The purpose of this assignment was to demonstrate knowledge on different kinds of definitions for technical words. I used the word ‘negligence’ because I felt it was a great example of a complex word with multiple meanings. I showed that by illustrating the parenthetical, sentence, and expanded definitions of the word.
In this assignment we are to define a term used within a particular discipline and provide that term with three different definitions; a parenthetical definition, a sentence definition, and an expanded definition. The main objectives of this assignment is to:
- Appreciate the importance and role of definitions in technical writing
- Understand how audience and purpose indicate the need for definition
- Differentiate between the levels of details in definition
- Select the right level of detail according to the situation
My term is ‘negligence’ , and the reading situation is a lawyer explaining the term to a perspective client (possibly future plaintiff). In the following definitions I touch on the term ‘Tort Law’ and an explanation may help understand the following definitions. A ‘tort’ is an act or omission that gives rise to an injury of an individual, and is the result of a civil wrong which liability can be claimed by the courts. Essentially, a harm done unto another person for which liability can be placed unto another individual.
Parenthetical definition: In this Tort Law case, we are observing a claim of negligence (causing a foreseeable harm, while not meaning to do so).
Sentence definition: Negligence can be defined as an act committed without intention to cause harm, but which a reasonable person would anticipate might cause harm.
Expanded definition: The term negligence is directly derived from the Latin term neclegentia, meaning “carelessness, careless, and unconcerned”. Negligence refers to the specific conduct that falls below the standards of behavior established by law for the protection of others against unreasonable risk of harm. A negligent act occurs if a person has not acted in the conduct expected of a reasonably prudent person acting under the same or similar circumstances. Furthermore, in order to establish negligence under the law of torts, a plaintiff must prove that the defendant had a duty to the plaintiff, and that the defendant breached that duty by not acting in the required standard of conduct. For example, driving under the influence can be observed as a negligent act. In this scenario, all drivers on the road owe a duty to each other to drive safe and responsibly; driving under the influence does not conform to this standard.
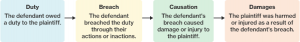
"Tort of Negligence", CourseHero. Figure 1: Outlines the four-step process of negligence in a tort case.
As seen in the diagram above, negligence takes on a four-step process. First, there must be a duty that the defendant owed to the plaintiff. It is imperative that this be proved to continue a claim of negligence. Next, the plaintiff must prove that there was a breach of this duty through either actions or inactions, purposefully or accidently. Causation is the next step, as this breach in duty must be the cause of the damage and/or injury the plaintiff sustained. If these three steps can all be made clear, then a case for negligence can be claimed and damages can be discussed. However, it is important to note that for an act to be determined negligent, all three steps must be proven.
Works Cited
Glossary of Legal Terms, Edmond Publishing – Canada’s Educational and Professional Publisher, 2019. https://emond.ca/resources/glossary-of-legal-terms.html.
Negligence, Collins Dictionary of Law, 2006. https://legal-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/negligence.
Negligence, Online Etymology Dictionary. https://www.etymonline.com/word/negligence.
Tort of Negligence. Course Hero. https://www.coursehero.com/sg/business-law/tort-of-negligence/.
