Report Title :
An Analysis of the Relationship between Children’s Language Skills and Early Development Level of the Children and Their Neighborhood using Geographically-Weighted Regression.
Abstract
This research analysis how children’s language skills level related to their and their neighbourhoods’ development level based on the Vancouver area. In order to understand their spatial correlation properties, the GWR (geographically-weighted regression) is used for modelling. The results indicate that GWR can provide relatively accurate results of local relations amongst a set of variable for spatially examining the data spatially with the use of ArcGIS software. Also, how a child’s language skills related to some important Early Development Instrument (a small set of variables related to that child and to their neighbourhood) explored in this lab can be helpful in understanding the neighbourhood development and distribution pattern of the development conditions.
Full text access: lab 2 REPORT
Highlight:
Further Discussion on different Usage of GWR
The Geographically weighted Regression method is also broadly used in many researches associated with spatial analysis. For instance, GWR can be used for modelling in soil chemical content or physical charachteristics pattern. A research doneby Zhang, Tang, Xu, and Kiely in 2011 use a geographically weighted regression (GWR) method for the spatial modelling of soil organic carbon contents in Ireland. The scientists included environmental factors of rainfall, land cover and soil type were investigated as the independent variables to establish the GWR model. They used GWR to create comparable and reasonable results while making use of the other chosen methods of ordinary kriging (OK), inverse distance weighted (IDW) and multiple linear regression (MLR). In this research, patial geochemical modelling was achieved using geographically weighted regression (GWR) as a basic step. The GWR also provided a promising method for spatial geochemical modelling of SOC and potentially other geochemical parameters.
GWR is also seen used in more social scientce sccociated research. An simple and typical example can be a case study based on a small town called Menghe in Changzhou, China(2010). The scientists did simulation on regional spatial sand sse patterns using Geographically Weighted Regression. The spatial non-stationary of the impact on the land use patterns change of the driving factors was considered.The simulation result was compared with OLS Logistic regression model. Geographically Weighted Regression model is not only able to improve simulation accuracy of regional land-use patterns,but also able to obtain spatial differentiation of the impact of the driving factors on land use patterns.The result of this study can support the government decisions on land use management for Menghe Town and similar areas.
GWR has good potential in helping studies associated with landscape, geochemistry and other phisical or chemical properties of the environment of an area (not only the propertoes on the ground, but also suitable in analysis the pattern of the properties of water; air weather, etc.).And then, researches in many fields (both in social and natural science) that needs spatial analysis especially which require higher accuracy probabaly need including GWR in the data analysis process in researches.







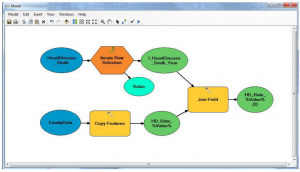 , one for each year and
, one for each year and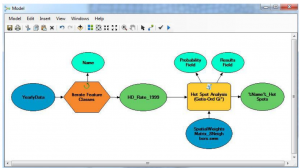 . Finaly we animate the
. Finaly we animate the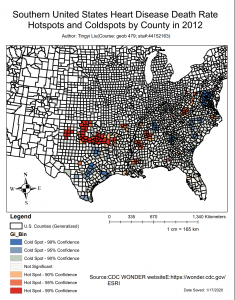
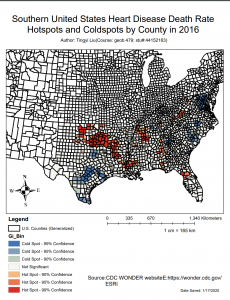 .
.