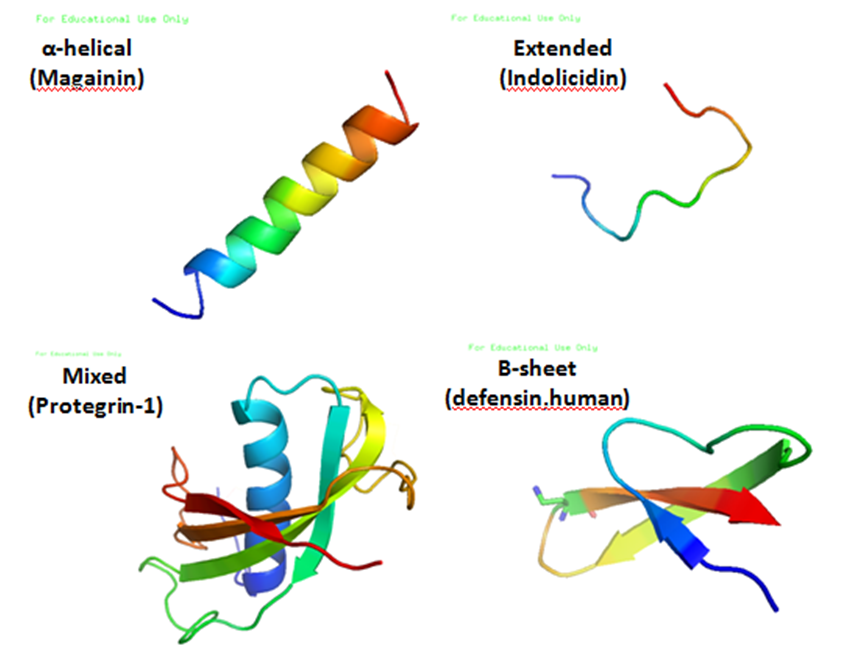
Drought. Source: Flickr
Costing around 80 billion dollars per year, droughts are one of the most expensive natural disasters in the world due to its negative impacts on agriculture. Additionally, because droughts are unavoidable, it is important for researchers to study the protective surfaces of crops, as it provides a better sense of how to prevent and minimize the devastating effects of droughts on global agriculture.
A study done by Dr. Reinhard Jetter and other researchers from the University of British Columbia, as well as researchers from the Northwest A&F University in China, focussed on this topic of protective plant surfaces, more specifically, the wax surfaces of wheat crops.

To gain insight on the genomic mechanisms involved in wax synthesis, researchers gathered and experimented on Chinese wheat crops. In particular, the team wanted to determine the gene involved in wax synthesis. Therefore, they placed the wheat crops under stressful drought conditions, so that the crops would overproduce wax. This overproduction allowed for researchers to isolate and study the gene permitting this wax production.

Wheat. Source: Flickr
Through this study, Dr. Jetter and his colleagues confirmed that the TaCER1-1A gene was involved in wax production. TaCER1-1A is a protein, made by the TaCER1-1A gene, that was found to be located in the endoplasmic reticulum of the cell, an important compartment for wax synthesis. Thus, its location and the use of a variety of techniques, one being the production of multiple copies of this gene, were used in order to further study how wax synthesis occurs. From this, the researchers were able to verify that the TaCER1-1A gene was indeed involved in wax synthesis.
The information obtained from this study can help provide insight about the production of wax on crops. These results are particularly important for farmers, as this may aid them in maximizing their crop yield, by making the crops more drought resistant. Therefore, to improve the crop yield, crops can either be genetically modified (GMOs) or undergo selective breeding. Genetically modifying the crops directly alters the genetic material of the crops through genetic engineering in a laboratory. Both selective breeding and GMOs have their own advantages and disadvantages. To learn more about them, listen to the podcast below.
With global warming on the rise, droughts are occurring more than ever before. Therefore, in regards to agriculture, there needs to be an implementation of crops that are able to survive and grow under these stressful conditions without sacrificing one important mechanism to improve another. From the study done by Dr. Jetter and his colleagues, we now know that the specific gene, TaCER1-1A, is one that responds to abiotic stresses such as droughts by producing more wax. Therefore, through improving our understanding of plant mechanisms, how specific genes affect a plant, and how a plant responds to stresses naturally, we can find a pathway to help our crops thrive.
– Anum Khan, Karina To, Sharon Li, & Souvik Maiti