For as long as I can remember, my interest in science and science fiction have been deeply connected. Every Marvel movie I see inevitably results in hours long “study breaks”, where I scour the internet for any information on how these spectacular technologies match up with real world science. Does it obey the laws of physics? If not, is there something similar that theoretically could? Do we have related technology now? How would it work? Unsurprisingly, I’m not alone in this thinking. Countless inventions that have and will shape our society were initially conceived in fiction, including the atomic bomb, cell phones, self driving cars and many more.

Source: Star Trek
Most of the time, my Wikipedia rampages end with the second question: Is there something that theoretically could? This results in a lengthy hypothetical description of something that often doesn’t resemble its fictitious counterpart. So understandably, I get pretty excited when I see technology not only possible, but already close to becoming reality.
This is the case with the work recently published in Nature by Daniel Smalley, an electrical and computer engineering professor from Brigham Young University. The “Photophoretic-trap Volumetric display,” or more casually called “The Princess Leia Project,” is a revolutionary new 3D hologram design. The idea of 3D holograms is not a new one. Most famously, it has appeared in Star Wars with Princess Leia’s plea for help projected by R2D2, or the enormous head of Darth Sidious. More recently it has been popularized in films like Iron Man and Avatar.

Source: Star Wars: Episode V – The Empire Strikes Back

Source: Star Wars: Episode IV – A New Hope
Ironically, none of these depictions are actually holograms. A holographic display specifically refers to an image projected in 2 dimensions. In other words, if you aren’t looking directly at it, the image will appear distorted like viewing a TV at a sharp angle. A Volumetric Display occupies 3D space, so it can be viewed clearly from any angle. Smalley is able to do this using a single cellulose particle, a component of plant fibre. This particle is trapped in the air using a set of invisible lasers which can move it around in a small circuit. Then another set of lasers illuminate the particle with different colours. If the particle is moved fast enough around this track, it appears to be a solid line to the human eye.
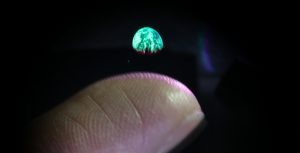
Source: Science News
Though Smalley isn’t the first scientist to research 3D displays, his multi-laser design is the first able to incorporate colour. Due to the use of a single particle, his prototype images are restricted by size, ranging from about the size of a pea to a postage stamp. But if his design is improved, many particles could be used to create much larger images. With the right imagination, Smalley says “the sky becomes the limit.”
Video Below
By Connor DeFaveri