Multi-Criteria Evaluation (MCE) involves identification and analysis of key factors that contribute to environmental decision-making process.
The first step of the analysis was to create a vector TIN:
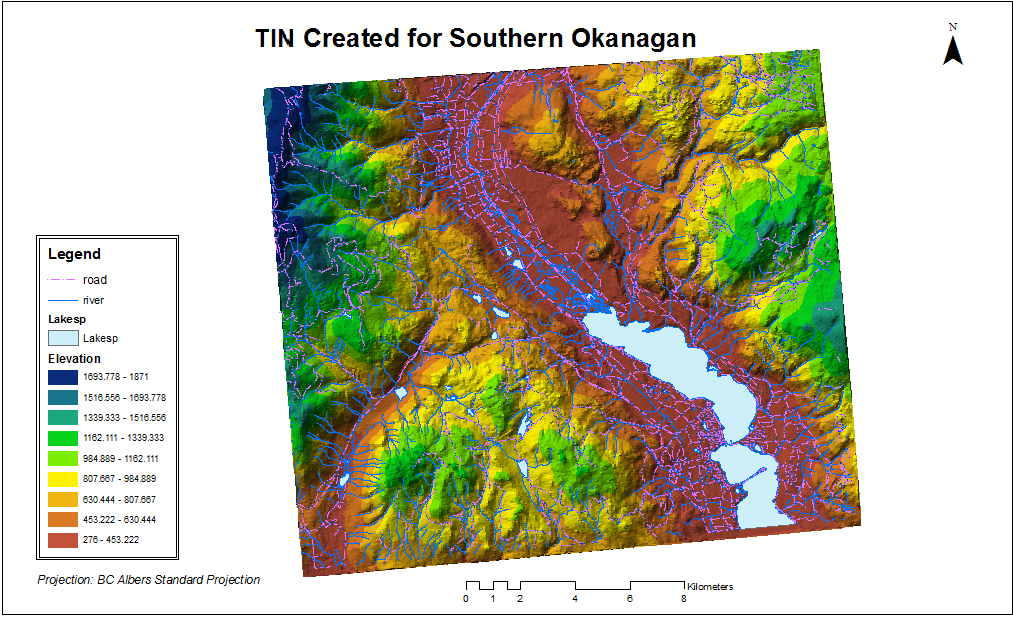
and the TIN was converted to a raster DEM to represent 3D surfaces. Then, the three factors that would be used in the multi-criteria evaluation (elevation, slope and aspect) were created, and normalized to a common scale of 0 to 1 in order for a fair comparison. After that, weights were assigned to each normalized factors to represent the relative importance of them. As aspect is determined as slightly more important, the weights was assigned as the following:
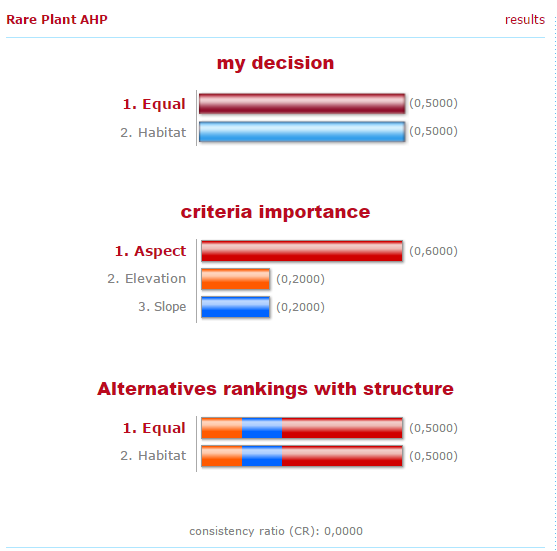
Then the Multi-Criteria Evaluation (MCE) was conducted to overlay the three factors with the assigned weights. Moreover, a sensitivity analysis was conducted to compare the MCE result we’ve got to one with unweighted variables, in order to examine how sensitive the results are to differently assigned weights. If the overlapping results are plenty, then the model would be stronger since the somehow subjective determination of the weights wouldn’t affect much of the results. If the overlapping results are few, then the level of uncertainty would be high, and the determination of the weights of factors would have to be very careful.
