Course Description
This course provides the opportunity for participants to examine teaching that aims to learners’ learning. It will examine literature on current research and practice concerning contemporary constructivist instructional strategies considered to be canonically effective. It will provide the opportunity to examine personal beliefs/worldviews about the nature of knowledge and truths and how these impact or influence our pedagogy of teaching and learning. Key instructional approaches and methods including project-based teaching/learning and cooperative learning will be critically discussed. The principles employed in these strategies will be considered and applied to practical experiences of designing and delivering online instructions. Existing learning sites will be critically examined through constructivist theories of teaching and learning.
Reflection
ETEC530, Constructivist Theories for E-Learning, was fascinating to me as this is a theory that I’ve always tried to adhere to in my learning as well as my teaching. I followed the work of Vygotsky and the socio-constructivist learning theory as well as the work of Bruner who suggested that learning should be situated within the context of authentic activity. I choose to follow the Constructivist Instructional Model (CIM) when I constructed an online lesson or set of lessons for teaching video editing using Adobe Premiere Elements 3.0. The CIM model suggests to:
- Identify learners’ views and ideas (prior knowledge);Prior knowledge is identified by the instructor before the unit begin. Students also identify their own understanding in the initial critique session.
- Create opportunities for the learners to explore their ideas and test their robustness in explaining phenomena, accounting for events and making predictions; Students have complete freedom in how they produce their videos given the feedback from peers and the video tutorials. There are over 90 effects in APE and there is no way a video can incorporate all of these effects and still be an effective video based on the rubric.
- Provide stimuli for students to develop, modify and where necessary, change their ideas and views; Since the students are working in a group, each will individually analyse their video, they will naturally discuss their thoughts with their group mates, allowing for modification of their ideas.
- Support their attempts to rethink and reconstruct their ideas and views. This would have to happen in their final video product. Each video is unique and will incorporate ideas from the student and his/her colleagues.
The benefit of this using approach, from a constructivist approach is that it allows student to build on their skills they have acquired through development and more importantly, social interaction with their colleagues. Constructivists who favor Vygotsky’s theory suggest that social interaction is important for learning because higher mental functions such as reasoning, comprehension, and critical thinking originate in social interactions and are then internalized by individuals. Children can accomplish mental tasks with social support before they can do them alone. Thus cooperative learning provides the social support and scaffolding that students need to move learning forward (Woolfolk, 2001, p.44).
Woolfolk, A. (2001). Educational psychology. Boston: Allyn and Bacon
Artefacts
Constructivism in the Desktop Publishing Classroom
http://www.scribd.com/doc/73053380/Constructivism-in-the-Desktop-Publishing-Classroom
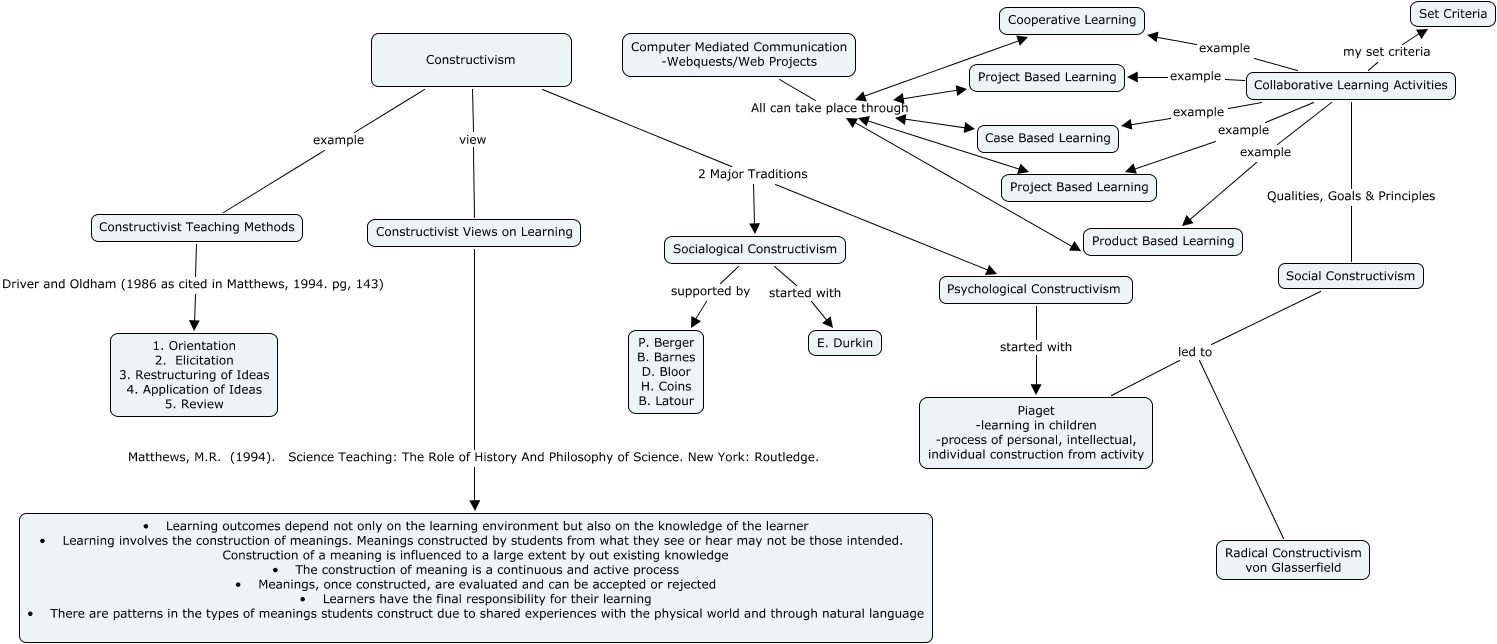
ETEC 530 – Concept Map