosive point source and examines and describes the transport of that material over 72 hours after the 6 hour release of materials. This is done through the HYSPLIT online trajectory model. The data that was used was assumed that is it forecast data. Two different dates of potential release are compared in order to illustrate how differences in synoptic situations will produce different impacts.
Objectives:
- Gain experience with the application and limitations of air quality models
- Investigate the role of synoptic situation on dispersion
Summary:
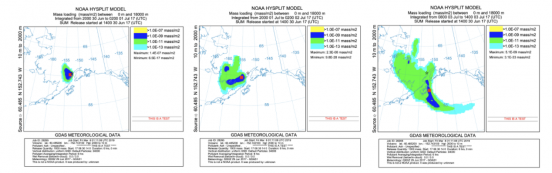
The Hybrid Single Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory Model (HYSPLIT) developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) is a computer model that is used to compute air parcel trajectories and deposition or dispersion of atmospheric pollutants. Explosive volcanic eruptions can eject large quantities of particulate matter (tephra), along with other aerosols, trace gases and droplets which are carried upwards into the atmosphere by the buoyant eruption column and are dispersed by winds. Mount Redoubt, is an active stratovolcano located in the highly volcanic arc of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. Located in the Kenai Peninsula, it is around 180 kilometers south-west of Alaska’s most populous city – Anchorage. Active for millennia, Mount Redoubt has erupted four times since it was first observed: in 1902, 1966, 1989 and 2009. According to a new volcano threat assessment which determines the greatest risks based on the potential for eruption and human impacts, Mount Redoubt came in fourth place behind: Kilauea, St.Helens and Rainier respectively. Located right in between a key flight path between North America and Asia, a potential volcanic event could cause temporary halts to global aviation.
Read the Paper: Assignment 2 – HYSPLIT Modelling