ROOT APEX
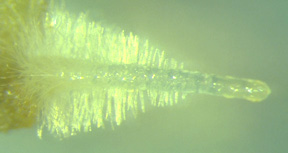
This is a root tip. You can see the root hairs which occur in the region of differentiation. It is in this region that the metaxylem elements are maturing. It is also the region of absorption of water and ions.
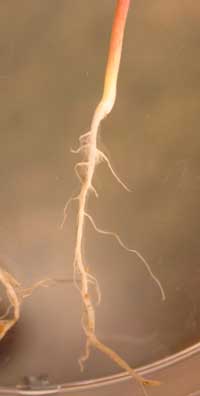
This is the root system of a radish seedling.
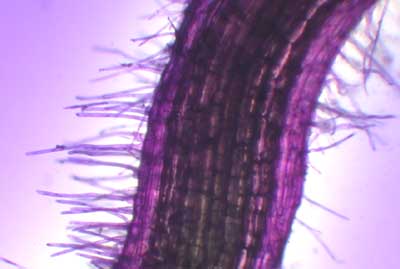
Here is a close up of a radish seedling root in the area of the root hairs. It has been stained with toluidine blue.
….and a little closer……
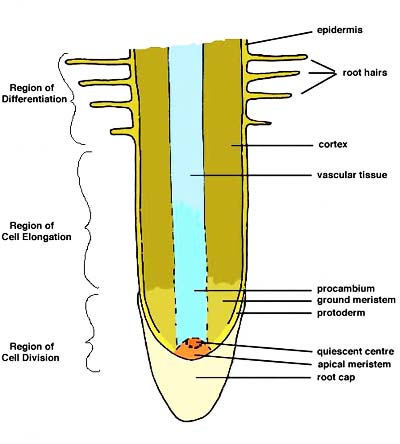
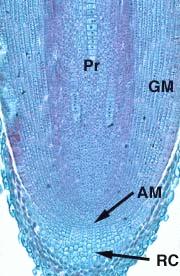
Root apical meristems consist of many regions:
Protoderm: the outermost layer of dense cells radiating out from the meristematic region.
Procambium region: comprising those cells in the central core of the meristematic zone. Some in the very centre are more elongated than those on either side.
Ground meristem: includes all those cells between the procambium and the protoderm.
Quiescent centre in which the cells are unstained, and apparently without nuclei.
Apical meristem: the zone of small, dense, darkly stained cells around the quiescent centre; this is the region of active cell division (mitosis)
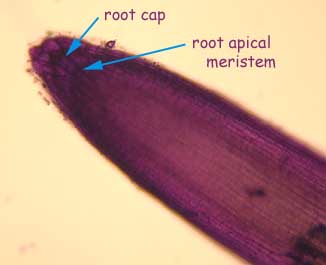
Root cap: the conical tip consisting of large, somewhat thickerwalled cells with small nuclei. The outer cells are sloughed off as the root penetrates the soil.
This is a picture very similar to what you will see in class. As you can observe some of the regions mentioned above are rather difficult to see. You should be able to discern the region of the root apical meristem (AM), the root cap (RC), the ground meristem (GM), and the procambium (Pr). Of course the outermost layer of cells is the protoderm.
This is the root tip of radish stained with toluidine blue. You should have seen something like this in lab.
ROOT APEX
HERBACEOUS AND WOODY ROOTS
ROOT MODIFICATIONS
BACK TO ROOT FRONTPAGE