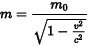Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of educational technology, Virtual Reality (VR) stands out as a beacon of potential, transforming traditional learning environments into immersive, interactive experiences. As educators and technologists, it’s crucial to explore how VR can be leveraged to enhance learning outcomes and engage students in ways previously unimaginable.
Breaking the Boundaries of the Classroom
VR technology transcends geographical and physical limitations. Students in a small town can explore the Great Barrier Reef, dissect a human heart, or visit the International Space Station—all without leaving their classroom. This accessibility is particularly transformative for schools with limited resources, offering students a world-class education through virtual field trips and labs.
Every student learns differently, and VR allows for customized learning experiences that cater to individual needs. Through VR, educators can create adaptive learning environments that adjust based on a student’s progress and preferences. Whether it’s slowing down a lesson for a student who needs more time or offering advanced challenges to fast learners, VR accommodates an array of learning styles and speeds.
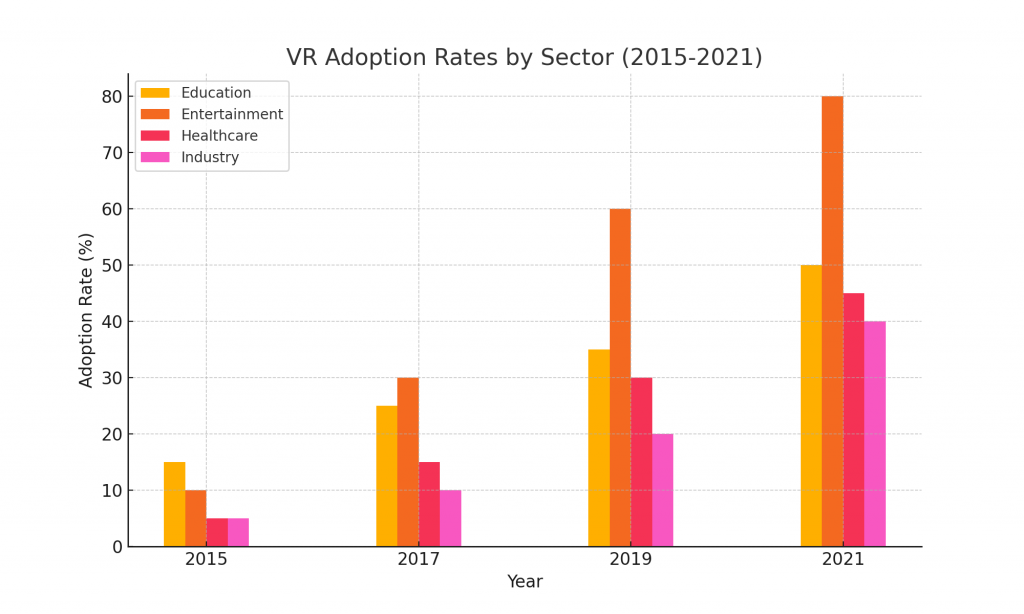
The concept of VR traces back to the mid-20th century, but it was in the late 20th and early 21st centuries that technological advancements made VR commercially viable. Innovations in display technology, motion tracking, and computing power enabled the creation of immersive environments that respond to users’ movements and interactions in real-time. Today, VR headsets like Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR provide users with compelling experiences that transport them to virtual worlds.Applications of VR Across IndustriesVR’s impact spans various industries, each harnessing its capabilities uniquely:VR enhances learning by creating interactive simulations that allow students to explore historical sites, conduct scientific experiments, or practice complex procedures in a safe environment.From surgical training simulations to therapy for phobias and PTSD, VR aids medical professionals in training, treatment, and rehabilitation, offering realistic scenarios that prepare them for real-world challenges.Entertainment: VR gaming has redefined interactive entertainment, placing players in immersive worlds where they can engage with environments and characters in unprecedented ways, enhancing realism and engagement.Industry and Manufacturing: VR facilitates virtual prototyping, remote collaboration, and safety training in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction, reducing costs and accelerating innovation.Challenges and ConsiderationsDespite its transformative potential, VR faces challenges that hinder widespread adoption:Cost and Accessibility: High initial costs of hardware and development limit access to VR technology, particularly in educational and healthcare settings.Issues such as motion sickness, visual discomfort, and latency continue to be obstacles that must be addressed to enhance user experience and comfort.Concerns about privacy in virtual spaces, ethical use in gaming and simulations, and the psychological impact of prolonged VR exposure require careful consideration and regulation.Future Trends and InnovationsLooking ahead, the future of VR holds promise for further advancements.Continued improvements in display resolution, haptic feedback, and spatial audio will heighten realism, making VR experiences more immersive and convincing.Integration with AI: AI-driven enhancements, such as intelligent avatars and predictive environments, will personalize VR experiences and improve user interaction VR is poised to extend beyond entertainment and training into fields like virtual tourism, telepresence, and virtual social interactions, reshaping how we work, learn, and connect.
Moreover, the integration of VR with other technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) is opening new frontiers for smart environments and interactive systems. AI enhances VR experiences by enabling more responsive and adaptive virtual worlds that can learn from and anticipate user interactions. For instance, in virtual training scenarios, AI can generate dynamic responses to the actions of a trainee, creating a more realistic and challenging environment. In retail and marketing, VR combined with AI allows consumers to engage in personalized shopping experiences, where the virtual environment adjusts in real time to their preferences and behaviors. The IoT, when combined with VR, extends the sensory reach of these systems, allowing users to manipulate and interact with physical objects that have digital twins in the VR space. This symbiosis could dramatically transform sectors like remote work, where physical presence is simulated through virtual proxies, enhancing collaboration across distances. As these technologies converge, the potential for innovative applications multiplies, setting the stage for a future where VR not only enhances reality but creates entirely new realms for human experience and interaction.
Conclusion
As we look to the future, the role of VR in education is only set to grow. The ongoing advancements in VR technology will likely make it more accessible and effective as an educational tool. For educators, staying informed about these changes and being prepared to integrate VR into curricula will be key to unlocking its full potential.
Educational technology is not just about using new tools; it’s about transforming how we teach and how students learn. Virtual Reality is at the forefront of this revolution, promising a bold new chapter in educational methodologies.
Resources
- Interesting video to learn about VR. click here.
- Go to http://www.ubc.ca/test/test/tes/tset/tes/tset/tes/tsetse/ to watch video about VR
Disclaimer
All of the content on this page was generated using ChatGPT-4. This page is solely used to identify accessibility errors and is not meant for informational purposes. The above information has not been verified.
Bonus:
Which of the following math formular is more accessible?
OR