Public Values & the Regulatory Status of Xenotransplantation
- Xenotransplantation is a controversial topic with broad implications for society. Public opinion influences regulatory decisions, and these opinions are based on values.
- Public consultations have been conducted by governments in Canada and Australia to align the regulatory and legislative status of xenotransplantation with public values.
Results of the Canadian Public Consultation on Xenotransplantation (2001):
- 62.9% felt that the risks were greater than the benefit
- 18.2% felt that the benefits were greater than the risks
- Primary concerns were:
- Risk of zoonotic disease & fear of a large-scale epidemic
- Animal welfare
- Redirection of health care dollars
- Regulatory oversight might be inadequate
- Ethical objections (meddling with nature, the use of animals as “spare parts” for the benefit of humans)
- Insufficient knowledge to move forward
Overall, Canadians favoured a precautionary approach.
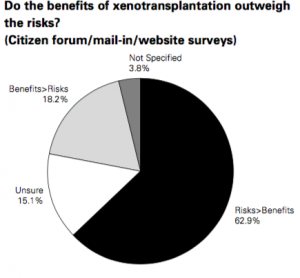
Canadian responses from public consult for xenotransplantation.
(Canadian Public Health Association, 2001)
Regulatory Status in Canada, Australia and US:
Cultural values are reflected in the regulatory status of xenotransplantation
| Public Values | Regulatory Status | |
| Canada | · Public consult (1997)
· Canadians favoured a precautionary approach. |
· Not permitted
· No trials underway |
| Australia | · Held two public consults (2004 & 2009)
· Favoured a precautionary approach in 2004 · Public was more accepting in 2009 with increased knowledge on the topic |
· Moratorium was placed on xenotransplantation human clinical trials in 2004
· Moratorium was lifted in 2009 · Human clinical trials approved |
| United States | · Based on the adoption of GM crops, US has had greater acceptance towards genetically engineered products | · Human clinical trials underway
· Regulated by the FDA |