Do you ever check how many photos or apps you have on your phone? Have you ever considered managing your personal data?

Image flicker
If you answered “No” to any of these questions, you might want to rethink about your personal data storage. Most users usually do not keep track of the data on their devices until they are notified that they are running out of storage.
Personal data can be social media accounts, favourite playlists, and even credit card details. You might be surprised to find out how much personal data is shared across devices and online platforms.
It is important to “derive value from your personal data over time,” says Dr. Francesco Vitale, a PhD candidate in Human-Computer Interaction at the University of British Columbia. The process of selecting what to keep and delete could be difficult for users because of their attachment to data. If that is the case, is there any kind of technology that can help facilitate data management?
This is exactly what Dr. Vitale questioned and studied. He used a Research through Design approach to come up with the five new design concepts to analyze people’s opinions towards different approaches of keeping and discarding personal data.
Design Concepts
Patina – a visualization of how frequent the users access the data.
The age of data is shown by using a spiral. A longer spiral means more frequently accessed data.

Patina Source: Francesco Vitale
Data Recommender – a system that tells users which data needs attention.
This system is partly incorporated into apps like Google Photos and Files on Android.
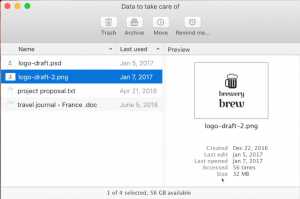
Data Recommender Source: Francesco Vitale
Temporary Folder and Temporary App – both with features that have an “expiration date.”
Users can decide how long they want to keep certain folders/apps for, and it will be uninstalled automatically.
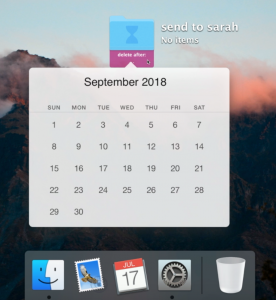
Temporary Folder Source: Francesco Vitale

Temporary App Source: Francesco Vitale
Future Filters – an app that allows the users to decide what to do with data in the future.
The users are given choices from a set of actions and criteria in order to decide what happens to the data.

Future Filters Source: Francesco Vitale
Impact in Our Lives
The result of the study showed that opinions on managing data vary between not trusting technology vs. being open-minded about technology managing their data for them.
Some have mentioned that they do not mind deleting their data off their devices for example, in the case of social media it is “never truly deleted, … there will always be a copy somewhere out there.” Many users store their personal data on online platforms without thinking about the consequences.
Recently, Dr. Vitale participated in a short interview that discusses his research and about how data management affects his life.

To further discuss the topic, Science 300 podcasters at UBC decided to cover Dr. Vitale’s research and see how data management affects the lives of students.
(Podcast credit: Francesco Vitale, Bernice Huynh, Kieffer Silva Pinto, Sara Uzama)
With different views on the topic, perhaps data management is a subject that should be taken more seriously and further investigated.
-Bernice Huynh, Kieffer Silva Pinto, Sara Uzama