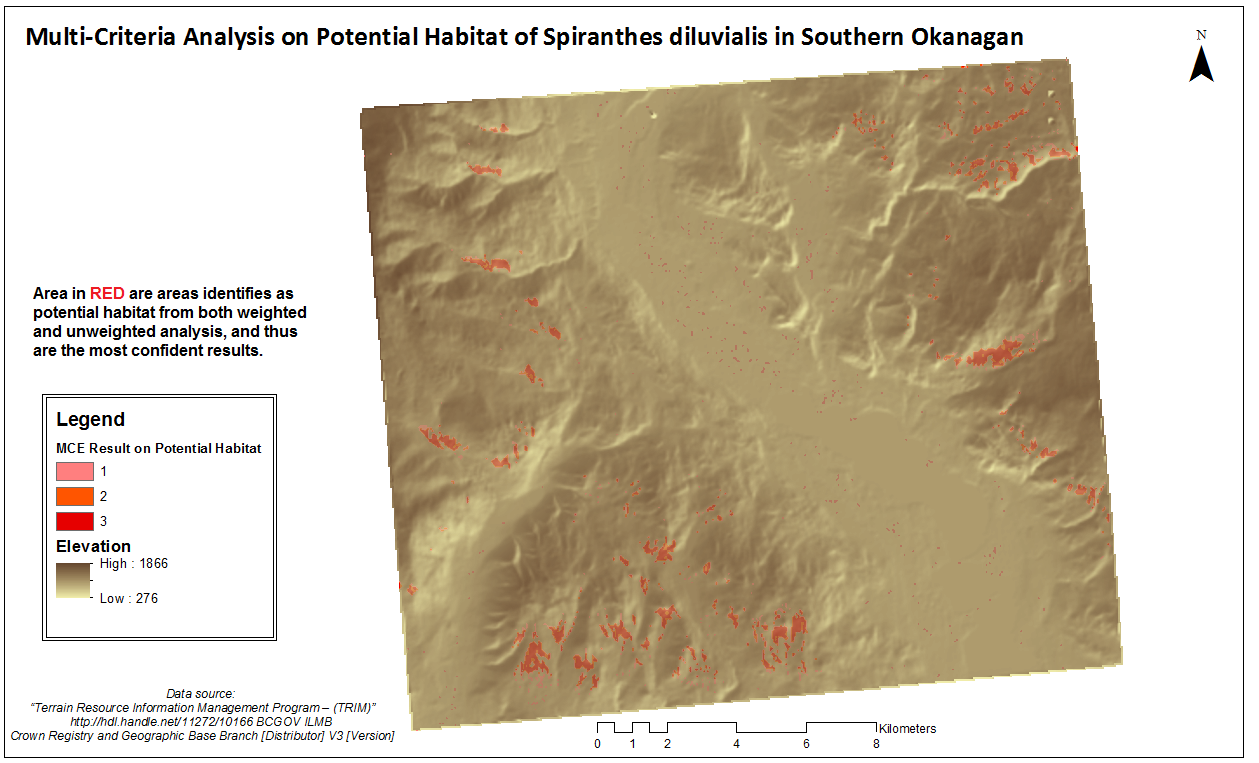
The results of sensitivity analysis are shown on the map as class 1 representing habitat identified in weighted MCE only, class 2 representing habitat identified in sensitivity model only, and class 3 representing overlapped results.
There are 865 values in class 1, 855 in class 2, and 2088 in class 3. Areas included in the three classes are all potential habitats for the rare plant and should be surveyed, with area in class 3 (highlighted in red) as the most confident potential habitat.