Climate change is becoming a serious issue as temperatures continue to rise due to increasing global greenhouse emissions. Greenhouse gases such as CO2 trap reflecting sunlight and radiation that would normally escape the atmosphere of Earth and this trapped heat then leads to warmer temperatures. Over the past 150 years, Carbon dioxide(CO2) emissions around the world have increased mainly due to human involvement through the burning of fossil fuels and industrial processes. The figure below outlines the percentages of various greenhouse gas emissions and their sources.
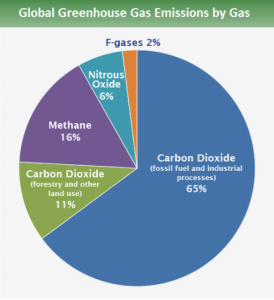
Credit: IPCC(2014)
Due to these rising emissions, there are many researchers and technology companies around the world that are looking at ways to reduce the amount of atmospheric CO2 and mitigate climate change before it is too late. In the past few years, many new technologies and techniques to capture excess carbon have emerged. Some of these main ones include Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage(BECCS or bio-CCS) and Direct Air Capture(DAC). Although the ultimate goal of both methods is to reduce carbon emissions, BECCS focuses on capturing CO2 released through combustion in industrial facilities while DAC aims to directly capture excess CO2 from the atmosphere. From these two methods, companies such as Carbon Engineering who are employing DAC have gained more traction as they have landed large investors such as Bill Gates and Chevron.
A study posted in 2018 outlined the process and cost of Direct Air Capture(DAC). Through this research, a Canadian company called Carbon Engineering based in Squamish, BC has tested the Direct Air Capture technology and hopes to make various large scale carbon storage plants over the next few years. Another company called Climeworks based in Switzerland is using similar methods to capture carbon from the atmosphere. Carbon Engineering has a plan to use the carbon from the atmosphere in 2 different ways which are reusing the stored carbon as a source of fuel and the second being storing solid carbon underground. According to the company, one large scale plant can store as much carbon as 40 million trees. They believe it is an efficient way to reducing carbon emissions and as they continue to get more funding they become closer and closer to their goal.
This video below explains the Direct Air Capture(DAC) method of removing CO2 and also outlines the various ongoing and future projects to mitigate climate change.
-Sandeep Singh
