Antibiotics is something that we all have had experience using. This technology although a relatively recent development in history it has conferred massive benefits on the human population. After the discovery of penicillin in 1928 the average life expectancy went from 47 years at birth in 1900 to 78.8 years today, leading cause of death went from infectious diseases to non-communicable disease, and the population expanded a few times over. However, the effectiveness of this new technology is diminishing and may even come to an end.
Recently it has been found that bacteria populations have been evolving to become resistant to antibiotics. This new development has led some to suggesting that the use of antibiotics in livestock and human populations be reduced, others are suggesting to look for new alternative medicines to replace standard antibiotics. This has led to many researchers around the world to start looking for new treatments to infectious diseases. Some break throughs have been made, one in particularly being the study and application of cationic peptide antibodies.
Cationic peptides are produced naturally in all organisms and are an important component in defense against microorganisms. Additionally, microbes don’t seem develop resistance to these compounds. Although in the early stages of drug development peptide antibodies have been shown to be extremely effective in killing bacteria in vitro and quiet a bit has been discovered about their chemical structures and properties.
Cationic peptide antibodies are compounds consisting of 12-15 amino acids linked in chains with a positive charge. The chemical structure of cationic peptides varies considerably and have been grouped into four types; β-sheet structures, α-helices, extended helices and loop structures. In addition, peptides have hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions letting them interact with lipids as well as with water.
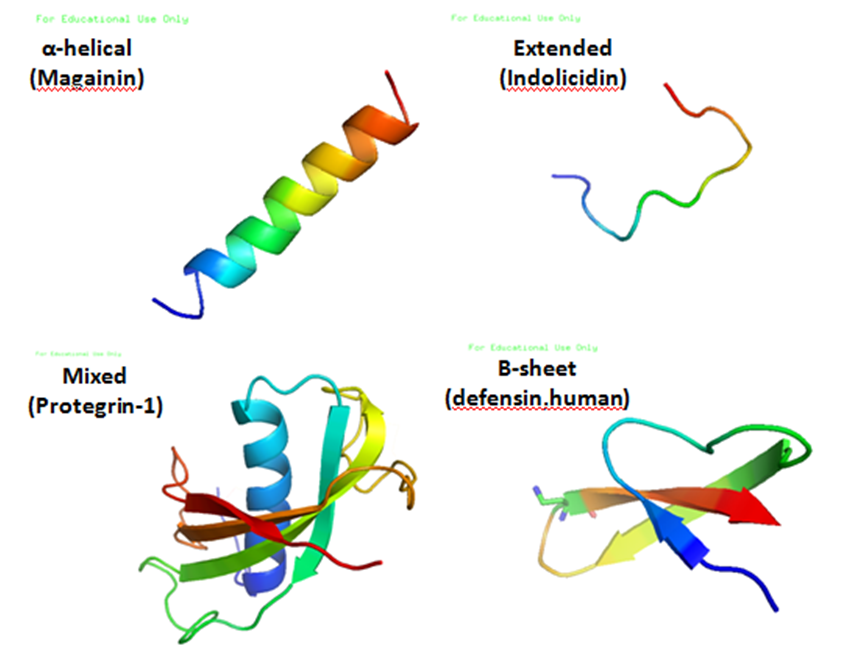
Although natural occurring in all life forms and some peptides structures being known exactly production has been costly and difficult. Peptide antibiotics are found in almost all cellular immune response mechanisms, but these quantities are insufficient even for research use let alone for industrial production. It is found in higher concentrations in amphibian skin and mucosal regions of the body but extraction from these mediums is not economically feasible and not all variations are available this way.
Another means of peptide production is chemical synthesis, which consists of three maim procedures; fragment condensation in solution, stepwise solid phase synthesis, and solid phase fragment condensation.

Kent, Stephen B H. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 1988. Title: Chemical Synthesis of Peptides and Proteins.
Fragment condensation in solution is when you take the amino acids in solution making up the peptides and link them then, link the chains just created and repeating till desired peptides is produced. Stepwise solid phase synthesis starts to a C-terminal amino acid attached to a solid base from there additional amino acids add chemically bonded in a step wise fashion then purified of resin bound intermediates by filtration and washing. Solid phase fragment condensation uses stepwise solid phase synthesis to create desired peptide fragments and then condense these fragments using resin support. All the methods of peptide chemical synthesis are sophisticated leading to a need for experts and specialized labs. The final means of peptide production is recombinant DNA procedures, in which the genetic code of bacteria is altered so that it will produce am abundance of the desired peptide, this procedure is showing to be the most efficient and so the most promising for future research and funding.
Noah Rudlowski