Nitric oxide (NO) is one of the most widely-produced gases in the human body, and has been shown to play a major role in the function of the cardiovascular, nervous, and immune systems. This means that it has implications in the treatment and management of many conditions such as erectile dysfunction, muscle soreness, and Type II diabetes. Despite the numerous processes in which nitric oxide play a role, there are only two known routes of production in living organisms.
Research jointly published by the Institute of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology at the Zhejiang University School of Medicine in Hangzhou, China and the Department of Chemistry at the University of British Columbia examined one alternative method to the production of nitric oxide. In this pathway, two enzymes are used to generate a chemical compound known as streptozocin that creates NO as a byproduct.
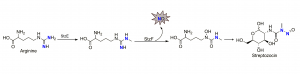
Simplified schematic of the two reactions that occur to produce the N-nitroso compound streptozocin and nitric oxide (NO) as products
This work provides support to the idea that there may be alternative routes to the synthesis of this critically important compound. We spoke to Alyssa Henderson about her work on the project, her experience with research in general, and some of the challenges she faced while working on this publication.
Streptozocin is part of a larger class of N-nitroso compounds, which are identified by the presence of an -N-N=O group in its structure. Alyssa’s research was motivated by the natural presence of N-nitroso compounds in natural products. It was proposed that these compounds, and the biological pathway of its production, could be significant in the production of NO.
Tests were done with a solution containing components of E. coli and stzE (one of the enzymes isolated from the genome of streptozocin), and it was found that stzE is necessary to produce the compounds involved in the second step of the process.
The next step in this two-enzyme pathway was similarly isolated from the streptozocin genome, and was found to be necessary for the production of the products shown below. Alyssa’s research suggested that nitric oxide is produced in the conversion of compound 3 to compounds 4 and 5, which is catalyzed by stzF.
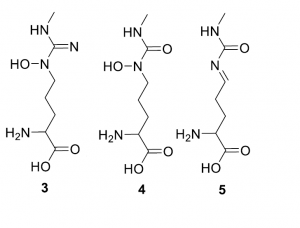
Structure of the products generated from the second step of the two-enzyme pathway.
In order to explore how widely distributed these genes are, Alyssa’s team found 40 enzyme pairs with similar functions to the stzE/stzF enzyme pair in a variety of soil-dwelling and plant-associated bacteria, which further supports the idea that natural routes to nitric oxide synthesis exist.
Cell cultures of some of the soil-dwelling bacteria found to have similar enzyme functions to the stzE/stzF pairs
The significance of enzymes in these soil microbes is discussed in the podcast below:
While this paper doesn’t fully explain all of the possible processes that may be involved in the natural production of nitric oxide in the environment, it sets the stage for important advancements in the field.