History of Xenotransplantation
Experimentation with animal-human transplants began as far back as the 1600s. The first experiments involved cells and tissues, and experimentation with whole organ transplants began later as surgical advances were made. Most attempts eventually resulted in the death of the recipient due to the immuno-incompatibility between species.
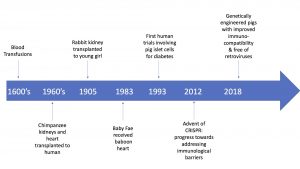
Timeline of xenotransplantation:
Why Pigs and not Nonhuman Primates (NHPs)?
It was previously thought that NHPs would serve as the best candidates for xenotransplantation due to their phylogenetic closeness. However, the pig is now the preferred candidate for a variety of reasons.
| NHPs | Swine | |
| Infectious potential | High | Low |
| Organ Size | Often too small | Good |
| Availability | Low | Unlimited |
| Age of Sexual Maturity | >5 years | 4-8 months |
| Gestation | 160-260 days | 114 days |
| Number of Offspring | Usually one | Up to 12 |
| Growth Rate | Slow | Fast |
| Cost of Rearing | High | Low |
| Public Opinion | Unfavourable | Favourable |
Advantages of Xenotransplantation
- Unlimited supply
- Would qualify “borderline” patients that do not meet the criteria for transplant lists
- Available immediately
- Reduced burden on health care systems treating patients awaiting transplant
- Reduced suffering associated with disease
- Reduced stress for patient and family while waiting for an organ to become available
- Medicinal benefits
- Allows patient to begin immunosuppressive regime in advance
- Eliminates the degenerative effects of brain death on organs from deceased donors
- Genetic modifications to improve immuno-tolerance may reduce the need for toxic, immunosuppressant drug therapy
Disadvantages of Xenotransplantation
- Immunological barriers
- Molecular incompatibilities result in immune response to reject xenografts (hyperacute rejection and acute humoral xenograft rejection)
- Risk of infection by endogenous retroviruses (PERVs), and other microorganisms
- Social barriers
- Public acceptance
- Compromised welfare for animals
- Opposition to transgenic animals — “meddling with nature”