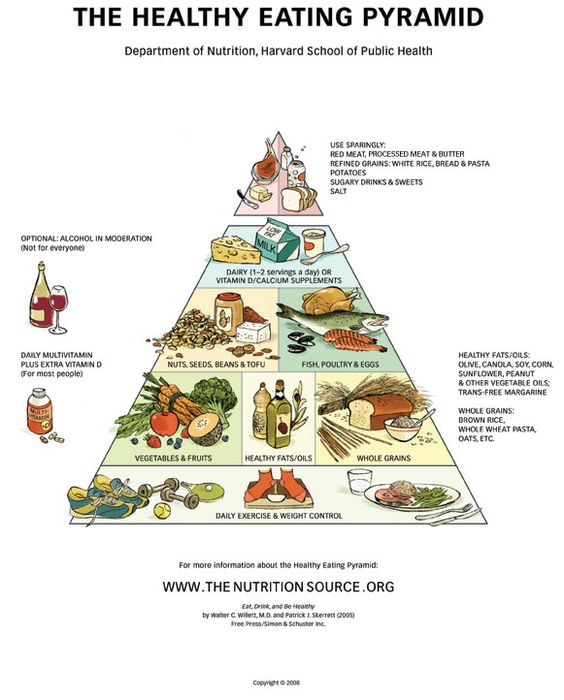
You may know that it is a good idea to eat fruits and vegetables to keep healthy; you may know that we can lose weight by controlling the calories input. But do you know that we can simply stay healthy and lose weight by having a “smart” eating pattern while not changing what we eat? What does the eating pattern mean in this case?
Different eating patterns including a regular way and a non-traditional way –TRF, which stands for time-restricted feeding. TRF simply means we restrict the total amount of time of food consumption every day. The time spread of the regular eating pattern is usually 16 hours. But if we eat the same amount of food but reduce the total time spread to less than 16 hours, we can easily stay healthy and even lose weight by maintaining a relatively stable heartbeat.
The figure below can better explain different eating patterns.
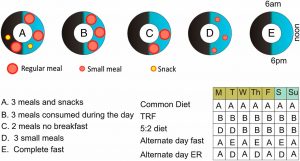
[source: http://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/111/47/16647/F3.large.jpg]
As the five figures are shown above: the blue area of the circle represents the daytime and the black area represents the night time. The regular eating pattern is shown as the pattern A. It includes three large meals plus snacks during a 16-hour period of wakefulness. Pattern B, C, and D illustrate the concept of TRF, which is what we recommend in this article. The common idea shared among the TRF eating patterns is the limited eating time — the total time spread of food consumption is less than 16 hours.
To be more specific, eliminating midnight snack and limiting eating to 12 hours is the “smart” eating pattern that we are encouraged to have. A research conducted by Tina Hesman Saef found that fruit flies with only 12-hour spread had steadier heartbeats in old age than flies with unrestricted eating time.
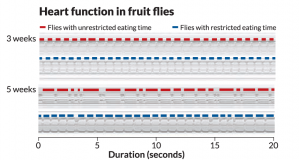
[source: www.sciencenews.org/sites/default/files/main/articles/ti_fly_feeding_graph.png]
The experiment was designed to have two groups of flies. One group ate a cornmeal diet anytime they want; another group had access to same food for 12 hours only. Both groups ate about the same amount of food and had similar amounts of activity. The result of the research shows that after 5 weeks, the group with TRF had the steadier heartbeat. Stable heartbeat can help maintain fat metabolism by adjusting the tolerance of glucose and adjusting blood pressure. Therefore, TRF helps weight loss due to its effect on the heartbeat and metabolism.
However, does this eating pattern mean we only need to consider the time sprints of food consumption without thinking about the frequency or time of food taken? The answer is no. If we do not stick to the same eating schedule every day, our body clock will be in a mess. This will cause unstable heartbeat and harm our immune system. In general, the recommended frequency of food intake should be three times a day. A research on female participants with different meal frequency supports this by analyzing the level of energy intake and expenditure.
Does this sound great? We can easily lose weight by limiting our meal time while eating the same things! Try to eat within 12 hours every day and don’t eat the midnight snack. Let’s see how easy and comfortable it is to live a healthy life!
by Qingyue Wang